3dImaging
Latest
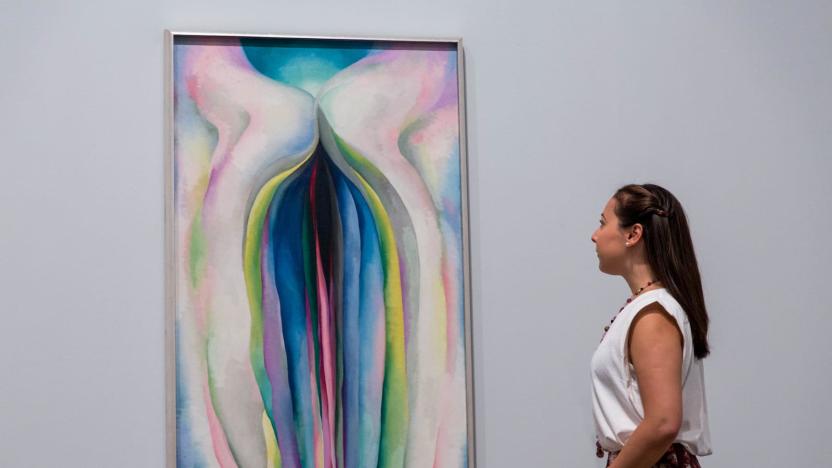

Experts will use 3D imaging technology to assess art damage
Preserving and restoring art is a very tricky business. Trying to maintain the balance between original work and repairing damage is difficult and oftentimes methods aren't always agreed upon by members of the art community. This has been seen over and over again with works like Leonardo da Vinci's The Last Supper and Michelangelo's Sistine Chapel ceiling work. But sometimes we can catch a break when new technology helps preservers analyze and repair damage with minimal disruption to the work itself. An example of that is taking place right now as experts will soon use 3D imaging technology to assess a certain type of damage being found on a number of Georgia O'Keeffe paintings.

Zillow is adding 3D tours to its real estate listings
Zillow is working on an app that will allow those hunting for homes on its site to get a 3D tour of houses they're interested in buying or renting. The company says that 44 percent of home buyers and 47 percent of renters look for a new home outside of the region where they currently live, making it really important to have access to as much information as possible online.
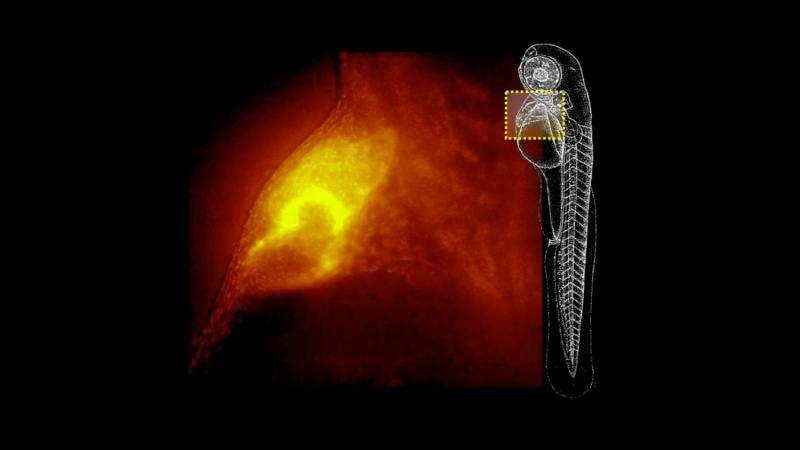
A new microscope can quickly generate 3D images of living organisms
A new microscope created by researchers at Universidad Carlos III de Madrid has the ability to take fast 3D images, making it easier to observe cells in living animals over time. For example, Jorge Ripoll, one of the researchers on the project and co-founder of the company set to produce the scope -- 4D Nature -- said in a statement, "We can see how the heart of a zebrafish beats and make a 3D- reconstruction of its beat."

Super-sharp 3D cameras may come to your smartphone
Many 3D cameras and scanners produce rough images, especially as they get smaller and cheaper. You often need a big laser scanner just to get reasonably accurate results. If MIT researchers have their way, though, even your smartphone could capture 3D images you'd be proud of. They've developed a technique that uses polarized light (like what you see in sunglasses) to increase the resolution of 3D imaging by up to 1,000 times. Their approach combines Microsoft's Kinect (or a similar depth camera), a polarized camera lens and algorithms to create images based on the light intensity from multiple shots. The result is an imager that spots details just hundreds of micrometers across -- you'd be hard-pressed to notice any imperfections.

Researchers measure 3D objects using just a camera and projector, can tell if you've ironed your shirt (video)
For years the projector and camera have served us well, performing their respective tasks. Now, researchers at Japan's Advanced Industrial Science and Technology institute are using them together to measure 3D objects. By projecting a special pattern onto the subject and then using the camera to "read" the amount of distortion in the image, a three-dimensional model can be constructed. This thing is accurate, too, with precision down to 1 - 2mm which means it can measure wrinkles in clothes, or even details in hands. The technology can even be scaled to work with microscopes. The creators say that it could be used in video games (much like Kinect), and even for tracking athletes' movements thanks to its ability to capture fast-moving images -- something existing systems can struggle with. Jump past the break to see the tech in action.

Apple '3D imaging and display' patent was cutting edge in 2005
An Apple patent for a "3D imaging and display system" staggers out into daylight after seven years buried in the USPTO. Its eyes steadily adjust to the brightness of a Kinect-dominated world and its heart sinks. But then a random guy approaches and says, "Hey little patent, what's wrong?" "I'm obsolete," comes the sullen reply. "I'm all about detecting user movements in three dimensions, but the competition has that covered. Sure, people might *think* I've patented some kind of wild holographic virtual reality stuff too, but my paperwork only mentions that in the vaguest possible terms. There's no way I can threaten Microsoft." "Nonsense!" cries the guy. "Follow me. I know a judge in Düsseldorf."

Sprint radar imaging system peeps inside walls, floors to detect bombs, tell-tale hearts
Back in 2005, we reported on a little something called the Prism 200, which allowed its holder to essentially see what folks were doing on the other side of a wall. Since then, we've seen plenty of devices that boast the same claims, but it wasn't until recently that the makers of the Prism 200 created a device that can actually see inside those walls. Looking something akin to an old school punch clock, Cambridge Consultants' Sprint in-wall radar imaging system provides 3D renderings of items embedded in walls, floors, and even ceilings. Where as existing X-ray systems require access to both sides of a wall, Sprint's radar setup allows users to see what's going on inside without dual access. As you might imagine, Cambridge is pushing this thing as a security tool, allowing for detection of bombs, drugs, dead bodies -- you know, the usual bad guy stuff. Sprint is currently undergoing testing. Full PR after the break.

Engineers create 3D microscope lens, see the tiny elephants in your ear
The ability to view tiny images in the third D has been made possible by Lei Li and Allen Yi of Ohio State University. The two have crafted a one-of-a-kind 3D lens that, unlike other three-dimensional microscopes that capture images by circling around the subject, sees teeny objects while stationary. Although the engineers crafted the lens on a precision cutting machine using a diamond blade themselves, they say it can be produced using traditional molding methods. At the size of a fingernail, the thermoplastic material, aka acrylic glass, was cut with 10 nanometer spacing (that's tiny) to ensure a flat plane. The top is surrounded by eight facets -- sort of like a gem stone, but not symmetric -- allowing the viewer to see 9 different angles at once. This should pave way for scientists to get better angles of microscopic objects, but they can always try using the 3DS and some DIY lens attachments, right?

UNC researchers develop a system for creating 3D models using images pulled from Flickr, off-the-shelf components
A group of researchers from the University of North Carolina and the Swiss university ETH-Zurich have teamed up to develop a system for creating 3D models of famous landmarks using photos from photo sharing websites like Flickr. Unlike previous projects at Microsoft and the University of Washington, the team at UNC used a home PC (albeit one with four GPUs) to process millions of images pulled from the Internet and construct 3D models of such landmarks as the Colosseum and the Roman baths at Sagalassos (above). And all the models were created in less than a day. According to UNC Chapel Hill's Jan-Michael Frahm, the process improves on current commercial systems by a factor of 1,000 to one. "Our technique would be the equivalent of processing a stack of photos as high as the 828-meter Dubai Towers, using a single PC, versus the next best technique, which is the equivalent of processing a stack of photos 42 meters tall – as high as the ceiling of Notre Dame – using 62 PCs," he said. "This efficiency is essential if one is to fully utilize the billions of user-provided images continuously being uploaded to the Internet." He sees any number of uses for this technology, from AR integration to 3D maps for rescuers in case of a natural disaster.

Boeing announces compact, energy-efficient 3D camera
Yes, even the military has gone 3D. Helping it in that endeavor is Boeing, which has just announced a tiny new 3D camera that's one-third the size and consumes one-tenth the power of comparable 3D imaging systems. While it will also be made available for commercial use, it seems like military will be first in line to use the cameras, with Boeing noting that it's potential applications including "mapping terrain, tracking targets and seeing through foliage," and adding that it's already testing the camera on unmanned aerial vehicles. The biggest drawback to the camera at the moment is that it's only able to take 3D still images, but Boeing says it will "soon" add 3D video capability as well. Details are otherwise pretty hard to come by, as you might expect, and pricing is no doubt best left unsaid. [Thanks, Graham]

Fujifilm intros 3D Print System, which probably requires wicked expensive ink
What do you do if you concoct one of the world's first 3D point-and-shoot cameras? Why, you concoct a 3D printer (definitely not pictured) to work with it, of course! Fujifilm has just kicked out its new 3D Print System, which enables 3D photographs to be created "on the spot" using dye-sublimation technology to print directly on to the base of a lenticular sheet. Unfortunately, prints will only be available in four sizes ranging from 4- x 6-inches to 6- x 9-inches, but we're hoping that some sort of magical firmware update will enable poster-sized prints for those really looking to drive their retinas batty. Mum's the word on a price, but it should hit UK shelves by April for an undisclosed rate.

3D camera breaks world record with 158 lenses
Sure, there are viable commercial options for taking photos in three dimensions, but if you really want to capture 3D images (and you happen to be attached to a major university) you can always go the route of Associate Professor Ishino Youzirou and company. The camera that they developed at the Nagoya Institute of Technology sports 158 lenses arranged on an 18.5-inch aluminum arc frame. The school's combustion engineers will use it to study irregular flames -- all the while content in the knowledge that they've entered the Guinness Book of World Records for building the camera with the most lenses. This is certainly safer than Youzirou's other attempt to enter the Guinness book, Most Live Rattlesnakes Held in the Mouth (the record for that, by the way, is ten).






