OhioStateUniversity
Latest
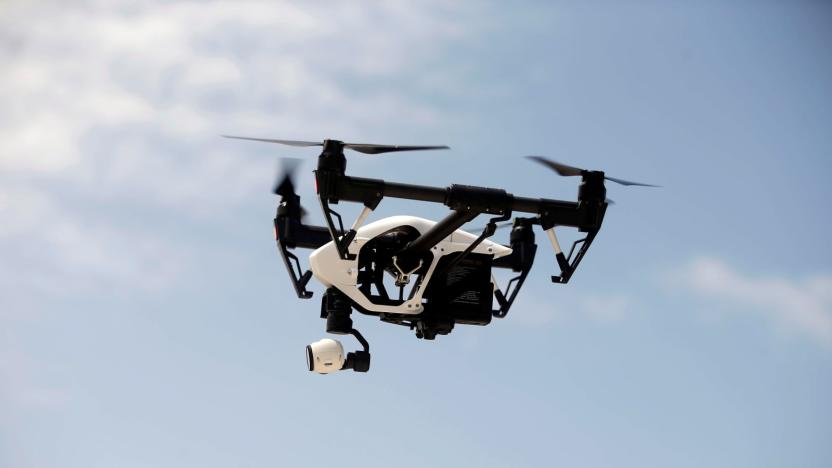

Ohio test uses drones to monitor highway traffic
Highway traffic monitoring is frequently... less than efficient. Fixed cameras can't catch problems beyond their immediate location, while aircraft are both costly and inevitably have to fly back to a distant base to refuel. These systems may soon get a robotic upgrade, though. Ohio State University is leading a pilot program that will use drones for roadway and traffic monitoring along a 35-mile highway stretch (the Smart Mobility Corridor) between Dublin and East Liberty. The dry run will see drones feed tracking data to the Ohio Department of Transportation's Traffic Management Center to complement data from existing systems. If there's a traffic-disrupting crash or a washed-out road, this might help spot it sooner.

'Hovering' antennas promise speedy 5G phone networks
Wireless networks already have to deal with increasingly crowded waves, and that's only going to get worse when 5G rolls around. Any boost to the signal could lead to a big jump in performance, especially when you're using very high frequencies that are more prone to interference. But how do you provide that boost? Researchers have an idea: 'hover' the antenna. They've developed millimeter wave antenna arrays that are almost entirely separated from the substrate you'd usually mount them on, preventing that substrate from weakening the signal like it does with conventional antennas.
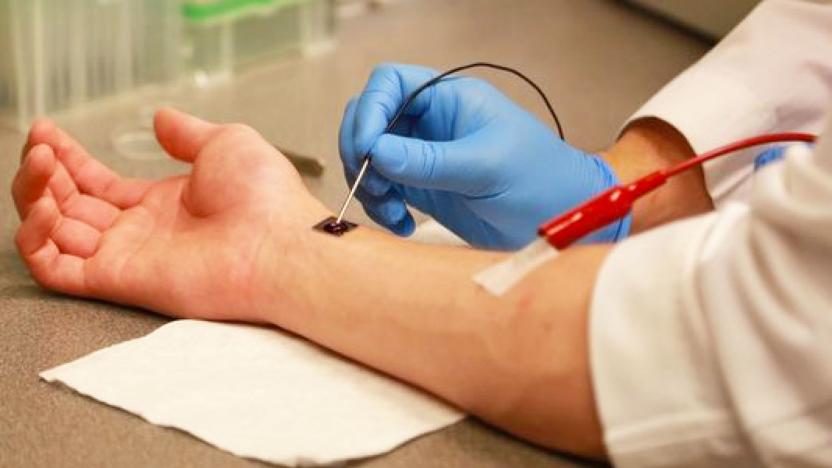
Fingernail-sized chip can repair damaged tissue in seconds
A new device can begin repairing damaged organs in seconds, heralding a major breakthrough for life-saving medicine. Developed at Ohio State University, the technology known as tissue nanotransfection (TNT) uses a small coin-sized silicon chip that "injects" genetic code into skin cells, converting them from one type to another.

Self-driving cars to prove their mettle on an Ohio highway
When you think of American states that are crucial to the future of transportation, you probably think of California, Michigan and maybe Nevada. Ohio, however, is determined to put itself on the map. Thanks to a mix of federal and local funds, the state is wiring a 35-mile portion of Route 33 for vehicle-to-infrastructure communication tests. Ideally, this will solve traffic issues by helping connected and self-driving cars talk to both highway systems and each other. With enough test data, these smarter cars could both take better advantage of the available lanes and drive in closely-packed platoons.

Big Ten Network adds 'League of Legends' to its tournament lineup
The Big Ten Network announced on Thursday that it's adding a less conventional sport to its conference title coverage. Now, in addition to everything from baseball and basketball to football and field hockey, subscribers will be able to see their favorite schools compete against one another in League of Legends. Yeah, the video game.

ICYMI: Skyjumping science experiments and more
try{document.getElementById("aol-cms-player-1").style.display="none";}catch(e){}Today on In Case You Missed It: University of Melbourne researchers studying non-sized crystals (that might one day be used to store greenhouse gases) needed to know what the nanoparticles would do in low-gravity, so they jumped off a plane while holding them. Scientists from Ohio State developed a bottle coating to let shampoo and soap inside of plastic bottles flow freely, rather than get stuck. This maker got really excited about visualizing what the inside of modern computer looks like, so he built a huge one. As always, please share any interesting tech or science videos you find by using the #ICYMI hashtag on Twitter for @mskerryd.
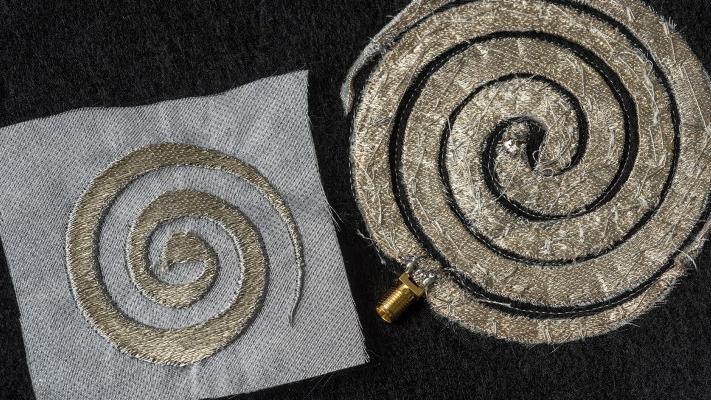

Stitch circuitry into your shirt for a better cell signal
Wearables are getting slimmer, but they're still oblong lumps worn over normal outfits. That's not enough for some tinkerers who are trying to make clothes themselves part of the computing (see: Drum Pants). Now, Ohio State University researchers are stitching conductive threads into clothing with precision that rivals printed circuit boards.

We're one step closer to a cure for paralysis
You wouldn't think that picking up a spoon was a staggering achievement, but that's because you're not Ian Burkhart. He's a quadriplegic and the subject of a lengthy experiment looking for an electronic cure for paralysis. The initial breakthrough took place in 2014 when Burkhart was able to pick up a spoon, and two years later he's now able to swipe a credit card, make a drink and even play Guitar Hero. The breakthrough is the result of ten years worth of research and a partnership between science non-profit Batelle and Ohio State University.

Doctors will use 3D modeling ahead of your next sinus surgery
Given the sinus' close proximity to your eyes and brain -- not to mention the area's super-sensitive nature -- the single slip of a surgeon's scalpel can have debilitating and permanent repercussions. That's why researchers at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center have developed a 3D-modelling technique that maps out each patient's sinus cavity prior to their surgery. By doing so, doctors will be able to practice the upcoming procedure as well as see exactly what sort of effect it will have on the patient.

Mechanical 'trees' generate energy by swaying in the wind
What if windmills looked more like trees? Well, a team of engineers at Ohio State University is looking for answer to that question with structures that resemble trees, but actually create energy when they move in the breeze. That swaying motion from the wind, and the resulting structural vibrations, is converted into electricity with electromechanical materials such as polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). The project isn't merely concerned with those tree-like structures, though. It also looks to harvest the energy generated from the vibrations of buildings and bridges.

Buckeyes to fire 500 trillion watt laser May 15th in a short, cheap burst
High-energy laser fusion experiments evoke extreme numbers -- not only in power but also in greenbacks. Sure, the current champ at the National Ignition facility in Livermore, CA can pump out a 411 trillion watt pulse, but at what price? A taxpayer-busting $200,000 per shot, with a $4 billion original construction cost. Compared to that, the new Ohio State University's 500 trillion watt model seems bargain-basement, built with a mere $6 million grant from the US Department of Energy. Admittedly, that paltry sum get you a much shorter burst, lasting 20 picoseconds compared to the NIF's several nanoseconds. But with the ability to fire 100 or more times per day, instead of just once like it's pricier kin, Ohio State will be able to assist the NIF with their fusion experiments, while also carrying on its own science, like simulating star formation. And money aside, the possibility of unlimited fusion-powered energy is always a noble goal, no?

Researchers capture first-ever images of atoms moving inside a molecule
The headline sums it up nicely but really, those photographic acrobatics account for only part of the story. Starting from the beginning, a research team led by Louis DiMauro of Ohio State University used an "ultrafast" laser to knock an electron out of its orbit, which scattered off the molecule as it fell back toward its natural path. That ripple effect you see in that photo up there represents any changes the molecule went through during the quadrillionth of a second that transpired between laser pulses. Yes, that's the kind of rare, psychedelic shot that's sure to earn DiMauro and team bragging rights, but the scientists also say this technique could have practical implications for observing -- and ultimately manipulating -- chemical reactions at an atomic level. Of course, it could be a long time yet before scientists analyze complex proteins in such detail: for the purposes of this experiment, the researchers stuck with simple nitrogen and oxygen molecules, with which chemistry scholars are already quite familiar. In fact, the researchers don't elaborate at all on specific studies where this technique might be useful, but you might want to hit up the source link nonetheless for some of the more technical details of how they pulled off this experiment in the first place.

Buckeyes embed antennas in clothes, couture to improve radio reception?
We like what's in our wardrobe to be multifunctional, and we've seen threads do double duty as keyboards, flashlights and even drum kits in our day. Now, researchers at Ohio State have come up with a way to turn the shirt on your back into an omnidirectional antenna to boost radio reception. To do so, they etched brass wires into plastic film to create flexible antennae, and stitched 4 of them into the shoulders, chest and back of a vest. Using a computer controller the size of a deck of cards clipped to the wearers belt, the system senses body movement and activates the appropriate antenna to get the best signal. You see, antennae don't work so well when touching human skin -- as any iPhone 4 owner can attest -- and the multiple antenna system alleviates that problem while providing "significantly greater signal strength" than a standard antenna. The researchers see the technology having great appeal for the military, law enforcement, and emergency personnel, but here's hoping they make a consumer version, too. It'd be nice to eliminate all those cell-service dead spots by simply donning a jacket, right?

Two universities adopt Wii Fit to monitor football concussions
As it turns out, there are quite a few uses for a $100 off-the-shelf computerized scale, above and beyond getting fit -- Nintendo's Wii Balance Board is now providing a mechanism by which college football teams at Ohio State University and the University of Maryland can cheaply determine whether players are suffering from concussions. Taking the place of force plate machines that can cost tens of thousands of dollars, the white plastic boards measure students' balance (using yoga poses) and coordination (in Table Tilt) before a game, to provide a frame of reference against which trainers can measure whether athletes are fit to keep playing. Though some scholars found Wii Fit didn't stack up favorably against the expensive force plates, the universities trialing the system called it "pretty decent," so the question is whether Nintendo's peripheral offers a reasonable enough benchmark for the price. We suppose the American Heart Association liked it well enough.

Paparazzi Bots will chase you down until you love them
Sony's Party-shot dock is fun and all but it suffers from one major limitation: it's fixed in space. Oh sure, it'll pan and tilt around its base until the last reveler is unconscious, but it won't go to where the action is. That's where the Ohio State University developed Paparazzi Bot comes in. The autonomous, sensor-laden, mobile robot stands at human height and decides for itself whether or not to snap your photo based upon your facial expression (hint: it likes smiles). If chosen, the bot stops, aims, shoots and uploads your image to a social networking site for other robots to mock, presumably -- a kind of fleeting celebrity anointment as described by the bot's inventor, Ken Rinaldo; or a kind of precursor to robots with automatic weapons, if you ask us. Video demonstration after the break.

Quantum computer chips get infinitesimally closer to happening
We've already seen at least one (sort of) functional quantum processor, and one breakthrough after the other in quantum computing, but it looks like some researchers at Ohio State University have now made a breakthrough of their own that could possibly speed things up considerably. The big news there is that they've apparently found a way to fabricate a quantum device called a resonant interband tunneling diode (or RITD) using a chip-making technique called "vapor desposition," which is commonly used today for traditional chips. While there's still quite a bit of perfecting to be done on the device itself, lead researcher Paul Berger says the RTIDs could be used for ultra-low-power computer chips that operate with small voltages and produce less excess heat, and may even allow for ultra high-resolution imaging devices that can "operate at wavelengths beyond the human eye" -- opening up possibilities for everything from advanced medical imaging to the ability to see through rain, snow, fog and dust storms.[Via Physorg]

Another team figures out how to convert waste heat into energy
Not that mad scientists haven't figured out a way to convert waste heat into energy, but a team from Ohio State University has developed a new material that does the same sort of thing... just way, way better. The new material goes by the name thallium-doped lead telluride, and at least in theory, it could actually convert exhaust heat from vehicles into electricity. According to a new report about to hit the journal Science, the material packs "twice the efficiency of anything currently on the market," though it still seems as if it's a good ways out from being ready for commercial applications. Nanotechnology geeks -- you've got a real treat waiting in the read link.[Via CNET]

OSU researcher developing GPS-like system for moon-bound astronauts
GPS on the moon may seem a bit far-fetched... that is, until you remember the US military's plans to launch a WiFi router into space. The same Ohio State University researcher who developed software for the Mars rovers Spirit and Opportunity is now developing a GPS-like system that would enable astronauts to navigate terrain as if they were simply routing themselves through a plot of land on Earth. Because of the moon's location (we're simplifying things here), Ron Li is having to create a similar system (read: not bona fide GPS) that relies on "signals from a set of sensors including lunar beacons, stereo cameras, and orbital imaging devices" in order to provide navigational output. Everyone involved is hoping to have it operational by 2020 (the next planned trip to the moon), but the team will be stuck testing in the Mojave Desert. Bummer.[Via Physorg]

Ford Fusion Hydrogen 999 breaks 200 miles-per-hour
Looks like minuscule RC cars aren't the only alternatively powered vehicles trying to break 200 miles-per-hour, as Ford just became the "world's first automaker to set a land speed record for a production-based fuel cell powered car." The whip used to set the bar, of course, is none other than the Fusion Hydrogen 999, and it reportedly reached over 207 miles-per-hour at the Bonneville Salt Flats in Wendover, Utah without using a drop of gas. Apparently, Ford is hoping that this showcase of speed will somehow translate into advancements that will help us common folk get to work and back sans gasoline, and while we've no idea when a fuel cell propelled Cobra will roll off the line, it did note that a number of fuel cell propelled Focus vehicles were still burning down the roads as part of an ongoing study.[Via AutoblogGreen]

Aruba Networks to install "world's largest" WLAN at OSU
We all know how sketchy these "world's largest" claims can be, but Aruba Networks is dubbing its ongoing deployment of WiFi coverage across the gargantuous campus of The Ohio State University just that. While numerous cities (and even the entire country of Singapore) are moving forward with far-reaching wireless access plans, Aruba's "Mobile Edge solution" will reportedly be the most expansive WLAN by the time it's complete. Although the installation is only partially finished, 1,700 access points in over 28 buildings have already been lit, and Ohio State's IT department has plans to cover all 25 million square feet of the main campus with WiFi. Once complete, over 77,000 students and staff will have "ubiquitous wireless access to the university's networks" thanks to the "nearly 10,000" APs that will beam 802.11a/b/g all across OSU. Although the entire rollout won't be finalized until 2011, the 31 Buckeye residence halls will supposedly get blanketed within the next month, but we aren't sure if the 101,568 fans in The 'Shoe can expect unadulterated WiFi access to collegiate message boards or Facebook when Michigan comes to town later this year.











