OpticalLattice
Latest
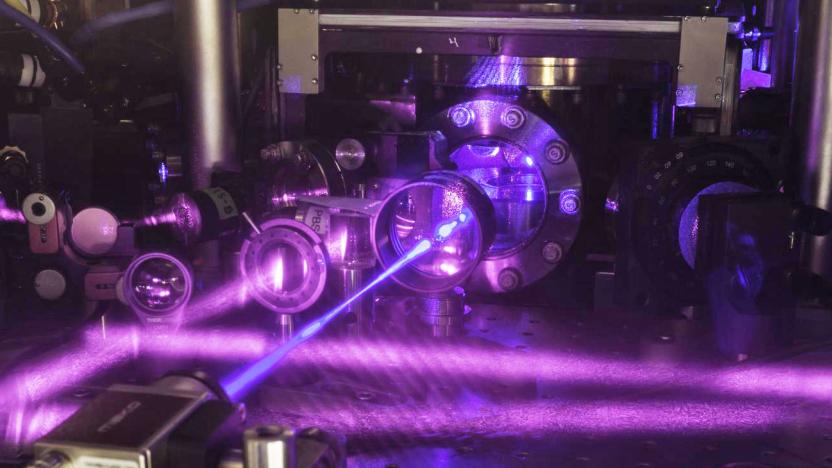
Researchers have increased atomic clock precision yet again
Researchers have pushed the precision and stability of atomic clocks to increasingly greater levels over the last few years. A big advancement was the introduction of optical lattices, lasers which essentially quarantine individual atoms and boost accuracy by keeping them from moving around and interacting with each other. Scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have used this method to develop clocks so stable, they can keep extremely precise time for thousands and even billions of years. The team's most precise clock was created in 2015, but research published this week in Science describes a new version that just took that top spot.

World's most precise atomic clock will still be spot-on in 5 billion years
Most of us only pay attention to time when it's causing headaches, but the same can't be said of a team of researchers working out of the University of Colorado at Boulder. Led by National Institute of Standards and Technology fellow Jun Ye, they've crafted an atomic clock that can keep precise time for billions of years, a world record. This hefty new timekeeper can tick off the seconds with the same unflinching regularity as the best of them, but it'll be about 5 billion years before it experiences its first temporal hiccup. For the morbidly curious, that means the clock will still be precise when the sun starts ballooning into a massive red giant. That may not sound like a huge deal now, but when our descendants start laying in escape routes to some more pleasant planets they'll be glad for that extra precision. How does the thing work? Well, strontium atoms are held in "traps" formed by lasers, and researchers are able to track how often they oscillate by using that laser light to get them moving. It's hardly a new technique, but you can't argue with the results: The new clock is 50 percent more precise than the last record-setter, and Ye says that there are plenty more breakthroughs to come.

Laser-powered atomic clock fuels temporal pedants' ire
If you thought that your regular atomic clock, which loses a second once every few years, is adequate for your needs, then Dr. Jerome Lodewyck wants a word. His team at the Paris Observatory claims to have invented an atomic clock which only loses a second every three centuries. Rather than measuring the oscillations of caesium atoms, the "Optical Lattice Clock" uses a laser to excite strontium atoms which vibrate much faster and are, therefore, more accurate. Of course, it's a cruel irony that just as soon as someone's plonked down $78,000 on a Hoptroff No. 10, a rogue gang of scientists find a way to make it obsolete.

Quantum speed limits within reach, present moves ever closer to future
Got your wire-rimmed spectacles on? Had a full night's rest? Eager to get those synapses firing? Here's hoping, because Marc Cheneau and co. are doing everything they can to stretch the sheer meaning of quantum understanding. The aforesaid scientists recently published an article that details a method for measuring quantum particle interaction in a way that has previously been considered impossible. Put simply (or, as simply as possible), the famed Lieb-Robinson bound was "quantified experimentally for the first time, using a real quantum gas." The technobabble rolls on quite severely from there, but the key here is realize just how much of an impact this has on the study of quantum entanglement, and in turn, quantum computing. For those interested in seeing what lives in a world beyond silicon, dig into the links below. You may never escape, though -- just sayin'.

New developments in atomic clock technology beat accuracy records, may inspire Ke$ha's next hit
According to a recent Penn State study that uses a new way to calculate time-telling precision, the CsF2 cesium-based atomic clock at the UK's National Physical Laboratory is almost twice as accurate as originally thought -- meaning it will only gain or lose one single second over the course of 138 million years. This atomic clock isn't the only competitor for best-in-show, as researchers at the University of Tokyo have also announced a new record, claiming their optical lattice atomic clock observes atoms a million times faster than a traditional atomic clock -- achieving accuracy up to 18 digits in a one second measurement. Although researchers say the technology would gain or lose a second significantly faster than the cesium-based variety (31.7 million years), it could change the way scientists perceive time and space, giving us new insights into fundamental constants of physics. "Until now, clocks have been thought of as tools for sharing common time. But with clocks like this, conversely, we can understand that time passes at different speeds, depending on the time and place a clock is at," said Hidetoshi Katori of the University of Tokyo. Of course, both atomic clocks can help us stay timely, but they also have practical applications for everything from deep-space networking, to predicting earthquakes and GPS navigation. With this type of accuracy, looks like none of us will be getting away with showing up late to work anymore. Check out a video about the optical lattice clock after the break.




