suturing
Latest

Researchers create a fast-sealing surgical 'glue' for closing wounds
Closing up wounds typically calls for sutures or staples, but neither are able to create a complete seal. And when it comes to internal injuries that are harder to get to and wounds on organs that move a significant amount, such as lungs, treatment becomes even more difficult. Sealants offer a solution to those problems, but none of those available meet all of the requirements of an effective surgical tool. However, researchers have just developed a new type of sealant that may actually check all of the boxes. Their work was published this week in Science Translational Medicine.
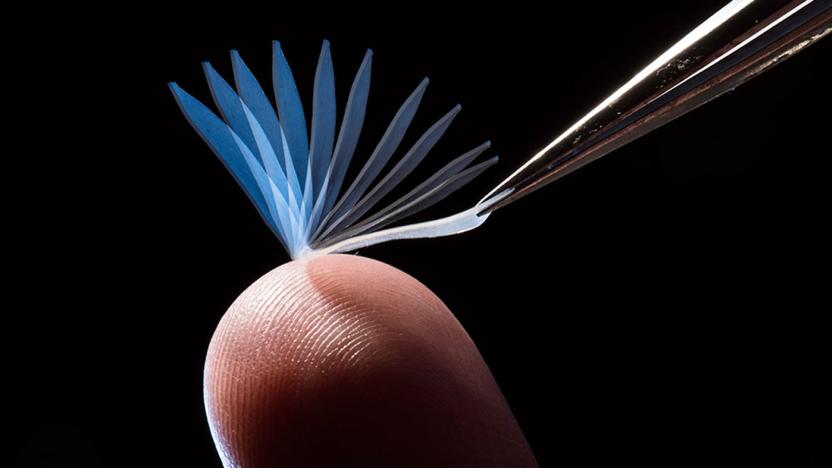
Shape-shifting polymer straightens out from body heat
There have been plenty of tries at shape-changing materials, but this one might be the most practical yet. The University of Rochester has created a polymer that returns to its original shape when subjected to body heat -- touch a curled mess of the stuff and it straightens out. The solution was to attach polymer strands using molecular links that inhibit crystallization, which prevents the polymer from returning back to its original shape. When you tweak the number and substances of the links, you can customize the temperature where that reversion happens (in this case, just below normal body temperature).

Laser-bonded healing could replace needle and thread
It sounds more like something you'd see in X-Men than on an actual operating table in real life, but a team at Massachusetts General Hospital has developed a way to heal surgical incisions with laser light. Christened laser-bonded healing, the methodology has been studied for years, but up until now, scientists have found it impossible to find the perfect balance of heat required to coax tissue into healing itself back together. Irene Kochevar described the process as "nano suturing," as diminutive collagen fibers are woven together in a way that the old-fashioned needle-and-thread method simply can't match. The benefits, as you can likely imagine, are numerous: less scarring, faster recovery, the potential for fewer infections and bragging rights that you were struck with lasers and survived. Still, the procedure is far from becoming commonplace in ORs, given that the dermatological procedure hasn't even been submitted to the FDA yet. 'Til then, it's up to you and Wolverine to figure things out.


