Cancer
Latest
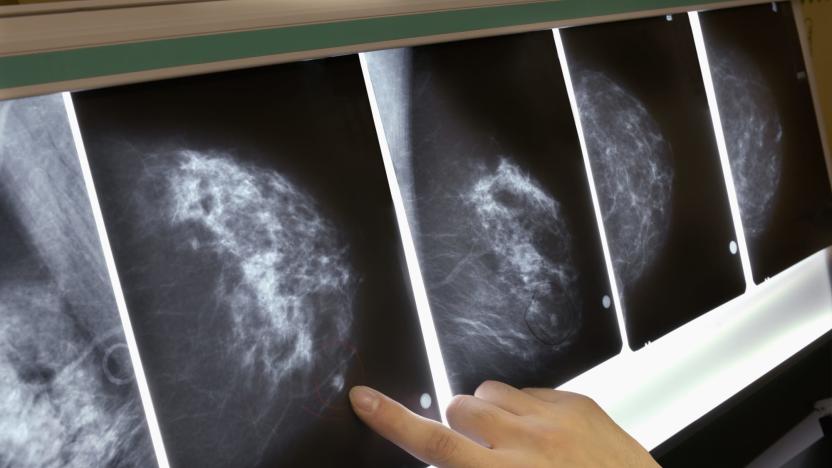
MIT AI model is 'significantly' better at predicting breast cancer
MIT researchers have invented a new AI-driven way of looking at mammograms that can help detect breast cancer in women up to five years in advance. A deep learning model created by a team of researchers from MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and Massachusetts General Hospital can predict -- based on just a mammogram -- whether a woman will develop breast cancer in the future. And unlike older methods, it works just as well on black patients as it does on white patients.

Researchers trick radiologists with malware-created cancer nodes
Security researchers in Israel have developed malware that can add realistic-looking but entirely fake growths to CT and MRI scans or hide real cancerous nodules that would be detected by the medical imagining equipment. The software, designed by experts at the Ben Gurion University Cyber Security Research Center, was created to highlight the lax security protecting diagnostic tools and hospital networks that handle sensitive information.
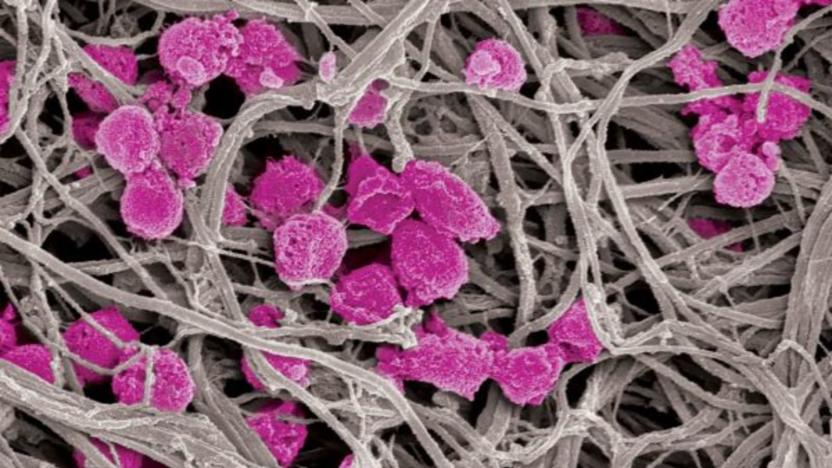
Scientists design 'decoy platelets' that reduce risk of blood clots
Heart disease, stroke, sepsis and cancer are incredibly serious conditions which together cause the greatest number of deaths around the world. They're unique illnesses, but they have something in common -- they're all associated with activated platelets, which play an important role in healing, but for some can also contribute to dangerous blood clots and tumors. Now, scientists think they've found a way to mitigate the risks associated with these platelets, thereby "outsmarting" the catalyst for these diseases.

Samsung reaches final settlement with cancer-stricken employees
After 11 years of controversy, Samsung has apologized for creating an unsafe work environment that resulted in a number of former employees contracting leukemia and other cancers, according to the Associated Press. The company has vowed to compensate ill workers by 2028, per Reuters. The announcement comes weeks after Samsung reached a final settlement with Banolim, a group representing ex-Samsung workers and their families.
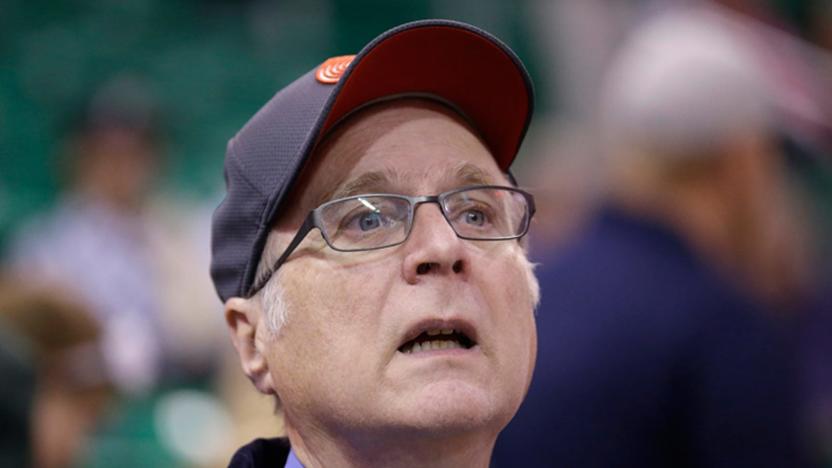

Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen dies from cancer at 65
It's a sad day for the technology world, as Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen has died at the age of 65 due to complications from non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The tech pioneer had been grappling with the cancer for years after being first diagnosed in 1982 and receiving treatment for it in 2009, but announced that it had returned on October 1st. He leaves behind his sister and had no children. His influence, however, will likely be felt for a long time to come.
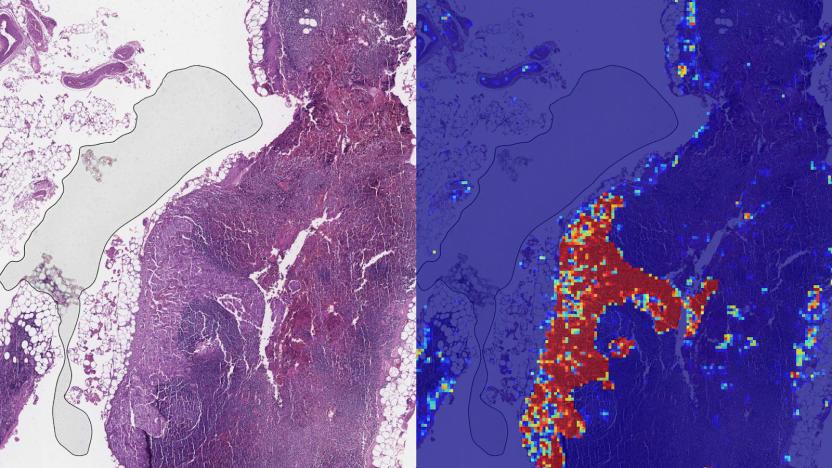
Google AI can spot advanced breast cancer more effectively than humans
Google has delivered further evidence that AI could become a valuable ally in detecting cancer. The company's researchers have developed a deep learning tool that can spot metastatic (advanced) breast cancer with a greater accuracy than pathologists when looking at slides. The team trained its algorithm (Lymph Node Assistant, aka LYNA) to recognize the characteristics of tumors using two sets of pathological slides, giving it the ability to spot metastasis in a wide variety of conditions. The result was an AI system that could tell the difference between cancer and non-cancer slides 99 percent of the time, even when looking for extremely small metastases that humans might miss.

IBM extends deal using Watson to support veterans with cancer
IBM is making further use of Watson in the fight against cancer. The tech giant has extended a team-up with the US Department of Veterans Affairs that taps Watson for help treating soldiers with cancer, particularly stage 4 patients who have few other options. The new alliance runs through "at least" June 2019 and will continue the partnership's existing strategy. Oncologists and pathologists first sequence tumor DNA, and then use Watson's AI to interpret the data and spot mutations that might open up therapeutic choices.
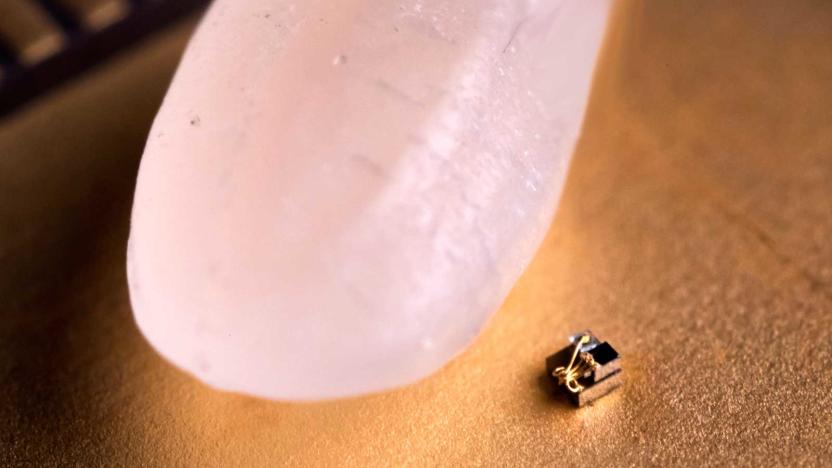

World's tiniest 'computer' makes a grain of rice seem massive
You didn't think scientists would let IBM's "world's smallest computer" boast go unchallenged, did you? Sure enough, University of Michigan has produced a temperature sensing 'computer' measuring 0.04 cubic millimeters, or about a tenth the size of IBM's former record-setter. It's so small that one grain of rice seems gigantic in comparison -- and it's so sensitive that its transmission LED could instigate currents in its circuits.
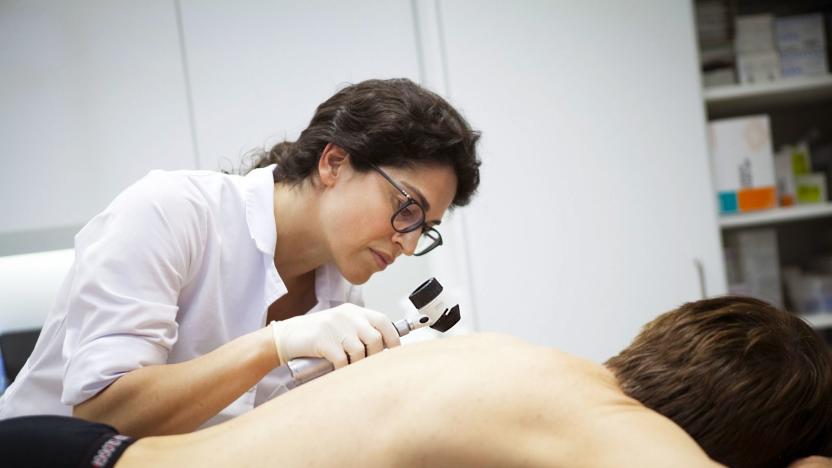
AI outperforms human doctors in spotting skin cancer
In January last year scientists reported that artificial intelligence was almost as effective at identifying skin cancer as dermatologists. Now, less than 18 months later, it's even better. In an experiment between a deep learning convolutional neural network (or CNN) and 58 dermatologists, researchers found that human dermatologists accurately identified 86.6 percent of skin cancers from a range of images, compared to 95 percent for the CNN.
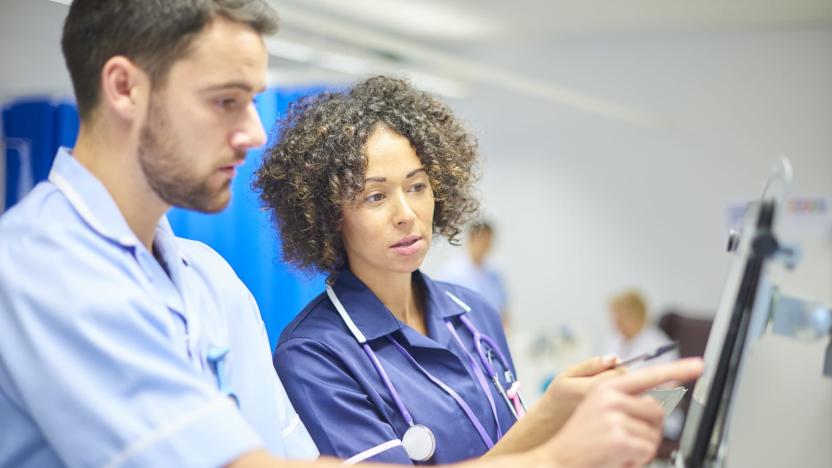

UK promises funding for AI-based early cancer detection
The UK is about to make a big bet on AI's ability to spot cancer. The Guardian has learned that Prime Minister Theresa May will commit "millions of pounds" in funding for research toward AI that can diagnose cancer and chronic diseases at an early stage. The technology could reduce "avoidable deaths," according to May's prepared speech, and is estimated to save as many as 22,000 lives per year by 2033. It would extend healthy living by another five years as of 2035. There is, however, an important catch.
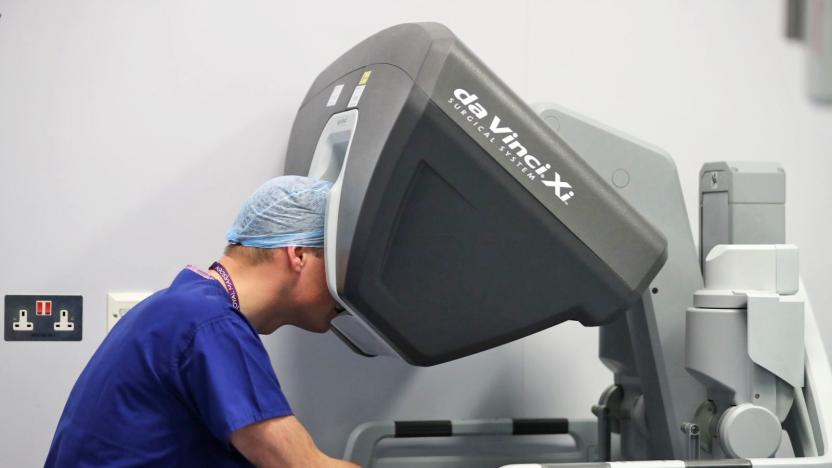
Penn doctors perform the first robot-assisted spinal surgery
Surgical robots are capable of feats that even the most skilled doctors can't manage, and the University of Pennsylvania just offered a textbook example. The school has confirmed that it performed the first-ever robot-assisted spinal surgery, using Da Vinci's robotic arms to remove a rare tumor where patient Noah Pernikoff's spine met his skull. The two-day operation, which took place in August 2017, started with neurosurgeons preparing the spine using ultrasonic cuts, and then brought in the robot to clear a path for removing the tumor through Pernikoff's mouth (you can see a slightly graphic illustration below). The team then used some of Pernikoff's own bone to reconstruct the spinal column section they'd removed.
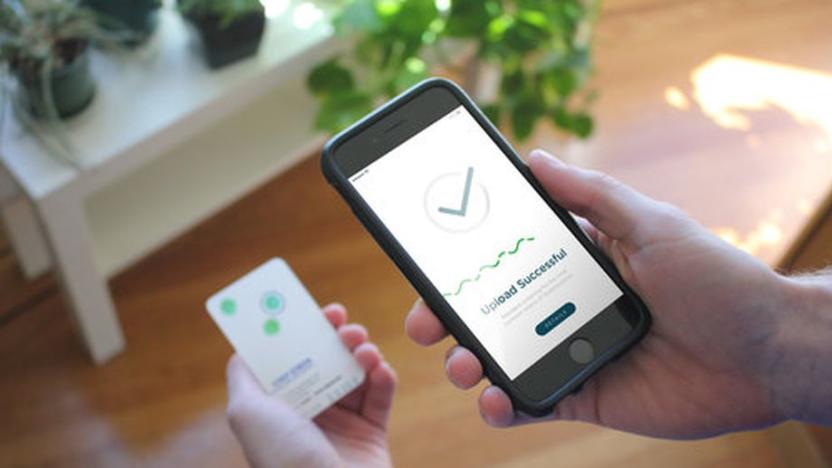

CRISPR pioneer wants to make an at-home test that detects disease
Biotech company Mammoth Biosciences is working on a simple, portable test that would give everyone, from healthcare professionals to just people at home, the ability to detect various diseases, infections and cancers quickly and easily. The test would use CRISPR to determine which bacteria, viruses or genetic mutations were present in a person's blood, saliva or urine and a companion app would inform users about what was detected. "Imagine a world where you could test for the flu right from your living room and determine the exact strain you've been infected with, or rapidly screen for the early warning signs of cancer," Mammoth CEO Trevor Martin said in a statement. "That's what we're aiming to do at Mammoth -- bring affordable testing to everyone."
Google made an AR microscope that can help detect cancer
In a talk given today at the American Association for Cancer Research's annual meeting, Google researchers described a prototype of an augmented reality microscope that could be used to help physicians diagnose patients. When pathologists are analyzing biological tissue to see if there are signs of cancer -- and if so, how much and what kind -- the process can be quite time-consuming. And it's a practice that Google thinks could benefit from deep learning tools. But in many places, adopting AI technology isn't feasible. The company, however, believes this microscope could allow groups with limited funds, such as small labs and clinics, or developing countries to benefit from these tools in a simple, easy-to-use manner. Google says the scope could "possibly help accelerate and democratize the adoption of deep learning tools for pathologists around the world."

Medicare now covers gene sequencing for patients with advanced cancer
Patients with advanced cancer will soon have access to more personalized treatment plans because Medicare will now cover genetic tests that sequence tumor cell DNA and help healthcare providers determine treatment strategies. As Wired reports, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) announced that for Medicare-enrolled patients with recurrent, metastatic, relapsed, refractory or stages III or IV cancer, such FDA-approved tests will be covered by their insurance. And since other insurance companies tend to take their cues from CMS, privately-insured patients will likely get similar coverage soon as well.

FDA greenlights 23andMe's direct-to-consumer cancer risk test
Cancer screening isn't all that accessible -- you typically need an obvious genetic background that suggests you're at risk, which doesn't help if you slip between those cracks. You shouldn't have to run that gauntlet for much longer. The US Food and Drug Administration has approved a 23andMe direct-to-consumer test that details the risks of breast, ovarian and prostate cancer based on BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic mutations. Once the report is available, you wouldn't have to worry about qualifying for a screening -- you could send in a saliva sample and find out on your own terms.
Researchers use nanorobots to kill tumors in mice
Our current methods of fighting malignant tumors are wildly inadequate. Chemotherapy and radiation treatments, while sometimes successful, come with massive side effects, mainly because every other cell in the body is also getting bombarded with chemicals and radiation even though the main targets are the tumor cells. Finding a way to specifically target tumor cells while leaving healthy cells alone is something that many researchers are working towards and a new study out today demonstrates that nanorobots made out of DNA could be an effective option.

Studies suggest cellphone radiation doesn't threaten humans
No, the debate over the risks of cellphone radiation isn't over yet. The US National Institutes of Health's National Toxicology Program has published details of draft studies which suggest that normal cellphone radiation levels aren't harmful to humans. The research subjected rats to very high levels of RF radiation at 2G and 3G cellular frequencies, and produced results where there was no clear pattern of harm even at the exaggerated radiation levels.
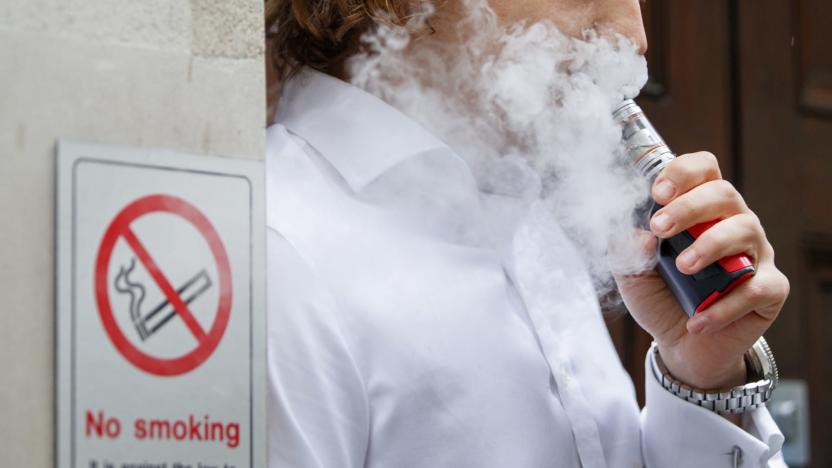

Study says e-cigarettes increase risk of cancer and heart disease
Regulators may have had a change of heart about the danger of using e-cigarettes, but scientists would beg to differ. A newly published New York University School of Medicine study indicates that vaping may put you at a "higher risk" of cancer and heart disease. Mice subjected to the equivalent of "light" e-cigarette smoking for 10 years (12 weeks in reality) suffered DNA damage to their bladders, hearts and lungs, in addition to limiting both DNA repair and lung proteins. In short: nicotine can become a carcinogen in your body regardless of how it's transmitted.

After Math: First!
It was a week of firsts for the tech industry. Facebook finally got around to adding its first African American board member (because it's not like it's already 2018 or anything), a lifeguard drone made its first Hasselhoffian beach rescue, Ferrari announced that it is indeed working on its first electric supercar, and Kodak took a break from slapping its brand on cryptocurrency mining rigs to release the first footage from its upcoming hybrid Super 8 camera. Numbers, because how else will you put entrants in order?

First human CRISPR study in the US could begin soon
In mid-2016, A federal panel had greenlit the University of Pennsylvania to pursue the first trials using CRISPR gene-editing in the US. It seems the institution has quietly gotten the ball rolling and could theoretically start the study at any time: A posting was found on a directory of trials describing a yet-to-be-scheduled UPenn survey using CRISPR techniques to treat cancer patients.






