GeorgiaInstituteOfTechnology
Latest
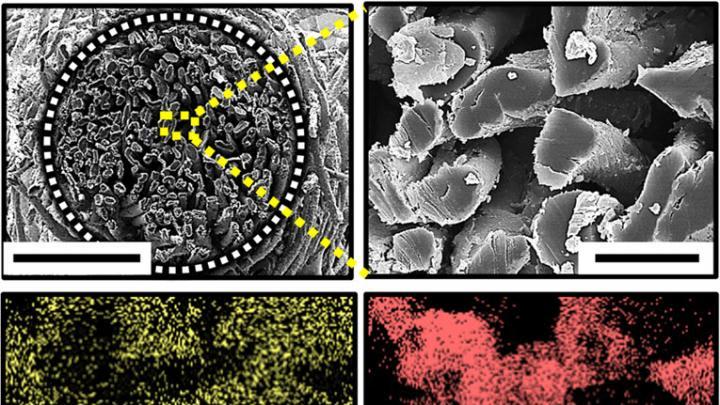
Researchers want to power pacemakers with cotton-based biofuel cell
Researchers at the Georgia Tech and Korea University believe they have found a way to power implantable medical devices like pacemakers with a new fuel cell made from cotton fiber. The glucose-powered biofuel cell could provide twice as much power as conventional options.

This year we took small, important steps toward the Singularity
We won't have to wait until 2019 for our Blade Runner future, mostly because artificially intelligent robots already walk, roll and occasionally backflip among us. They're on our streets and in our stores. Some have wagged their way into our hearts while others have taken a more literal route. Both in civilian life and the military battlespace, AI is adopting physical form to multiply the capabilities of the humans it serves. As robots gain ubiquity, friction between these bolt buckets and we meat sacks is sure to cause issues. So how do we ensure that the increasingly intelligent machines we design share our ethical values while minimizing human-robot conflict? Sit down, Mr. Asimov.

Researchers create prosthetic hand that offers more lifelike dexterity
Researchers at Georgia Tech have developed a prosthetic hand inspired by the bionic one given to Star Wars' Luke Skywalker. What sets this one apart from other prosthetics is the amount of dexterity it offers, allowing users to move individual fingers at will. With it, Jason Barnes, the amputee working with the researchers, was able to play piano for the first time since losing part of his arm in 2012.
Tiny 'engine' turns natural gas into hydrogen
Here's the dilemma with hydrogen: fueling your car with the stuff is faster than charging an EV, but making and distributing it is inefficient and polluting. A team from the Georgia Institute of Technology has created a four-stroke "engine" that converts natural gas (methane) into hydrogen from just about anywhere, while capturing the CO2. It could one day hook up to your natural gas line, letting you fuel your car from home in a non-polluting way like you can with an EV -- pleasing both green tech boosters and oil companies.

Google Glass can tell if you're stressed
It's not always easy to tell when your stress levels are through the roof, and you may not always want to break out a heart rate sensor just to find out when it's time to relax. You might not have to, if researchers at Georgia Tech and MIT have their way; they've developed BioGlass, an Android app that uses Google Glass to determine how frazzled you are. The software measures your heart and breathing rates by checking for tiny movements picked up by Glass' accelerometer, gyroscope and front-facing camera. In theory, you'd only have to wear the smart eyepiece to know when it's time to calm down.

Apple says iOS 7 will patch exploit that lets rogue chargers install malware
Recently, Georgia Tech researchers discovered an unusual way to attack iOS: a third-party charger with a hidden computer can install malware when an iOS device is plugged in and unlocked. That won't be an issue for much longer, however, as Apple has confirmed that iOS 7 beta 4 and future releases contain a fix. While the company hasn't said what that solution is, Georgia Tech's Billy Lau says that the new OS can tell when it's plugged into a computer instead of a charger -- there shouldn't be any rude surprises. The dependence on an iOS 7-based fix could leave many users vulnerable until the fall, although the hardware-specific nature of the exploit means it's unlikely to be a major concern.

Ford teams up with Eaton, Whirlpool and SunPower to create MyEnergi Lifestyle, hopes to reduce everyone's CO2 footprint
Trying to lower your utility bill? Maybe it's time you talked to a motor company -- Ford is on the warpath to reduce energy consumption. In a collaborative effort with SunPower Eaton and Whirlpool Ford is trying to show the world how it can drastically lower its electricity bills through the use of technology. The effort is called MyEnergi Lifestyle, and according to a model cooked up by the Georgia Institute of Technology, its energy-saving tricks could reduce the energy costs of an average single family home by as much as 60-percent. If every home in the U.S. got with the program, Ford explains, it would be like taking every home in California, New York and Texas off the grid. The team's ideas incorporate a wide range of technology -- though much of it works around using utilities during off-peak hours. Dishwashers and water heaters that are programmed to do most of their high energy tasks at night, for instance, or Ford's Value charging system, which leverages a cloud database to charge electric vehicles when utility rates are at their lowest. Solar power and other renewable energy sources can augment off-peak use too, further reducing energy costs. For now, it's a lot of talk and computer models -- but the companies involved are ready to put their money where their mouths are. In order to create a real-world model, MyEnergi Lifestyle is planning to launch a contest awarding one lucky family an energy efficient home makeover. Details on the promotion haven't been announced yet, but winners would presumably be outfit with enough technology to recreate the Georgia Institute of Technology's model on a real power bill. The team plans to showcase some of its ideas at CES throughout the week, but you can get the gist of it now by skimming the press release after the break.

Georgia Tech develops self-charging battery that marches to the owner's beat
One of the last times we saw the concept of a self-recharging battery, it was part of a high-minded Nokia patent whose ideas still haven't seen the light of day. Researchers at Georgia Tech are more inclined to put theory into practice. Starting from a regular lithium-ion coin battery, the team has replaced the usual divider between electrodes with a polyvinylidene difluoride film whose piezoelectric nature produces a charging action inside that gap through just a little pressure, with no outside voltage required to make the magic happen. The developers have even thumbed their noses at skeptics by very literally walking the walk -- slipping the test battery under a shoe sole gives it a proper dose of energy with every footstep. At this stage, the challenge mostly involves ramping up the maximum power through upgrades such as more squeezable piezoelectrics. Georgia Tech hasn't progressed so far as to have production plans in mind; it's nonetheless close enough that we could see future forms of wearable computing that rarely need an electrical pick-me-up.

Georgia Tech models swimming, cargo-carrying nanobots
The nanobot war is escalating. Not content to let Penn State's nanospiders win the day, Georgia Tech has answered back with a noticeably less creepy blood-swimming robot model of its own, whose look is more that of a fish than any arachnid this time around. It still uses material changes to exert movement -- here exposing hydrogels to electricity, heat, light or magnetism -- but Georgia Tech's method steers the 10-micron trooper to its destination through far more innocuous-sounding flaps. Researchers' goals are still as benign as ever, with the goal either to deliver drugs or to build minuscule structures piece-by-piece. The catch is that rather important mention of a "model" from earlier: Georgia Tech only has a scientifically viable design to work from and needs someone to build it. Should someone step up, there's a world of potential from schools of tiny swimmers targeting exactly what ails us.

Vibrating glove gives piano lessons, helps rehab patients regain finger sensation and motor skills
We've seen a good number of electronic gloves before, and now researchers at Georgia Tech have devised one to rehabilitate patients who suffer from paralyzing spinal cord injuries while teaching them how to tickle the ivories. Christened Mobile Music Touch, the black mitt pairs with a keyboard and cues individual fingers with vibrations to play notes. The handgear also buzzes constantly for several hours to stimulate recovery while users go about their day, similar to another yellowjacket-developed solution. After treatment, some patients could pick up objects and feel textures they hadn't been able to -- especially remarkable since, according to the university, little improvement is typically seen a year after injuries are sustained. Folks who learned to play the piano with the device also experienced better results than those who did without it. Project leader Dr. Tanya Markow believes that the rehab's success could be caused by renewed brain activity that sometimes lies dormant. For the full skinny, head past the break for the press release and a video of the gauntlet in action. [Thanks, Timothy]

Nuclear clocks could be 60x as accurate as atomic counterparts, less prone to errors
For years, atomic clocks have been considered the most accurate devices for tracking the slow march towards obsolescence, a subatomic particle vibrating a given number of times per second with relatively few issues. Now the reliability crown might be passed to the nuclear clock, which in addition to sounding gnarly, could prove to be less susceptible to errors from outside stimuli. It goes like this: although an atomic clock will measure a certain number of vibrations per second, external forces such as ambient electric and magnetic fields affect the electrons used in atomic clocks, causing mishaps. The particles used in nuclear clocks that are measured for vibrations -- and thus timekeeping -- can be excited with a relatively low-energy ultraviolet light, allowing for fewer variations from the aforementioned fields. To wit, Corey Campbell and colleagues at the Georgia Institute of Technology in Atlanta have devised a scheme that uses lasers to carefully control the spatial orientation of the electron orbits in atoms. A nuclear clock containing a thorium nucleus controlled in this way would drift by just one second in 200 billion years, the team claims. Before nuclear clocks become a reality, researchers must identify the precise frequency of light needed to excite thorium nuclei; but this is what grad students are for, right? [Image credit: University of Colorado / Science Daily]

Researchers use inkjet acumen to create wireless explosive sensor from paper
Meet Krishna Naishadham and Xiaojuan (Judy) Song. They're researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology, and those little devices they're holding may one day save you from an explosive device. This petite prototype is actually a paper-like wireless sensor that was printed using basic inkjet technology, developed by professor Manos Tentzeris. Its integrated lightweight antenna allows the sensor to link up with communication devices, while its functionalized carbon nanotubes enable it to pick up on even the slightest traces of ammonia -- an ingredient common to most IEDs. According to Tentzeris, the trick to such inkjet printing lies in the development of "inks" that can be deposited at relatively low temperatures. These inks, laced with silver nanoparticles, can then be uniformly distributed across paper-based components using a process called sonication. The result is a low-cost component that can adhere to just about any surface. The wireless sensor, meanwhile, requires comparatively low amounts of power, and could allow users to detect bombs from a safe distance. Naishadham says his team's device is geared toward military officials, humanitarian workers or any other bomb sniffers in hazardous situations, though there's no word yet on when it could enter the market. To find out more, careen past the break for the full PR.

Georgia Tech engineers pull energy out of atmospheric hat, go on electromagnetic scavenger hunt
Mankind's about to plunge into the depths of a wireless sensor-powering ether binge -- braincell annihilating vapors not included. Spearheaded by Georgia Institute of Technology's professor Manos Tentzeris and his engineering team, this ambient energy scavenging tech harnesses electromagnetic frequencies in the 100MHz - 15GHz range -- anything from your FM car radio to radar -- and converts it into a useable DC power source. So, it's free energy -- kind of. The cheap, self-powering paper or flexible polymer-based sensors are created using standard inkjet printers and Tentzeris' "unique in-house recipe" of circuit-building silver nanoparticles. Current testing hasn't yet yielded significant enough wattage to power your PS3 Slim, but it could soon via the help of supercapacitors and future solar cell integration. Imagine clothing embedded with health-monitoring biometric sensors, airport security run by something other than aloof TSA agents, or even spoilage-aware drink cartons -- milk that tells you when it's gone sour. The invisible radio band-charged possibilities are endless, but with storage still in the microwatt to one milliwatt range, it's more concept than solid vaporware reality.

Sand-swimming robot gets vertical manipulation via doorstop-shaped head (video)
So it looks like a half-stuffed sock -- and it is, sort of -- but this sandfish-inspired search and rescue robot has the potential to change the way machines maneuver through disaster zones. Playing off its previous endeavors, a team of Georgia Tech researchers has designed a wedge-shaped head to manipulate the vertical movement of its sand-swimming invention through "complex dirt and rubble environments." By mimicking the pointy snout of the sandfish lizard, and attaching it to the body of its robot -- which sports seven servo-powered segments stuffed in a latex sock and sheathed by a spandex "swimsuit" -- the team found that subtle changes in the positioning of the robot's head made for drastic differences in vertical movement. When it was placed flat on the horizontal plane, the robot descended; when it was inclined above seven degrees, it ascended. For now, the robotic sandfish has been relegated to swimming in a sea of tiny yellow balls, but it's slated to dive into a pool of debris in the name of research soon. You can check out a rather dry description of the project in the video after the break.

Nanogenerators produce electricity by squeezing your fingers together, while you dance
It's been a while since we last heard about nanogenerators -- you know, those insanely tiny fibers that could potentially be woven into your hoodie to juice up your smartphone. Dr. Zhong Lin Wang of the Georgia Institute of Technology has reported that he and his team of Einsteins constructed nanogenerators with enough energy to potentially power LCDs, LEDs and laser diodes by moving your various limbs. These micro-powerhouses -- strands of piezoelectric zinc oxide, 1 / 500 the width of a single hair strand -- can generate electrical charges when flexed or strained. Wang and his team of researchers shoved a collection of their nanogenerators into a chip 1 / 4 the size of a stamp, stacked five of them on top of one another and can pinch the stack between their fingers to generate the output of two standard AA batteries -- around 3 volts. Although it's not much, we're super excited at this point in development -- imagine how convenient to charge your phone in your pocket sans the bulky battery add-ons. And that's only one application of this technology. Yea, we know.

Robo-nurse gives gentle bed baths, keeps its laser eye on you (video)
When they're not too busy building creepy little humanoids or lizard-like sand swimmers, researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology like to concern themselves with helping make healthcare easier. To that end, they've constructed the Cody robot you see above, which has recently been demonstrated successfully wiping away "debris" from a human subject. The goal is simple enough to understand -- aiding the elderly and infirm in keeping up their personal hygiene -- but we'd still struggle to hand over responsibility for granny's care to an autonomous machine equipped with a camera and laser in the place where a head might, or ought to, be. See Cody cleaning up its designer's extremities after the break.

Lizard-style bot 'swims' through sand, straight into your worst nightmare
While robots still struggle to do basic things like hang out with us or bring us cookies, it's comforting to know that the variety of locomotion methods for this burgeoning race shows no sign of slowing. The latest of these "this would be a cool way for a robot to make its way through a disaster site and rescue people" solutions is a robot from a team at the Georgia Institute of Technology that can "swim" through sand, much like a lizard. Sand's a bit of a toughie, in case you've never found out for yourself in an ill-fated game of sand volleyball, thanks to its combo of solid and fluid dynamics. The spandex-clad, squirmy solution uncovered by Georgia Tech gets along nicely, however, going mainly with the fluid approach. Check it creeping creepily on video after the break.

Simon the robot gets upgraded with voice and face recognition, still loves organizing blocks
The last time we checked in on Simon, he was moving pretty slowly, moving some blocks from one bin to another, and while he was creepily silent, we still had high hopes for his future. Well, Simon's seemingly come a long way -- if recent footage of him and his creator, Georgia Institute of Technology researcher, Andrea Thomaz -- are to be believed. Simon's host of new features now include voice recognition (he's got a Stephen Hawking-style voice of his own), facial recognition, sound localization, plus he's way speedier now. All of this helps Simon learn how to do things on his own without constantly being commanded. And in case you were wondering -- Simon the robot is no fanboy -- his various software programs run on Windows, Linux, and Mac machines. Hit the read more to view the video.

Video: Google Earth animated with real time human and vehicular traffic
Mmm, real time dynamic maps of the Earth. It seems nowadays that supervillainy just isn't as hard as it used to be. Back in the days of Hugo Drax, you had to be a filthy rich eccentric to ever get to spy on the whole world, whereas today all you need is Google Earth and some Georgia Institute of Technology students. Using motion capture data and the veritable litany of CCTV cameras people have surrounded themselves with, the team have succeeded in mapping and animating the real time movements of cars, people and clouds. A proper unveiling is coming up at a symposium next month, by which point they might have added weather patterns, birds and river motions to that list, but for now you can enjoy the video demo after the break. [Via Engadget Polish]

EI-E: Now robots hope to put dogs out of work too
Nothing fulfills the need for companionship like the cold hard steel of a robot. The gentle whooshing of gears and servos floats misty lavender doughnuts of joy into the hearts of even the most severely disabled farmers. So we're stoked to see that researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have taken the best attributes of our canine helpers and applied them to the EI-E helper robot. Like a service dog trained to grab hold of a towel to manipulate doors and drawers, the domestic robot can navigate the complexities of your home decor and respond to laser pointed or voice-commands such as push, pull, and a variety of hot tugging actions. Drape that thing in a plush, doughboy suit and we'll be singing Ee i Ee i Oh! all the way home.Read -- VideoRead -- Article











