newcastleuniversity
Latest
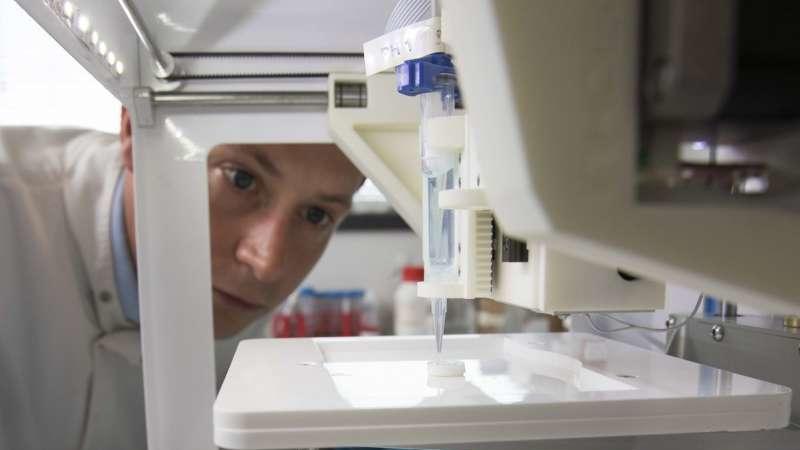

Scientists create the first 3D-printed human corneas
Newcastle University researchers have devised a groundbreaking experimental technique that could help millions on the corneal transplant waiting list. By using a simple 3D bio-printer, Professor of Tissue Engineering Che Connon and his team of scientists were able to combine healthy corneal stem cells with collagen and alginate (a type of sugar sometimes used in tissue regeneration) to create 'bio-ink' -- a printable solution that enabled them to reproduce the shape of a human cornea in just 10 minutes.
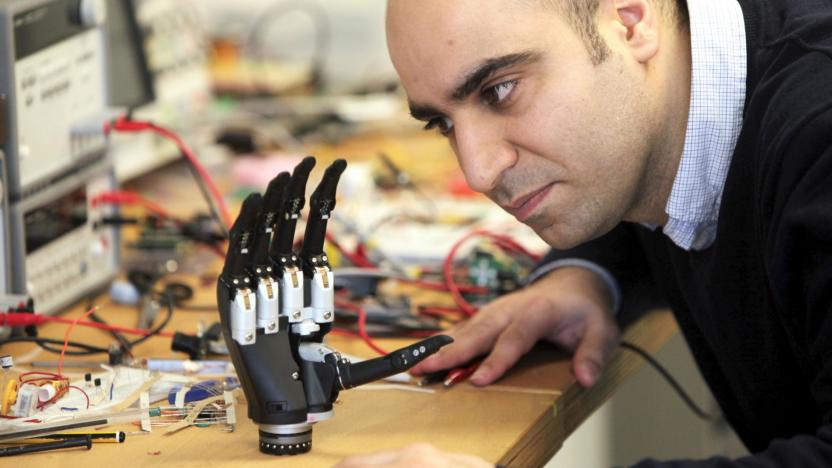
'Intuitive' prosthetic hand sees what it's touching
Even as we begin to wire prosthetics directly into our peripheral nervous systems and wield Deus Ex appendages with only the power of our minds, many conventional prosthetic arms are still pretty clunky, their grips activated through myoelectric signals -- electrical activity read from the surface of the stump. The "Intuitive" hand, developed by Dr Kianoush Nazarpour, a senior lecturer in biomedical engineering at Newcastle University, offers a third approach. It uses a camera and computer vision to recognize objects within reach and adjust its grasp accordingly.

Your phone's motion sensors can give away PINs and passwords
You could be the most careful mobile user ever, but hackers can still steal your PINs and passwords simply by spying on your phone's motion sensors. A team of cyber researchers from the UK's Newcastle University have demonstrated how easy it is to steal a four-digit PIN by analyzing the way your phone tilts and moves as you type. You might think your phone's movements are random, but they apparently create distinct patterns. During their tests, they were able to crack four-digit PINs on the first guess 70 percent of the time and 100 percent of the PINs they used by the fifth guess.

Mantises get tiny 3D glasses to test depth perception
The praying mantis is the only known invertebrate with 3D perception, however this fact was originally proven in the 1980s using prisms and occluders, which only support a limited number of images. Scientists want to deepen their understanding of the insect, so they've taken this research a step further by testing a few mantises with tiny 3D glasses. A team from Newcastle University created a miniature cinema in the hope that the insects would move when they perceived 3D images with the appropriate lenses. The trick worked, but only with a specific kind of spectacles.

Praying mantises get extra-tiny 3D glasses to test their vision
While 3D video may not be very popular these days, someone's still wearing 3D glasses -- or rather, something. Newcastle University scientists are outfitting praying mantises with very small 3D eyewear to test their depth perception, which is unique in the insect world; most species are limited to 2D. The researchers want to see if the bugs are fooled by the effects of a 3D movie like that you'd see in a theater. If they are, we'll know that they evolved 3D vision similar to that of humans and monkeys.

Neuroscientists develop game for stroke rehabilitation, give the Wii a run for its money
Think the Wii has the market cornered on gaming rehab? Think again -- neuroscientists at Newcastle University are developing a series of motion controlled video games to make stroke rehab more fun and accessible. The team's first title, dubbed Circus Challenge, lets patients digitally throw pies, tame lions and juggle to help them build strength and regain motor skills. As players progress, the game ratchets up its difficulty, presumably to match pace with their recovery. Although Limbs Alive, the game's publisher, has only described their motion controller as "next-generation," it affirms that the game will be playable on PCs, laptops and tablets later this year. In an effort to lower costs and provide at-home therapy, the team hopes to leverage a £1.5 million award from the UK's Health Innovation Challenge Fund to build a system that will allow therapists to monitor patient progress remotely. The whole enchilada still needs some time to bake, but you can hit the break for a video and the full press release.

BinCam posts photos of your trash on Facebook, shames you into recycling (video)
We're not sure how comfortable we are with everyone online being able to examine our, as the Brits would say, "rubbish." But our friends across the pond are apparently ok with it, seeing as it's the home of BinCam -- a research project out of Newcastle University that posts pictures of people's trash on Facebook. At the heart of the experiment is an Xperia X10 Mini strapped under the lid of a garbage can that automatically snaps a photo every time it's opened and closed. That image is then uploaded to the BinCam Facebook app, where you're showered with public shame for failing to sort your recyclables or celebrated for not wasting food. And, just in case you think this is all an elaborate joke, check out the BBC report after the break the the study of how it affected student behavior at the source.

Silicon carbide sensors developed for transmitting inside volcanos
There's one serious obstacle to volcano research: volcanos, like, shoot lava. Sure, you could aim a thermal camera at one from a safe distance, but where's the fun in that? On the other hand, researchers at Newcastle University are developing silicon carbide-based components for a device that they say will be able to withstand 900° Celsius temperatures -- just the thing to sense what's going on inside a volcano and transmit the info in real-time. Not only will this allow researchers to better understand conditions leading up to an eruption, it might also someday signal an eruption before it occurs. "At the moment we have no way of accurately monitoring the situation inside a volcano," says NU's Dr. Alton Horsfall. "With an estimated 500 million people living in the shadow of a volcano this is clearly not ideal." Since silicon carbide is more resistant to radiation than plain ol' silicon, the tech can also be used inside nuclear power plants or even as radiation sniffers in places that might face a terror attack.






