universityoftoronto
Latest
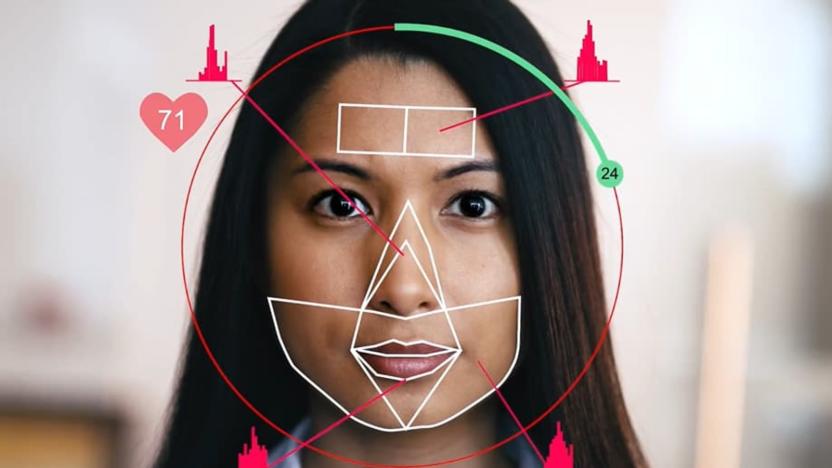
Researchers find way to measure blood pressure with a selfie video
In the near future, you might not have to traipse to your doctor or pharmacy to determine your blood pressure. Researchers have figured out a way to accurately measure it with your phone's camera.

Researchers teach a computer to compose sonnets like Shakespeare
In addition to penning 37 plays, William Shakespeare was a prolific composer of sonnets -- crafting 154 of them during his life. Now, more than 400 years after his death, the Bard's words are influencing a new generation of poets. It's just that these writers do so with silicon imaginations and digital quills.

ICYMI: Genetically-based cancer meds, taste's base and more
#fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-37143{display:none;} .cke_show_borders #fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-37143, #postcontentcontainer #fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-37143{width:570px;display:block;}try{document.getElementById("fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-37143").style.display="none";}catch(e){}Today on In Case You Missed It: Scientists managed to turn taste on and off in mice by activating and silencing brain cells, putting to bed the notion that taste is determined by the tongue. University of Toronto cancer researchers used a patient's genetic material to craft a cancerous mass on a long strip of collagen, then wound it up and gave it the same radiation and chemo drugs a patient would get for that type of illness. They can then stretch the roll out to see whether the treatment killed the cancer cells. The team hopes to eventually tailor people's cancer treatments to their own genetics. And the first battle in the private company space race may have gone to Blue Origin over Space X, for landing its reusable rocket first.

Doctors grow tumors that roll up like toilet paper
Modern medicine still takes a decidedly ham-fisted approach to treating cancer -- it attacks with radiation and chemotherapy drugs that are just as toxic to healthy tissues as they are to tumors. What's more the effects of these treatments vary between patients. However, a novel (albeit gag-inducing) new research method from the University of Toronto hold the key to personalizing oncology: 2D tumors grown from the patient's own genetic material.

Mandatory South Korean parental control app is a security nightmare
Back in April, South Korea required that wireless carriers install parental control apps on kids' phones to prevent young ones from seeing naughty content. It sounded wise to officials at the time, but it now looks like that cure is worse than the disease. Researchers at the University of Toronto's Citizen Lab have discovered 26 security holes in Smart Sheriff, the most popular of these mandatory parental apps. The software has weak authentication, sends a lot of data without encryption and relies on servers using outdated, vulnerable code. It wouldn't be hard for an intruder to hijack the parent's account, intercept communications or even scoop up the kids' personal details. The worst part? Some of these vulnerabilities apply on a large scale, so a particularly sinister attacker could compromise hundreds of thousands of phones at once.

This telescope is really just 10 Canon lenses strapped together
Hunting for extremely dim galaxies is especially difficult with single-lens telescopes. That's because, no matter how technologically advanced, the device's design cannot fully eliminate detail-obscuring scattered light from the resulting images. The University of Toronto's Dragonfly Telephoto Array, however, deftly avoids that issue. This array -- one of the smallest multi-lens astronomy telescopes in use today -- is comprised of 10 Canon 400mm f/2.8 L IS II USM telephoto lenses, each costing $10,000. What's more, each lens is coated in a unique subwavelength nanomaterial that drastically reduces light reflection within the optic. And, like its insect inspiration, the Dragonfly's ten eyes can work in concert with one another to further reduce unwanted illumination in the resulting image, bringing out otherwise unseen detail in cosmic structures. According to the University of Toronto spokesman Roberto Abraham, this $100,000 system is ten times as accurate as its nearest rival. [Image Credit: U of Toronto]

Tiny glass fibers are the secret to boots made for walkin' (on ice)
A team of Canadian researchers don't think cleats and studs are the way to go when it comes to winter boots. In fact they've developed what they believe are superior alternatives: ones that use minuscule bits of glass instead. The team has designed boot soles embedded with glass particles than can grip slippery surfaces and yet feel like regular rubber on ordinary flooring. These particles give the soles a sandpaper-like texture, with each one acting as a microscopic stud. To make sure their creation provides enough grip, the researchers test their prototypes in a self-contained room with smooth, tiltable floors.

Students build a robot arm you control with the wink of an eye
Want proof that you don't need big, specialized equipment to produce a mind-controlled robot arm? Just look at a recent University of Toronto student project. Ryan Mintz and crew have created an arm that you control using little more than a brainwave-sensing headset (which is no longer that rare) and a laptop. The team's software is smart enough to steer the arm using subtle head movements, such as clenching your jaw or winking your eye; it also knows when you've relaxed.

AeroVelo's human-powered helicopter bags $250,000 Sikorsky Prize
We're sure AeroVelo team members think every sleepless night and pedal push are worth it now that they can add the prestigious $250,000 Sikorsky Prize to their pile of bragging rights. They've completely demolished all the requirements needed to win the human-powered helicopter competition during one of their recent attempts. Atlas, their flying contraption, stayed in the air for 64.11 seconds, flew at a max altitude of 3.3 meters (10.8 feet) and never meandered beyond the designated 10 x 10 meter (33 x 33 feet) area. The University of Toronto's creation was locked in head-to-head battle with the University of Maryland's Gamera chopper for quite some time, but it's finally bagged the prize that had remained unclaimed for 33 long years. That's a tremendous accomplishment for anyone, especially for a project with humble beginnings, and if Leonardo Da Vinci were still alive, he'd extend a big congratulazione.

University of Toronto student tech shoots HDR video in real-time (eyes-on)
Sure, you love the HDR pictures coming from your point-and-shoot, smartphone or perhaps even your Glass. But what if you want to Hangout in HDR? An enterprising grad student from the University of Toronto named Tao Ai -- under the tutelage of Steve Mann -- has figured out how to shoot HDR video in real-time. The trick was accomplished using a Canon 60D DSLR running Magic Lantern firmware and an off-the-shelf video processing board with a field programmable gate array (FPGA), plus some custom software to process the video coming from the camera. It works by taking in a raw feed of alternatively under and over exposed video and storing it in a buffer, then processing the video on its way to a screen. What results is the virtually latency-free 480p resolution HDR video at 60 frames per second seen in our video after the break. When we asked whether higher resolution and faster frame rate output is possible, we were told that the current limitations are the speed of the imaging chip on the board and the bandwidth of the memory buffer. The setup we saw utilized a relatively cheap $200 Digilent board with a Xilinx chip, but a 1080p version is in the works using a more expensive board and DDR3 memory. Of course, the current system is for research purposes only, but the technology can be applied in consumer devices -- as long as they have an FPGA and offer open source firmware. So, should the OEM's get with the program, we can have HDR moving pictures to go with our stationary ones.

Google acquires neural network startup that may help it hone speech recognition and more
Mountain View has just picked up some experts on deep neural networks with their acquisition of DNNresearch, which was founded last year by University of Toronto professor Geoffrey Hinton and graduate students Alex Krizhevsky and Ilya Sutskever. The group is being brought into the fold after developing a solution that vastly improves object recognition. As a whole, advances in neural nets could lead to the development of improved computer vision, language understanding and speech recognition systems. We reckon that Page and Co. have a few projects in mind that would benefit from such things. Both students will be transitioning to Google, while Hinton will split his attention between teaching and working with the search giant.

Autodesk researchers develop 'magic finger' that reads gestures from any surface (video)
By combining a camera that detects surfaces with one that perceives motion, Canadian university researchers and Autodesk have made a sensor that reads finger gestures based on which part of your body you swipe. The first camera can detect pre-programmed materials like clothing, which would allow finger movements made across your pants or or shirt to activate commands that call specific people or compose an email, for instance. Autodesk sees this type of input as a possible compliment to smartphones or Google Glasses (which lack a useful input device), though it says the motion detection camera isn't accurate enough yet to replace a mouse. Anyway, if you wanted that kind of device for your digits, it already exists -- in spades.

Alt-week 9.22.12: Quantum Scotch tape, moving walls and scientific beer
Alt-week peels back the covers on some of the more curious sci-tech stories from the last seven days. Sometimes, here at alt.engadget.com, we're literally on the bleeding edge of technology. We get to explore concepts and ideas that are almost nebular in nature. Not this week though, where there's a distinct utilitarian aroma in the air. The glittery overcoat of future science is replaced by the rolled-up sleeves of good old-fashioned engineering. A bit of sticky tape, a proof of concept omnidirectional bike and a hardware matrix wall. After all that, you'll probably want a beer to wash it down with. Fortunately for you, it's all here. This is alt-week.

Researchers create record-breaking solar cell, set bar marginally higher
Solar cell development is typically a small numbers game, and a group of researchers at the University of Toronto have managed to eke out a few more percentage points in efficiency with a new record-breaking cell. Setting a high mark for this type of cell, the team's Colloidal Quantum Dot (CQD) film harvests both visible and non-visible light at seven percent efficiency, a 37 percent increase over the previous record. The breakthrough was achieved by leveraging organic and inorganic chemistry to make sure it had fewer nooks and crannies that don't absorb light. With the advantages of relatively speedy and cheap manufacturing, the technology could help lead the way for mass production of solar cells on flexible substrates. In the meantime, check out the source for the scientific lowdown.

Insert Coin: Atlas human-powered helicopter gunning for elusive Sikorsky prize (video)
In Insert Coin, we look at an exciting new tech project that requires funding before it can hit production. If you'd like to pitch a project, please send us a tip with "Insert Coin" as the subject line. The AeroVelo group, a team of students and professional engineers, wants its Atlas helicopter to hover for one minute, reaching at least three meters (10 feet) powered by human muscle alone. If the grunt-powered machine succeeds, it'll nab the American Helicopter Society International's $250,000 Sikorsky Prize, which has gone unclaimed since it launched in 1980 -- with the best efforts barely leaving the ground. But the University of Toronto-based team reckons it has the chops, with two PhDs aboard and Snowbird, the first successful human-power ornithopter, under its belt. The Atlas will feature four rotors like a 1994 design from Japan, which flew for 19 seconds, a simple and stable configuration that required less pilot power than other models. The would-be flyers have rustled up more than $27k toward the $30k target with 35 hours left, so if you'd like to help out -- and fulfill the dream of eccentric inventors everywhere -- hit the source link for details.

Quantum dots could coat the world in nano-sized solar panels
We've long believed in the mystical power of quantum dots, so it makes perfect sense to us that one day they'll be used to fully harness the Sun God's rays and thereby save the planet. The nano-particles turn light into electricity, and could potentially be manufactured cheaply and abundantly enough to coat surfaces in current-generating paint. The main obstacle to this has so far been efficiency: the clever little dots just don't work very hard. However, scientists at the University of Toronto now claim to have discovered a fix. Instead of using a single layer of particles, which can only harvest one meager wavelength from the full gamut of solar light, they added a second coat on top and configured it to be sensitive to an additional part of the spectrum. By adding third and fourth layers, the researchers hope to achieve a commercially viable efficiency of 10-percent within the next five years. We humbly call on Ra to be pleased with their efforts.

Chlorine could be key to the cheaper, more efficient OLED TV of your dreams
Chlorine -- it's not just for keeping your clothes white and your pool clean anymore! Soon, layers of the stuff, just a single atom thick, could play a pivotal role in OLED manufacturing. Researchers at the University of Toronto have found that this tiny amount of Cl can almost double the efficiency of existing displays while reducing complexity and driving down costs. Using a rather simple procedure involving UV light, the team was able to chlorinate standard electrode panels found in conventional OLEDs without having toxic chlorine gas wafting about. While this is good news for manufacturers, it's even better news for consumers. We've been itching to mount a big, organic flat-screen in our parents' basement living room. Finally, we may see cheap OLED TVs on Walmart shelves -- right next to the Clorox.

Snowbird ornithopter sets record for human-powered flight (video)
In August this year, a Canadian engineering student achieved a first -- in fact, one of the last firsts in aviation. A human powered ornithopter (a craft that flies by flapping its wings) flew for 19.3 seconds, traveling some 475 feet at an average speed of 15.9 miles an hour. Built by University of Toronto grad students Todd Reichert and Cameron Robertson, the project required that the pilot (Reichert) lose 17 pounds, maintain a special diet, and train daily. Named Snowbird, the craft weighs under 95 pounds and has a wingspan of some 105 -- comparable to a Boeing 737. It was towed aloft by a car, after which the pilot pumped a set of pedals with his feet, which caused the wings to flap. Unlike previous attempts in the past, the Canadian group was able to provide telemetry data to prove that the craft flew under its own power. On confirmation by the Federation Aeronautique Internationale, the craft is set to receive the award for the longest sustained flight by a human-powered ornithopter. Video after the break.

Researchers develop robotic tweezers that can grasp single cells
Usually when we talk about robot grip strength, it's in the context of being slowly crushed to death during a violent robot uprising, but it appears we now have to fear our bodies being stolen away cell-by-cell as well. That's the terrifying reality being brought to life at the University of Toronto, where researcher Yu Sun and his team have developed semi-autonomous microscopic robo-tweezers that can sense touch and grip strength acutely enough to pick up and move individual heart cells during tests without damaging them. The tiny rig is just .1 inches long, and the grippers on the ends are fine enough to pick up cell just 10 micrometers wide. So far they've just been arranging cells during testing, but Yu says eventually they can be used to assemble silicon parts on circuit boards, or even engineer tissue. No word on when these might hit production, but when they do Yu says he expects them to cost just $10 each. At least the revolution will be inexpensive, we guess.

Researchers develop algorithm to combat photo blur
Since it's unlikely that your hand will get any steadier with age, and we probably won't see optical image stabilization in cameraphones anytime soon, researchers are concentrating on ways to fix your crappy photos once they've already been captured. The latest salvo in the war against so-called hand motion blur comes from a team of computer scientists at MIT and the University of Toronto, who have developed an algorithm that can create a sharper picture by "estimating the distribution of a number of probable images" and coming up with a happy medium. Introduced at this year's Siggraph Conference in Boston, the algorithm could potentially be included in future versions of Adobe Photoshop -- which currently fights blur with a rather ineffective unsharp mask tool -- although it will do nothing for blurring caused by moving objects or improperly-focused shots. Unfortunately, it sounds like this product is still at least a year away from commercial release, so tripods and nerve-steadying Pentazemin are still your best bets for the time being.[Thanks, Alex]










