greenhousegases
Latest

'Minecraft' mod fosters a collaborative effort against climate change
A Minecraft modder has added some fresh gameplay issues for players to deal with in the form of climate change. Nick Porillo's GlobalWarming mod alters the atmosphere based on certain actions like smelting ores. Temperatures will rise as carbon emissions increase, leading to violent storms, forest fires and a drop in snowfall levels as climate change takes hold.

California has already hit its 2020 greenhouse gas emissions goal
The EPA may be in shambles after Scott Pruitt's short but brutal tenure, but California actually has some good news on the global warming front. The state is well ahead of its schedule for cutting greenhouse gases. According to data released by the California Air Resources Board this week, greenhouse gas emissions dropped to 429.4 million metric tons in 2016, below the target of 431 metric tons for 2020. The total in 2015 was 441.4 million metric tons.

11 states sue EPA over attempt to reverse ban on ozone-harming HFCs
The Scott Pruitt-era EPA is facing yet more legal action over its attempts at reversing US environmental regulations. A group of 11 states (including New York and California) and the District of Columbia have sued the EPA for violating the Clean Air Act by "effectively" lifting a ban on climate-changing hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). The states contend that the agency's April "guidance" document illegally removed the entire HFC ban rather than going through the necessary public rulemaking process.

Investigators say China is behind illegal CFC emissions
A global environmental "whodunit" emerged last month, when researchers revealed that someone, somewhere, was pumping tonnes of banned chemical CFC-11 into the atmosphere. Now, investigators think they've found the culprits. According to The New York Times, the ozone-damaging gas is likely being emitted by illegal refrigerator factories in China, which claim no-one told them the chemical was prohibited by the 1987 Montreal Protocol.

EPA scientific advisory board to review agency's recent rollbacks
This week, the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) Scientific Advisory Board (SAB) met to discuss some of the changes the agency has proposed under Administrator Scott Pruitt. And ultimately, the 44-person board voted to review a number of the EPA's proposals and write a letter to Pruitt. "The leadership of the board was chosen by Pruitt himself, so their decision today is a sharp rebuke of his leadership and this dangerous proposal," Ana Unruh Cohen, managing director of government affairs at the Natural Resources Defense Council, told Bloomberg.

Treaty ending use of planet-warming HFCs takes effect in 2019
The treaty phasing out the use of Earth-warming hydrofluorocarbons now has an official start date. Sweden has become the 20th country to ratify the Kigali Amendment, invoking a clause that has the measure taking effect on January 1st, 2019. From then on, wealthier countries (less fortunate nations have until 2024 or 2028) must cut back on use of the greenhouse gas in everything from air conditioning to refrigerators. Ideally, this pushes companies to use and develop eco-friendly coolants.

Federal report says humans are the cause of climate change
Today, over a dozen federal agencies released the Climate Science Special Report, which is a product of the National Climate Assessment -- a congressionally mandated review that takes place every four years. In it, hundreds of scientists from dozens of government agencies and academic institutions present evidence that supports the existence of a human-caused warming planet and all of the consequences that come with it. "This assessment concludes, based on extensive evidence, that it is extremely likely that human activities, especially emissions of greenhouse gases, are the dominant cause of the observed warming since the mid-20th century," the report stated. "For the warming over the last century, there is no convincing alternative explanation supported by the extent of the observational evidence."

California continues to lead the US in renewable energy
In 2006, California adopted aggressive legislation aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and boosting renewable energy production throughout the state. And since then, the state has been tracking its progress through its annual California Green Innovation Index report. The ninth report was just released this week and it shows that the state has made some major progress towards its renewable energy goals while hitting a bit of a bump in regards to its emission reductions.

Research finds deadly heatwaves will occur more often
A study published today in Nature Climate Change predicts that deadly heatwaves will become more frequent in the future. The study found that currently, around 30 percent of the world experiences life-threatening heat for at least 20 days per year. But if greenhouse gas emissions continue to grow, that number could jump up to 74 percent by 2100.

Bacteria could lead to cleaner methane power
Methane as a greenhouse gas isn't all that eco-friendly when used for power, but scientists might have a way to keep the damage to a minimum. Penn State researchers have crafted microbial fuel cells that can convert methane into electricity right at the well, without leaking loads of gas into the atmosphere by sending it through pipes. The team created a cocktail of bacteria (including a synthetic microbe you can't normally grow) that produces the necessary materials to grab and transport electrons from the methane. Not only is this a relatively clean process, the bacteria can run on waste products -- it might clean up the site as it generates power.

Dear Donald Trump: 'Clean coal' doesn't exist
"Clean coal" is an oxymoron. Even if you took a hunk of coal, doused it in bleach and scrubbed it for six hours with a soapy horsehair brush, it would still cause lung cancer and fill the air with carbon emissions when you burned it. Anyone who says otherwise is lying. However, the phrase "clean coal" is ridiculously tenacious in public discourse. Just this week, President Donald Trump used it: As he signed an executive order rolling back a bevvy of environmental protections laid out under the Clean Power Plan, he turned to the coal miners staged around his desk and promised to "end the war on coal and have clean coal, really clean coal." The president of the United States is lying.

Trump rolls back Obama-era climate change policies
President Donald Trump has signed an executive order that rolls back policies designed to combat climate change implemented by former President Barack Obama. The order is a broad stroke, touching everything from federal policy-making to Energy Star regulations on home appliances. However, today's move specifically targets the Clean Power Plan, allowing the Trump administration to rewrite carbon emission rules for new and existing power plants. It also restarts the federal coal leasing program, enabling energy companies to once again buy the rights to mine on federal lands.

Trump's EPA proposal cuts funding for climate change, pollution programs
Ever since the election, we've been wondering what the new presidential administration has in store for environmental programs, and the proposed new EPA budget may provide answers. First, the Washington Post reported the proposal would cut EPA staff by one fifth in the first year and eliminate dozens of programs.

Republicans poised to roll back environmental protections
With astonishing speed, US Republicans are set to strike down laws or vote on new bills that eliminate environmental protections for the air, streams and national parks. The measures are being proposed so quickly that it has been difficult for environmentalists and Democrats to muster opposition. Much of the Republican strategy depends on a little-used law called the Congressional Review Act, signed into power by Bill Clinton in the '90s to prevent presidents from creating new laws on their way out of office.
NASA mission will study Earth's 'breathing' from space
Scientists know that the Earth "breathes" carbon, particularly through plants that absorb carbon through photosynthesis when they're healthy and give it up when they lose their leaves or die. They haven't had an extremely detailed look at that breathing cycle, however, which is where NASA and the University of Oklahoma come into play. They're launching a satellite mission, the Geostationary Carbon Cycle Observatory, that will both study plant health as well as the exchange of key gases (carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and methane) between the land and the atmosphere.
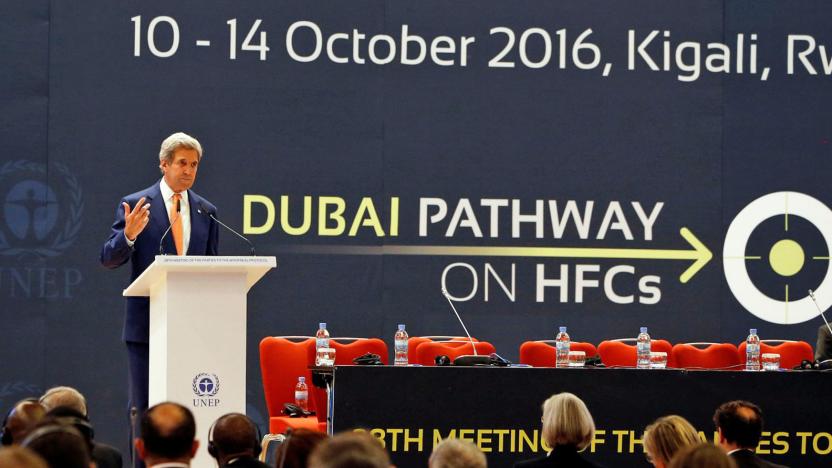

Kigali Amendment reached to cut use of planet-warming HFCs
Today, more than 170 nations have settled on a plan to cut the use of hydrofluorocarbons (or HFCs), a refrigerant that causes warming in the Earth's atmosphere. Called the Kigali Amendment for the location of negotiations in Rwanda, it's the result of seven years of work to expand the Montreal Protocol reached in 1987. That deal phased out the use of ozone-depleting chemicals, and by adding to it, this agreement carries its legally binding weight as a treaty, without needing to wait for ratification like last year's Paris Agreement.
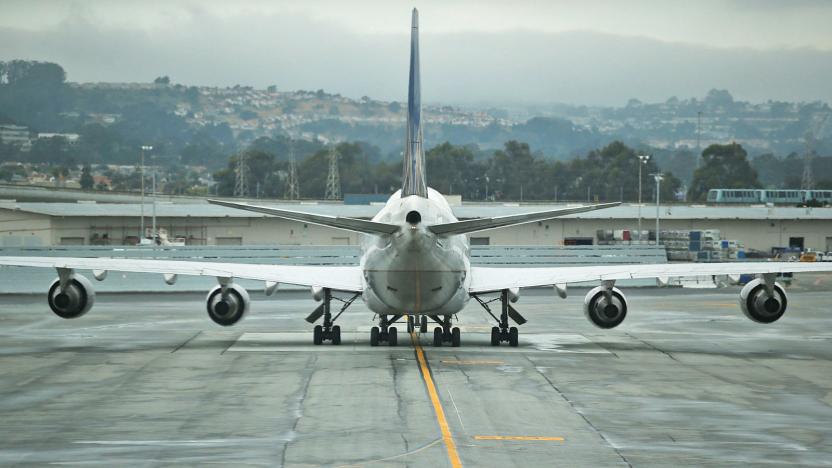

EPA findings should lead to caps on aircraft emissions
It's no secret that aircraft contribute to harmful emissions like road-going vehicles, and the Environmental Protection Agency is one step closer to keeping that pollution in check. It recently finalized findings showing that some aircraft produce air pollution that contributes directly to climate change. As a result, the EPA is now free to set standards for aircraft emissions that help the US honor the Clean Air Act and, ultimately, its commitment to the Paris climate change agreement. While the US is already backing an international standard, this gives it the chance to demand tougher (or at least, more America-specific) requirements.

Climate change is pushing clouds up and toward the poles
For the first time, researchers have found evidence that global warming caused by humans is affecting clouds -- and not in a good way. A study by team from the Scripps Institution of Oceanography shows that clouds are being pushed up and out of mid-range latitudes toward the poles. "It's really the first credible evidence that we have of climate change and clouds in the observed record ," says Scripps atmospheric scientists Joel Norris. The cloud shift could push temperatures even higher than predicted, and also shows the need to improve atmospheric measurements.

Human climate influence means we're skipping an ice age
According to a new study published in Nature, human-generated climate change -- specifically the massive additions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gasses to the atmosphere -- is causing the Earth to effectively delay the start of the next ice age by 100,000 years. Typically, ice ages occur once every 50,000 years or so; as they have in at least eight regularly intervalled times in the Earth's history.

Draft climate change deal lowers greenhouse gases by 2050
Earth just took a tentative step toward a new, comprehensive plan for improving the environment. Representatives from 195 countries have approved a draft UN climate change agreement that will ask all participants to lower their carbon dioxide emissions. There are still many, many details left to resolve ahead of a final deal (ideally signed next week), but the ultimate goal is to have countries reduce their greenhouse gas levels by 2050, and to eliminate emissions completely between 2060 and 2080.








