mindcontrol
Latest
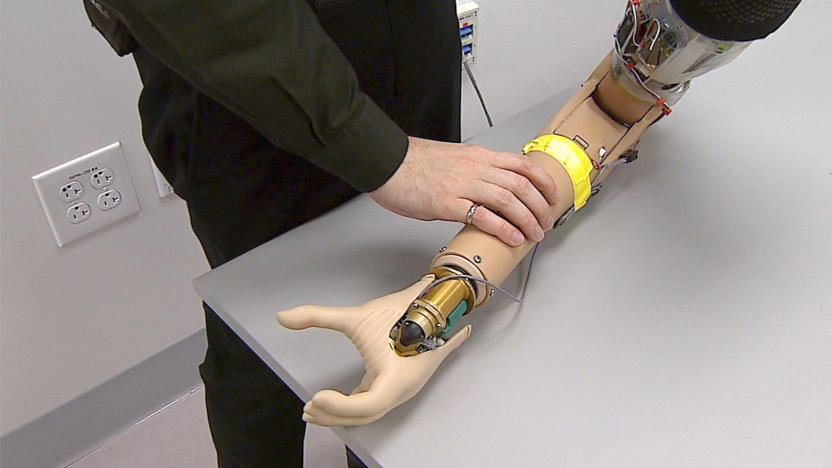
Brain interface adds sense of presence to bionic limbs
It's been possible for a while to control bionic limbs with your brain, but there's been something missing: kinesthetic feedback, or the nervous system signals that give your limbs a sense of presence. You frequently have to stare at your artificial arm to ensure that you're grabbing a cup instead of operating on instinct. That elusive quality may soon be a regular staple of prosthetics, however. Researchers have developed a neural interface that generate this feedback and make bionic feel like they're part of your body.
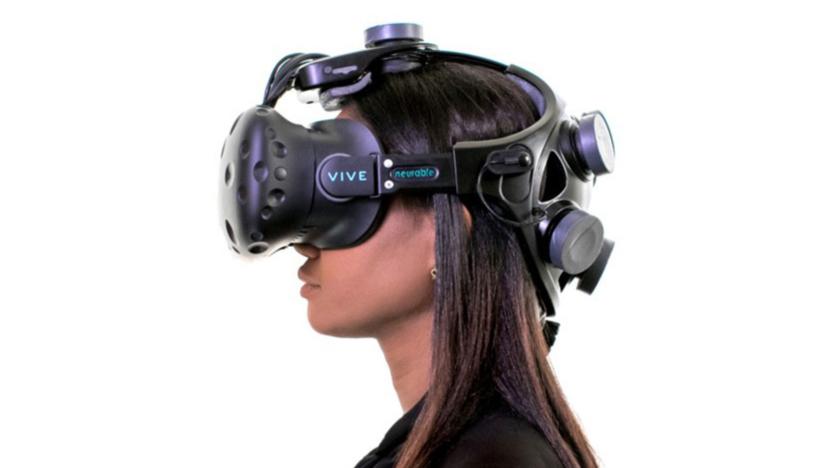

Brain-controlled VR game hints at a hands-free future
We may be a long way off from a Holodeck-like virtual reality where your body is the controller, but Neurable might have the next closest thing. It recently unveiled a prototype peripheral that adds brain control to VR experiences. The device replaces the regular strap on an HTC Vive and uses specific brain signals (event-related potentials, not the EEG patterns you usually see) to trigger actions. In a showcase game, Awakening, you use your mind to escape a lab as if you had telekinetic powers -- you don't have to hold plastic wands as you battle robots and grab objects.

ICYMI: Mind-controlled mice kill on command
try{document.getElementById("aol-cms-player-1").style.display="none";}catch(e){}Today on In Case You Missed It: You might have thought things couldn't get any worse, but you'd be wrong. A recent study published in Nature showed that first, mice could be bred so that the neurons in their brains respond to laser lights. Then, the adult mice were hooked up to laser light helmets and when turned on, the hunt and kill area of the brain was triggered so that mice instantly attacked crickets in their cages. I have one thing to say: You can watch the 2009 movie, Gamer, if you want a prophecy of our future lives.
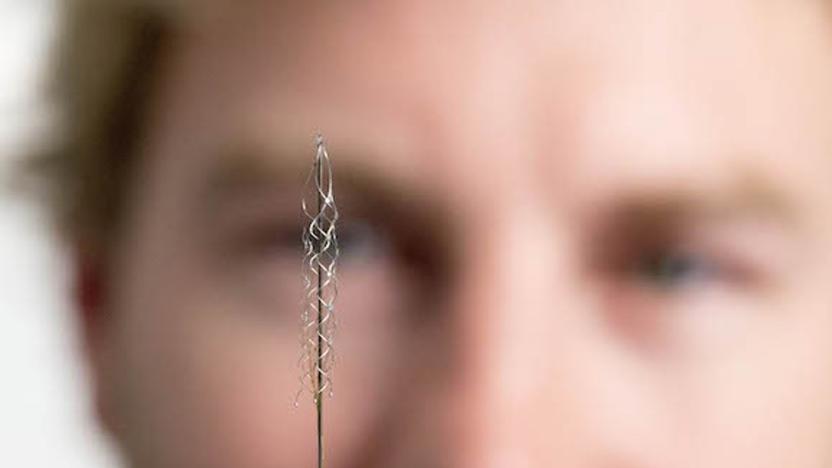
Brain-machine link helps you steer exoskeletons with your mind
Right now, mind-controlling a machine isn't pretty: you typically wear a silly cap or headset, or else subject yourself to open brain surgery to get a deeper link. Australian scientists might have a better way, though. They've developed a brain-machine interface that taps into your motor cortex through a relatively simple operation -- you won't need to gamble with your health to have a permanent connection to robotics. The device (known as a stentrode) would let you directly steer an exoskeleton or artificial limb through thoughts alone, even if you need the implant for "many months" at a time.

ICYMI: Cockroach torture, an app for Parkinson's and more
#fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-567613{display:none;} .cke_show_borders #fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-567613, #postcontentcontainer #fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-567613{width:570px;display:block;} try{document.getElementById("fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-567613").style.display="none";}catch(e){} Today on In Case You Missed It: A cybernetic cockroach how-to describes how to use an Arduino to control where a cockroach goes, which makes all of us uncomfortable.

Mind-controlled robot gives the disabled a taste of home
Brain-controlled robot limbs have already helped the disabled gain some mobility, but full-fledged robots have proven elusive: how do you use thoughts to steer a free-roaming machine? Swiss researchers think they have the answer. They've developed a mind-controlled telepresence robot that lets those with motor disabilities travel when it would otherwise be impractical. It's ultimately a laptop on a pedestal, but it uses clever semi-autonomous software to take the hard work out of controlling where the robot goes. You only have to don an EEG-based cap and imagine moving your hands or feet -- the robot plots a path based on your commands, and avoids obstacles all on its own.

ICYMI: Worm mind control, a creepy new Barbie and more
#fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-630410{display:none;} .cke_show_borders #fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-630410, #postcontentcontainer #fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-630410{width:570px;display:block;} try{document.getElementById("fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-630410").style.display="none";}catch(e){}Today on In Case You Missed It: A new $75 Barbie with speech recognition software can talk to your kids and give them career advice, as well as store previous conversations to refer back during girlfriend chats. Holy hell, yes? Meanwhile, some scientists figured out how to use mind control on worms in a lab with an ultrasonic pulse that gets the slimy suckers to change course. And a group of friends gathered in the desert in Nevada to build a scaled seven mile solar system. Bummer alert: They left off Pluto.

Scientists control a worm's brain cells using sound waves
Forget using clunky headsets and implants to control brain cells... one day, you might only need to use sound waves and some chemicals. Salk Institute scientists have found a way to control the brain cells of a tiny nematode worm through ultrasound. All they need to do to trigger activity is add a membrane ion channel to a neuron cell and blast it with ultrasonic waves -- in this experiment, the researchers changed the worm's direction through sound bursts. The approach is not only relatively unintrusive, but can reach deep into the body. You could trigger neural activity without ever hooking up an electrode, even for much larger animals.

BBC experiment lets you control iPlayer with your mind
Instead of grabbing the remote or poking at your smartphone, the BBC thinks the future of TV navigation could lie in mind control. For its latest experiment, the broadcaster is testing a brainwave reading headset developed by This Place that lets you launch iPlayer and choose programmes with your thoughts. The device uses two sensors, one on your forehead and one on your ear, to interpret electrical activity as "concentration" or "meditation." Depending on your preference, focusing your mind will trigger a contextual command, such as launching the app or selecting from one of five programmes on a scrolling carousel. Once the app lands on your chosen TV show, you simply have to "think" until a pink volume bar fills on the left-hand side of the screen. The functionality is basic, but the BBC hopes it can be adapted to assist viewers with disabilities. For now it's just a proof of concept, but maybe in the future we'll all be using brainwaves to tune into BBC Two.

Mind-controlled drones promise a future of hands-free flying
There have been tentative steps into thought-controlled drones in the past, but Tekever and a team of European researchers just kicked things up a notch. They've successfully tested Brainflight, a project that uses your mental activity (detected through a cap) to pilot an unmanned aircraft. You have to learn how to fly on your own, but it doesn't take long before you're merely thinking about where you want to go. And don't worry about crashing because of distractions or mental trauma, like seizures -- there are "algorithms" to prevent the worst from happening.

Control Google Glass with your mind... and a second headset
Up until now, you can only navigate Google Glass by touching or talking to it, but London-based firm This Place just made it possible to control the device using something else: your brainwaves. The company just released an open source application called MindRDR that gives you something akin to very, very limited telekinetic abilities -- so long as you have both Google Glass and Neurosky's EEG biosensor headset. See, MindRDR serves as the bridge that connects the two, translating the brain activity from the EEG biosensor into executable commands for the high-tech eyewear. At the moment, the software can only take pictures and upload them to either Facebook or Twitter, but This Place released the app for free on GitHub in hopes that other developers will use it for more advanced projects.

Students build a robot arm you control with the wink of an eye
Want proof that you don't need big, specialized equipment to produce a mind-controlled robot arm? Just look at a recent University of Toronto student project. Ryan Mintz and crew have created an arm that you control using little more than a brainwave-sensing headset (which is no longer that rare) and a laptop. The team's software is smart enough to steer the arm using subtle head movements, such as clenching your jaw or winking your eye; it also knows when you've relaxed.

RoboRoach surgery kit comes to Kickstarter: a remote control for real cockroaches
What DARPA does with animal test subjects behind closed doors is one thing, but here we have something else entirely: mad-scientist kits that allow anyone at home to control the movement of a real-life cockroach. Backyard Brains, the crew behind Twitter Roach, have been selling RoboRoach sets for creating cyborg insects for some time. But today, after getting as far as they can on their own, they're seeking Kickstarter funding to improve their design and develop "educational materials" to go with it. The project will go live in the next 30 minutes or so, and pledges of $100 or more will get you a surgery kit consisting of a PCB "backpack," battery and three sets of electrodes. The PCB pairs with mobile devices via the Bluetooth LE profile and a companion app delivers commands to the 'roach, allowing you to steer the creature by swiping across your screen. Cough up $150 or more and they'll send you a dozen 'roaches to get you started. The electrodes we mention need to be implanted into the cockroach's antennae so directional triggers can be sent to the nerves within -- effectively fooling the creature into thinking it's hit an obstacle and needs to change course. This is where it starts to get uncomfortable. Backyard Brains are touting the RoboRoach as an educational tool, specifically stating that "this product is not a toy." Something that's glossed over on the Kickstarter page, however, is the allegedly painless surgery step: how you attach the electrodes to the insect. People can make their own minds up regarding the ethics of the campaign, and can start by heading to the Kickstarter source link once it goes live at 9am ET. We've also embedded an old tutorial video below we found on the company's site, which demonstrates the surgery process. Be warned: there's antenna-clipping and other mutilations involved, which make our skin crawl even more than the thought of handling the cockroaches in the first place.

University of Minnesota researchers demo AR.Drone controlled by thought (video)
Researchers from the University of Minnesota seem hellbent on turning us all into X-Men. Why's that, you ask? Well, back in 2011, the team devised a method, using non-invasive electroencephalogram (EEG), to allow test subjects to steer computer generated aircraft. Fast forward to today and that very same team has managed to translate their virtual work into real-world mind control over a quadrocopter. Using the same brain-computer interface technique, the team was able to successfully demonstrate full 3D control over an AR.Drone 1.0, using a video feed from its front-facing camera as a guide. But it's not quite as simple as it sounds. Before mind-handling the drone, subjects underwent a training period that lasted about three months on average and utilized a bevy of virtual simulators to let them get acquainted with the nuances of mental navigation. If you're wondering just how exactly these human guinea pigs were able to fly a drone using thought alone, just imagine clenching your fists. That particular mental image was responsible for upward acceleration. Now imagine your left hand clenched alone... that'd cause it to move to the left; the same goes for using only the right. Get it? Good. Now, while we wait for this U. of Minnesota team to perfect its project (and make it more commercial), perhaps this faux-telekinetic toy can occupy your fancy.

Samsung explores touchless tablet interaction with brainwave technology
Try and wrap this one around your noggin. Samsung is currently working with researchers at the University of Texas on a project involving EEG caps that harnesses the power of one's mind to control tablets and smartphones, and if that weren't enough, the company's actually hoping to take it mainstream. Now, before we get too far ahead of ourselves, let's be clear: in its current stage, the system is cumbersome and aimed at those with disabilities, but Samsung's already proven that it's interested in alternative input methods, and this could certainly be the logical conclusion. As is, participants are asked to wear EEG caps that measure the electrical activity along their scalp. Then, they're able to make selections by focusing on an icon that flashes at a distinct frequency from others, which the system recognizes as a unique electrical pattern. Overall, the accuracy of the system is in the ballpark of 80 to 95 percent, and users are able to make selections on average of every five seconds. In order to make the system more approachable, the researchers hope to develop EEG hats that are more convenient and less intrusive -- in other words, ones that people can wear throughout the day. We can't promise this type of futuristic tech will come anytime soon, but for a closer peek, hit up the source link for a peek at Samsung's next wild idea.

Harvard lets human minds control rats, private rodent armies remain distant (video)
Sure, we've seen rats control other rats, but that won't give us a legion of mind-controlled creatures to unleash upon an innocent public, will it? Harvard Medical School may unwittingly assist with solving our (rather misguided) plight, as it just experimented with a system that lets a human mind trigger actions in a rat's motor cortex. The test had sensor-equipped humans watch a screen that flashed in sync with their EEG brain patterns for visual stimulation; as soon their attention shifted to controlling the rat, they triggered an ultrasonic pulse that twitched the rodent's tail. There's a few problems with the implementation beyond the obvious lack of autonomy for the poor target creature, though. The rat's anaesthetized state likely affected the results, and the system isn't currently sophisticated enough to map specific thoughts to corresponding actions. The Harvard team is working to refine the technology, however, and there may be a day when we can satisfy our megalomania... or at least, put the Pied Piper on notice.

A look around Haier's CES 2013 booth: HaiPads, plenty of panels and a wireless blender
Haier had a pretty formidable booth here at CES, so naturally, we had to swing by and cast our eyeballs over anything and everything there. A wall of TVs greeted us, which turned out to be the company's 2013 Roku-ready HDTVs and Android-packing smart models. Screens were everywhere, but there was also a table with some finger-friendly equipment like 9.7-, 7- and 5.3-inch HaiPads, as well as a Windows 8 laptop, touchscreen all-in-one and tab / laptop slider. The slider looked pretty nice, but all the aforementioned hardware was set up in Chinese, so we lost interest pretty quickly. A central hall booth wouldn't be the same without a 4K TV, but not to worry, Haier had a couple on display -- unfortunately, glare from all the other screens dotted around kind of dampened their impact. What we were most interested in was all the prototype technologies on show, but all the Haier reps were from the US sales department, so not a soul could talk about the demonstrations. The eye-controlled TV we saw at IFA last year was getting quite a lot of attention, while the mind-controlled set we've also seen before was almost certainly playing a looping video to give the illusion something was happening. There were also several gesture-controlled models, but one wasn't working and the other was hosting a very basic Kinect-type game. A ping-pong game played with a "Sensory Remote" was also up on one TV, but looked unresponsive and therefore, unfun. A multi-view demo using dual 3D specs did what it was supposed to, and a glasses-free 3D TV prototype showed nice depth as long as you were 12+ ft away (the camera can't really replicate the effect, but there's a quick video of it below anyway). The booth also had a household section which we thought was safe to ignore, until a "wireless blender" caught the eye. "It's just a blender with a battery in it, surely?" this editor asked. "No, there's an inductive coil built into to the underside of the counter," was the reply. Thus was our Haier experience at CES, and to revisit it through our eyes lens, check out the gallery below. Kevin Wong contributed to this report.

Muse brain-sensing headband thoughts-on (video)
Plenty of companies are experimenting with thought-reading gadgets, and in the cluttered South Hall here at CES, we came across the folks from InteraXon showing off their Indiegogo-funded "Muse brain-sensing headband." It measures EEG signals from four forehead sensors and two tucked behind the ears, and sends those brain measurements to other gear via Bluetooth. InteraXon has developed an app suite for mobile devices to showcase the headband's capabilities, including thought-controlled games and brain tracking, exercise and fitness software for improving cognitive function, memory, attention and for reducing stress. That'll come bundled with any purchased units, but an SDK is also available for third-party developers to explore other possibilities. They had a demonstration set up on the show floor, so we thought we'd sit down and take it for a spin. The headband was flexible and surprisingly comfortable, and with a bit of fiddling, we were good to go. One monitor showed brain activity on a couple of complicated graphs, while a scene on a second monitor grew busier as our concentration increased. Watching one graph react to blinking was pretty cool, and once concentration levels reached over 85%, it started to snow on the animated scene. While this obviously isn't very relevant to any potential applications, it was fun to watch the hardware clearly working as intended. You can check out our shots of the headband in the gallery, or check out the video of us trying it out below. Unfortunately we were only allowed to use it for a limited time -- the demonstration was in danger of breaking due to this editors' massive brain. Kevin Wong contributed to this report.

Axio's EEG headband helps you teach your brain to focus (hands-on)
Usually when an EEG sensor headset graces these pages, it's used to peer into your thoughts or grant the wearer the power to control other gadgets with his or her mind. While such uses have appeal, start-up company Axio has a new EEG headband that aims to help you learn to better control your own brain. It tracks your level of mental focus in real-time and provides positive reinforcement audio feedback when you're mentally locked in. The neoprene band packs a trio of electrodes, a PCB with a Bluetooth radio and audio out, and a battery pack to power everything. It works by identifying the brainwave readings that correlate to ideal executive function in your pre-frontal cortex and shooting that data to your computer or phone via Bluetooth. Axio's software then shows an onscreen graph that charts your focus level in real-time, and for folks who prefer a more literal tracking method, there's a photo above the chart that moves in and out of focus along with your mind. Additionally, the headband provides pleasing audio neurofeedback when you're focused in order to train you to stay mentally engaged.%Gallery-158654% Unfortunately, we couldn't get much more information about the neurofeedback functionality, as the technology behind it is the company's secret sauce, and it won't divulge more until it's got the cash to bring the band to market. We also weren't able to actually test the band to see how it works, as it's still in the prototype phase and there's still a kink or two left to work out. Axio did tell us that the prototype we got our mitts on was the result of just six short months of work, and that after hacking together the original design using Arduino, the current iteration has a custom PCB better suited to Axio's needs. Co-founder Arye Barnehama also informed us that the band should be on sale by the end of summer, though he wouldn't say for how much or where we'll be able to pick one up. Sometime after it hits store shelves, Axio plans to release an SDK so that enterprising devs can make their own focus-aiding software and implement whatever audio feedback they prefer to help them take care of business -- a dose of Bachman-Turner Overdrive ought to do the trick.

Mind-operated robot arm helps paralyzed woman have her cup o' joe (video)
Researchers at the Braingate2 consortium have made a breakthrough that allows people with spinal cord or stroke injuries to control robotic limbs with their minds. The original project allowed subjects with motor cortex-implanted chips to move cursors on a screen with their minds, but they can now command DEKA and DLR mechanical arms to grasp foam balls and sip coffee. Researchers noted that dropped objects and missed drinks were frequent, but improved brain sensors and more practice by subjects should help. To see the power of the mind move perhaps not mountains, but good ol' java, jump to the video below.








