selfhealing
Latest
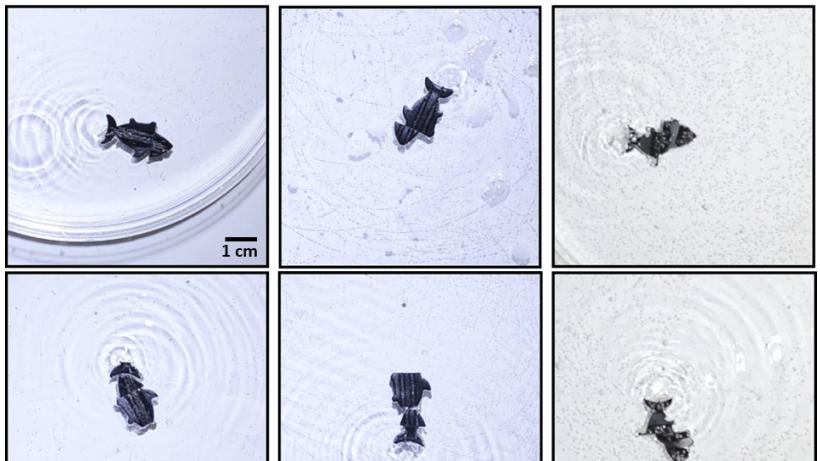
Researchers create a swimming robot that can 'heal' itself
Researchers at UC San Diego created a tiny robot shaped like a fish that could reassemble itself when broken apart.

Self-repairing shoes may be a reality thanks to 3D-printed rubber
Shoes will invariably wear out with enough use, but scientists might have found a way to delay the shopping trip for their replacements. A USC team has created a self-healing 3D-printed rubber that could be ideal for footwear, tires and even soft robotics. The effort involves 3D printing the material with photopolymerization (solidifying a resin with light) while introducing an oxidizer at just the right ratio to add self-healing properties without slowing down the solidifying process.
Researchers build a self-healing 'robot skin'
Most conventional androids are fairly rigid, susceptible to damage and difficult to repair. However, scientists are determined to (literally) give them thicker skins. They've experimented with soft, deformable circuits that are flexible, and could reduce business expenses in the long term -- but are still prone to tearing and puncturing. The solution to these issues may lie in one recent advancement.

This self-healing material could solve many wearable woes
The physical limitations of existing materials are one of main problems when it comes to flexible electronics, be it wearables, medical or sports tech. If a flexible material breaks, it either stays broken, or if it has some self-healing properties it may continue to work, but not so well. However, a team from Penn State have creating a self-healing, flexible material that could be used inside electronics even after multiple breaks.

Watch this iPhone screen protector heal scratches within a second
The folks who came up with the self-healing iPhone case is now back with something a lot more impressive. Innerexile's earlier technology could repair light scratches within about half a minute (given the right temperature, that is), but the latest version can do the same within just a second! Seriously, you'd have to study very hard to witness that brief magical moment, which proved to be tricky in our brass brush test video after the break. So what's the secret sauce behind this new coating? Well, it's dotted with microcapsules that contain an adhesive-like liquid, and when damaged, the liquid will fill the void so quickly that you probably won't even realize you've just scratched your case or screen protector.

Just add water and this squid-inspired plastic heals itself
While you've been busy scarfing down fried calamari rings, scientists at the University of Pennsylvania have been doing something else with squid. Namely? Studying the cephalopod's ring teeth for a way to create a material that heals when water's present, much in the way that those tentacle-bound choppers do. The way the report spotted by Popular Science tells it, the researchers were able to reproduce the type of proteins found in the self-healing squid teeth and trigger bacteria to make it in a lab environment.

Watch this self-healing material handle a bullet
NASA-funded research has created a material that could self-heal in seconds. Two layers of solid polymer sandwich a gel that with an ingredient that solidifies on contact with air (i.e. when one or both of the outer layers is damaged). This differs from other approaches that rely on a mostly-liquid compound, or similar, slower techniques. The protective applications in space craft (like the ISS) are obvious, and could add a vital line of defense against dangerous debris. The ISS already has shields to protect it, but reactive armour in the event of damage would be even more reassuring. Back down here on earth, the same material could be used in cars, pips, containers and even phones (beyond scratches). Watch the material get shot and self-heal in the video below.

Caltech self-healing chips can recover from laser blasts, save power while healthy
While many scientists have heard the call for self-healing electronics, their previous projects have usually had just a limited capacity to come back from the brink. Caltech has developed an integrated circuit that could take much more of a bruising. Its prototype power amplifier chip has a dedicated circuit and sensors that can change actuators in microseconds if there's damage, re-optimizing the connections on the spot. And the chip can take a lot of that damage -- 76 examples in a penny-sized cluster endured multiple laser strikes in tests (like the one above) while still ticking. The self-healing even helps while everything is in tip-top shape, as it can cut power use by watching for the usual hiccups in load and voltage. So long as Caltech can develop the technology beyond its currently expected niches of communication and imaging, many of our computing devices could eventually take a few bumps and scrapes on the inside, not just their rugged exteriors.

Graphene heals itself, powers our dreams and nightmares
Slowly, but surely graphene is pushing our technological hopes, dreams and, yes, nightmares towards reality. The stuff is capable of extending battery life, generating electricity, powering high-speed data connections and super computer-worthy CPUs. It's water proof, stretchy, bendy and apparently self healing. (This space reserved for T-1000 reference.) Researchers at the University of Manchester discovered that, if you put a hole in a sheet of graphene, it simply stitches itself back together. This is thanks to carbon's tendency to latch on to other atoms, including its own, which can make the futuristic material difficult to work with, but gives it this highly unique quality. Thankfully, we're no where near self-healing robots. But, the discovery could lead to a simple method for molding it into almost any shape. Once pierced, the form of the mend is determined by the type of molecules introduced -- pure carbon simply regrows the perfect honeycomb structure, while a few foreign atoms can lead to "defects." Of course, if they're intentional and predictable, defects merely become "features." For more check out the source link.

Researchers develop new plastics that 'bleed' and heal like human skin
It looks like plastics may not be something for the squeamish in the not-too-distant future. Researchers from the University of Southern Mississippi recently revealed a new type of plastic they've been working on that takes its inspiration from human skin -- it "bleeds" red when it's scratched or cut and then heals itself when it's exposed to light. As Popular Science notes, self-healing plastics aren't something entirely new, but the "bleeding" (achieved using small molecular links or "bridges" that break when the plastic is scratched) is, as is the fact that this plastic can heal itself over and over again in the same spot. What's more, as it's made from water-based copolymers, it's also more environmentally-friendly than other plastics. Of course, it's all a ways from being used in actual products, but the researchers see no shortage of possibilities, including everything from self-healing car fenders to aircraft applications that could warn of problems before they get too severe.

Researchers develop self-healing electronics, adamantium sadly not included
In today's feature-laden electronics devices, the failure of one little electronic component can scuttle the entire package. To make matters worse, if the damage happens to strike something like a multilayer integrated circuit, then you pretty much need to replace the whole computer chip. But what if the chip could repair itself like a certain vertically challenged Canadian mutant? That's exactly what researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign managed to do after placing self-healing polymers on top of a gold circuit. Once a break occurred, microcapsules with liquid metal filled the crack and restored 99 percent of conductivity in mere microseconds. Self-healing electronics would especially be helpful on things like aircraft, where miles of conductive wires can make finding a break difficult, researchers said. The research is just the latest in a field that also has seen self-healing sensors and shape-memory polymers, but sadly, there's still no word on using this stuff to self-heal a broken heart....

NC State builds self-healing structural stress sensor, moves on to other alliterative projects
"Sensor, heal thyself," goes an old saying, and North Carolina State University researchers have given it a new spin. Structural stress monitors can break during, say, an earthquake or explosion: just when you most need information about a building's integrity. So the NCSU crew added a reservoir of ultraviolet-curable resin; if their sensor cracks, the resin flows into the gap, where a UV light hardens it. An infrared light, which does the actual monitoring, then has a complete circuit through which to pass, and voila: stress data flows once more, aiding decision-makers. Obviously we never tire of UV-reactive gadgetry, especially for making safer buildings, and we're doubly glad to see self-healing that doesn't involve the phrase "he's just not that into you." To see the self-repair in action, check the picture after the break, and hit the source link for more info.

Self-healing polymer serves up quick fixes under UV rays (video)
As many self-healing polymers as we've seen roll across our screens, we never really tire of them -- chalk it up to our unending quest for perfection, but we like our gadgets devoid of nicks and scratches. Lucky for us, a team of scientists that shares our need for clean has produced a material that fixes its imperfections in a mere 60 seconds when exposed to UV light. The typically rigid material basically melts down when exposed to rays of a specific wavelength, allowing it to fill in any nicks or dings. When the light is lifted, the polymer goes back to its original form, and voila -- the surface is like new. Its creators say the material could be used on everything from cars to dining room tables, but we've already come up with laundry list of devices that could do with a truly scratch resistant surface. Video of the stuff in action after the break.

Artificial muscles let cadavers (and someday paralyzed humans) wink with the best of 'em
The above contraption, aside from looking really uncomfortable, is the latest advance in electroactive polymer artificial muscle technology. Using soft acrylic or silicon layered with carbon grease, EPAMs contract like muscle tissue when current is applied -- making 'em just the ticket for use in UC Davis's Eyelid Sling. Billed as the "first-wave use of artificial muscle in any biological system," the device is currently letting cadavers (and, eventually paralyzed humans) blink -- an improvement over current solutions for the non-blinking, which include either transplanting a leg muscle into the face or suturing a small gold weight into the eyelid. Look for the technology to become available for patients within the next five years.

UCLA researchers create self-healing, power-generating artificial muscle
We've seen self-healing materials and artificial arms, but a team of researchers hailing from UCLA have taken two fabulous ideas and wed them together to create "an artificial muscle that heals itself and generates electricity." Put simply, the contracting / expanding of the material can generate a small electric current, which can be "captured and used to power another expansion or stored in a battery." The scientists have relied on carbon nanotubes as electrodes rather than metal-based films that typically fail after extended usage, and in an ideal world, the research could eventually lead to (more) walking robots and highly advanced prosthetics. Integrate an AC adapter in there and we're sold.[Via CNET]












