Ossur
Latest
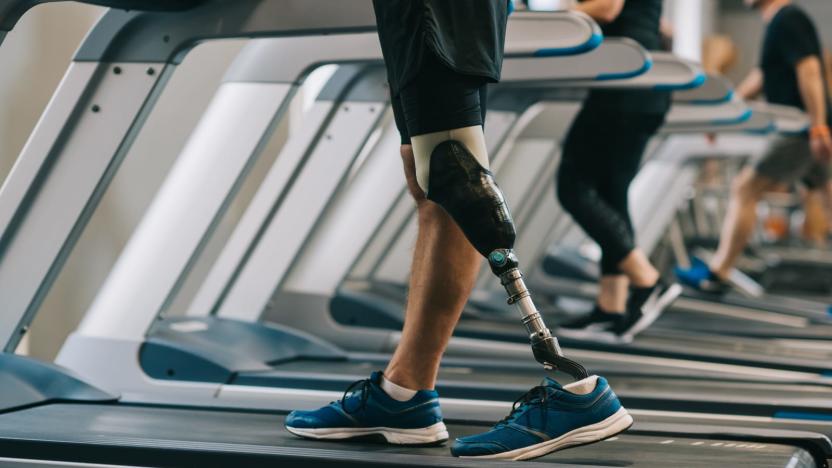
New prosthetic legs let amputees feel their foot and knee in real-time
There's been a lot of research into how to give robots and prosthesis wearers a sense of touch, but it has focused largely on the hands. Now, researchers led by ETH Zurich want to restore sensory feedback for leg amputees, too. In a paper published in Nature Medicine today, the team describes how they modified an off-the-shelf prosthetic leg with sensors and electrodes to give wearers a sense of knee movement and feedback from the sole of the foot on the ground. While their initial sample size was small -- just two users -- the results are promising.

The first Cybathlon pushed the limits of bionic technology
Andre van Rüschen slowly climbed a five-step ramp at the end of his race. With a black processor strapped to his back and leg supports on either side of his lower limbs, he stayed focused on the body-machine coordination that was keeping him upright. He had walked over a wooden slope, criss-crossed bright yellow bars and tried to step on gray discs that were placed irregularly on the floor. Now, standing atop the last obstacle in the exoskeleton race, he took a moment to pause and look up at his opponent on the adjacent track. They were both on the ramp, going head-to-head at the world's first Cybathlon, a sporting competition designed for people with severe disabilities. The crowd inside the Swiss Arena in Zürich cheered them on. Van Rüschen, the German pilot who was using a ReWalk exoskeleton, quickly regained his focus and prepared to walk down the next five steps to complete the race. He hit a button on the remote around his wrist to change the settings from "walk" to "climb" and quickly adjusted his upper body to balance his weight on the crutches in his hands. With his competitor, Mark Daniel, right on his heels, he leaned forward to pick up the pace.

Powered prosthetics turn mundane tasks into monumental feats
Lukas Kalemba was walking home with some friends after a night of partying and drinking in Dortmund, Germany, in 2003. While crossing a bridge along the way, he stopped to rest but lost his balance and fell over. In an attempt to break his fall, he instinctively reached out and grabbed a wire that stretched across. It kept him from falling 20 feet to the ground immediately but the wire sent a high-voltage current through the left side of his body, causing irreparable damage to his leg. Kalemba became an above-the-knee amputee when he was 19 years old. He was in an induced coma for three weeks until the doctors brought the pain down to a manageable level. "The first time I noticed it was in the hospital when I stood up at night to go to the toilet," he says. "I wanted to stand on my left foot [but] I crashed on the floor."

Prosthetic foot only needs 'mind control' for movement
During a press conference in Copenhagen on Wednesday, prosthetics manufacturer Ossur announced the release of an implantable sensor that allows users to mentally control a mechanical limb. The technology, known as an Implanted MyoElectric Sensor (IMES) will allow users to move the company's motorized Proprio Foot just like they do the real thing.

Power Knee motorized prosthetic officially available in US, Europe -- race of cyborgs still in infancy
We reported on Ossur's robotic prosthetic back in 2009, and now amputees in Europe and the United States have become the first official recipients of the Power Knee. According to the company, "the world's first and only motor-powered prosthetic knee" was recently approved for reimbursement by the German National Health System, covered by private insurance in France and the UK, and picked up by select healthcare providers in the US. Power Knee combines "artificial intelligence," motion sensors, and wireless communication to learn and adjust to the walking style of its users -- that's one small step for real-life cyborgs and one giant leap for prosthetic technology.

Ossur's new POWER KNEE prosthesis sports A.I., motorized actuators
Perhaps it's a sobering reminder of the world we live in, but we've seen prosthetic technology grow in leaps and bounds over the last couple years. Continuing the upward arc, Ossur has just announced its second generation POWER KNEE device. Developed in partnership with Victhom Human Bionics, the device is billed as "the world's first and only motor-powered, artificially intelligent prosthesis for above-knee amputees." Features include: advanced torque and accelerometer sensors that keep an eye on the ground level and compensate accordingly; actuators that actively lift and stimulate the users own muscles for walking up stairs, inclines and ramps; and what the company is calling its "artificial intelligence" features, which allow the device to "observe the whole state of the respective human-system interface." Currently in use at Walter Reed Army Medical Center, a full commercial release is expected by 2010.



