biomimetics
Latest
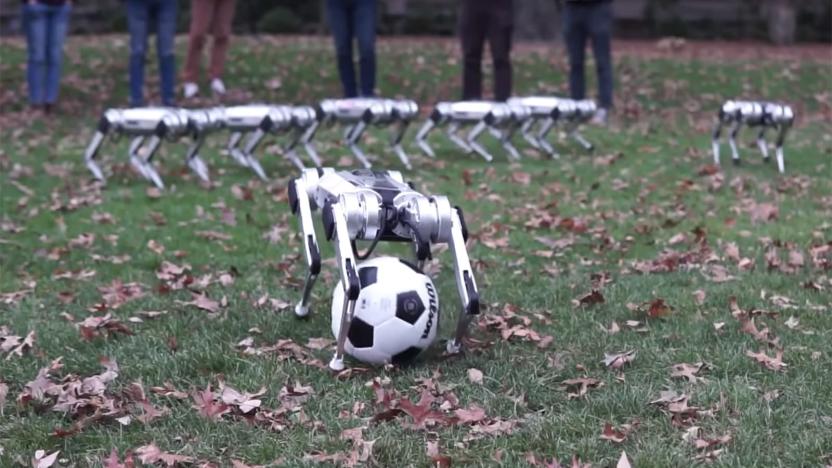

Watch a herd of MIT's Mini Cheetah robots frolic in the fall leaves
MIT wants to show that its Mini Cheetah robots aren't just solitary creatures. The school's Biomimetics department has posted a video of nine of the bots frolicking in the fall leaves, showing just what these pet-sized quadrupeds can do. The remote-controlled machines can backflip out of leaf piles, kick a soccer ball and have friendly tussles... well, if a bodyslam can be considered friendly. There's even some eerie coordinated dancing, in case you want to know how robots will socialize once the robopocalypse is over.
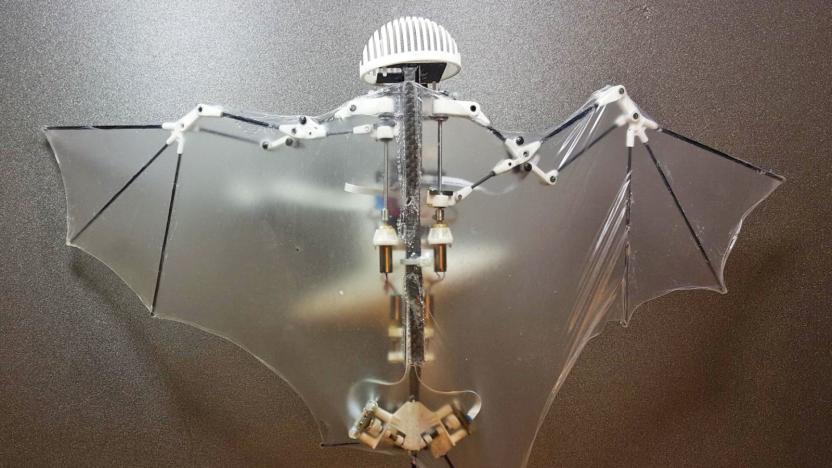
Bat Bot is an autonomous drone that mimics a bat's flight
For roboticists working in the field of biomimetics, copying a bat's complex flight patterns has been a difficult problem to solve. Or, as Caltech professor and Jet Propulsion Laboratory researcher Soon-Jo Chung put it during a press conference, "bat flight is the holy grail of aerial robotics." And according to a new research paper published by Chung and his JPL colleagues in the journal Science Robotics this week, that holy grail has officially been discovered.

Stanford's 'Gecko Glove' makes Spider-Man climbing possible
Never let anyone crush your dreams. Last week the results of a University of Cambridge study spread through the news, claiming that the dream of Spider-Man-like abilities for humans is simply impossible. By their reasoning, sticky pads need to scale up in order to support increased weight, and as a result, the size of a gecko is about as big as a vertical climber can be. The only problem? An engineer at Stanford showed off a way around that problem back in 2014. Now Elliot Hawkes has dropped a diss track on YouTube firing shots at Cambridge and Stephen Colbert, showing off his climbing skills thanks to a "Gecko Glove."

13 scientific breakthroughs inspired by nature
Biomimicry, the field of science that takes direct R&D cues from nature's own solutions, has provided us with breakthrough materials, inspired developments in robotic locomotion and informed new medical techniques. We've even gotten introspective and looked at our own biological functions in order to create useful technologies. We're bootstrapping our way into the future on the back of nature's hard work, and that's a good thing, so long as we tread cautiously without manufacturing our own obsolescence. Of the myriad advances, we've collected just a few that exhibit how nature's influence is helping us craft our own future.

Robot sea turtle will map shipwrecks that humans can't reach (video)
Some shipwrecks are too costly or dangerous for humans to explore, but many underwater robots are too disruptive and unwieldy to serve as substitutes. The Tallinn Institute of Technology's new U-CAT mapping robot solves that dilemma by imitating one of the ocean's more graceful creatures: the sea turtle. The small machine uses flippers to get around instead of propellers, preventing it from kicking up silt (which would obscure its camera) and letting it turn on a dime. It's also autonomous, which helps it venture deep into a wreck without worrying about cables. It's sure to have a big impact on underwater archaeology, and you can see it in person if you swing by the London Science Museum between November 28th and December 1st. However, It will eventually map shipwrecks in the Baltic and Mediterranean Seas as part of the EU's ARROWS Project, providing more detail than any diver could manage. [Image credit: Tallin University of Technology, Flickr]

Researchers fake sense of touch in monkey brains, hope to build a better prosthetic
Medical prosthetics have come a long way in recent years, but with a few exceptions, artificial limbs still lack the tactility of their fleshy counterparts. Scientists at the University of Chicago are looking to plug those sensory gaps by researching how to simulate touch sensations within the brain, via electrical impulses. By implanting electrodes into the area of the brain that governs the five senses, scientists used electrical stimulation to artificially create feelings of touch and pressure in test monkeys. The Phoenixes posit that this could increase the dexterity of upper-limb neuroprosthetics without extensive patient training and that this is an important step toward restoring touch to those who've lost it, like those with spinal cord injuries. While the scientists realize these operations require incredibly invasive surgery, they believe the procedure's potential could eventually justify the risk for those who don't have other options.



