electromyography
Latest
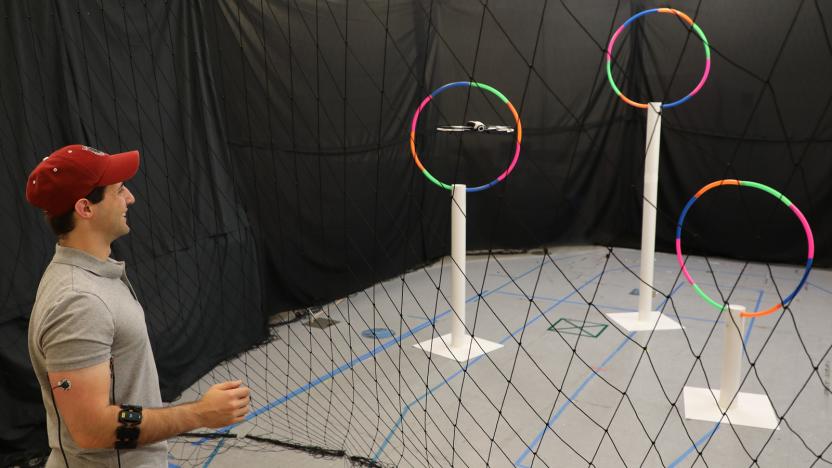
Muscle sensors may let you control a drone by clenching your fist
MIT has developed a system that uses muscle sensors to control robots more intuitively.

Researchers create prosthetic hand that offers more lifelike dexterity
Researchers at Georgia Tech have developed a prosthetic hand inspired by the bionic one given to Star Wars' Luke Skywalker. What sets this one apart from other prosthetics is the amount of dexterity it offers, allowing users to move individual fingers at will. With it, Jason Barnes, the amputee working with the researchers, was able to play piano for the first time since losing part of his arm in 2012.

Microsoft granted patent for wearable EMG device
Those muscle spasms? They're now good for something. Okay, so Microsoft's just-granted patent for a wearable EMG device doesn't really thrive off of involuntary twitching and such, but it does use your movements to control your smartphone, notebook and other gadgets. The "Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller," which we first glimpsed back in 2010, uses sensors to interpret the electrical signals generated by a user's muscles, and then communicates with the wearer's computer via a wireless (or wired) connection. Redmond envisions the wearable device in various incarnations: as an armband equipped with sensors, a shirt, eyeglasses and even nodes attached directly to the user's body. In the armband example, motion control could be used to interact with a PMP while the user is jogging. No matter the setup, a calibration process allows the system to locate specific sensors and collect information based on specific gestures or movements, which means playing Guitar Hero with only an air guitar may someday be a reality after all.

USB Biofeedback Game Controller lets you play Mario with your guns (video)
Those gun-show tickets you've been offering out to everyone (that nobody ever takes) can suddenly do a lot more, thanks to Advancer Technologies. It's developed an Arduino-based plug-and-play bio-feedback game controller that uses EMG (electromyography) sensors to monitor the electrical activity in your skeletal muscles and turn them into game controls. For example, a bicep twinge represents jump, a gripped fist means run forwards -- as long as you've sufficient definition for those two to be distinctive. Check out the must-see muscle action after the break, or see how it's done at the source link. [Image courtesy of Dreamworks]

Electronic neural bridge helps paralyzed mice walk again, human application might prove tricky
It's only been a week since we heard about age reversal in mice, yet already we've got another big advancement in rodent medical care: a solution for ameliorating the devastating effects of spinal cord injuries. A UCLA research team has shown off a new system that can restore walking motion to a mouse's hind legs, but not only that, it also grants control to the little fella by responding to its front legs' actions. Electromyography sensors detect when a mouse starts to walk up front, triggering electronic signals to be sent to the functional lower portion of its spine, which in turn starts up the rear muscles for a steady walking gait. It's only been tested on a treadmill so far, but the result seems to be a seamless restoration of walking capacity in rodents that doesn't require any outside assistance. The same will be pretty hard to replicate in humans, bipeds that they are, but that's why it's called research and not reobvious.

Lip reading mobiles are wunderbar, still at the prototype stage (video)
We came across this lip reading prototype during our exploration of the CeBIT 2010 halls, and while we're a bit tardy in bringing it to your attention, there's a certain timeless quality to strapping your face with wired sensors that transcends conventional restrictions of timeliness. That's our story anyway. Devised by researchers at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, it picks up the motion of speech (via electromyography) without requiring the sound, and then translates it into audible communication via a delightfully cold and robotic voice. The purposes of such a project are obvious -- from helping people who've lost their speech to making private telephone conversations actually private -- but the fun is in seeing someone use the thing in its current unrefined form. You'll be able to do that just past the break.

Brain-reading biofeedback caps on the rise, NeuroSky returns
Pushing the envelope is what it's all about, and for companies cranking out Wiimote-like devices to make gaming and PC experiences more eventful, even that's not enough to satisfy a bevy of outfits with their eyes set on getting biofeedback into games. Companies such as Emotiv Systems, CyberLearning, and our old friend NeuroSky are all looking to take advantage of the public's current curiosity about thought-controlled (and influenced) gaming by offering up electrode-laced headsets that read a variety of brain impulses to effect gameplay. Essentially, these gel-free caps rely on technology such as electromyography (EMG), which records twitches and other muscular movements, and electrooculography (EOG), which measures changes in the retina, in order to change the way games are experienced. For instance, a nervous, uneasy GTA player would barely be able to aim at his / her enemies, while a daydreamer would have a hard time staying on course and reaching full speed while playing Gran Turismo. Unsurprisingly, said companies have noted that "finding their target markets" have been the most difficult aspect, and certain analysts rightfully question whether gamers would actually enjoy such "mentally taxing restrictions" on their games, but if all goes as planned, we should start seeing a few more options in the commercial brain-interface market before too long.




