Amazon's AI camera helps developers harness image recognition
The new edge device will run Ubuntu and use on-board deep learning to power image-based projects.
Far from the stuff of science fiction, artificial intelligence is becoming just another tool for developers to build the next big thing. It's built in to Photoshop to help you knock out backgrounds, Google is using AI to figure out if you have a person peeping on your phone and Microsoft uses the technology to teach you Chinese. As Amazon's Jeff Barr says, "I think it is safe to say, with the number of practical applications for machine learning, including computer vision and deep learning, that we've turned the corner" towards practical applications for AI. To that end, Amazon has announced AWS DeepLens, a new video camera that runs deep learning models right on the device.
The DeepLens has a 4 megapixel camera that can capture 1080P video, along with a 2D microphone array. It's powered by an Intel Atom Processor with more than 100 gigaflops of power, which means it can process tens of frames of video through the deep-learning AI systems per second. The DeepLens camera has WiFi, USB and micro HDMI ports, and 8 gigabytes of memory to run all that code on, too. It runs Ubuntu 16.04, and can connect to Amazon Web Serivces, too.

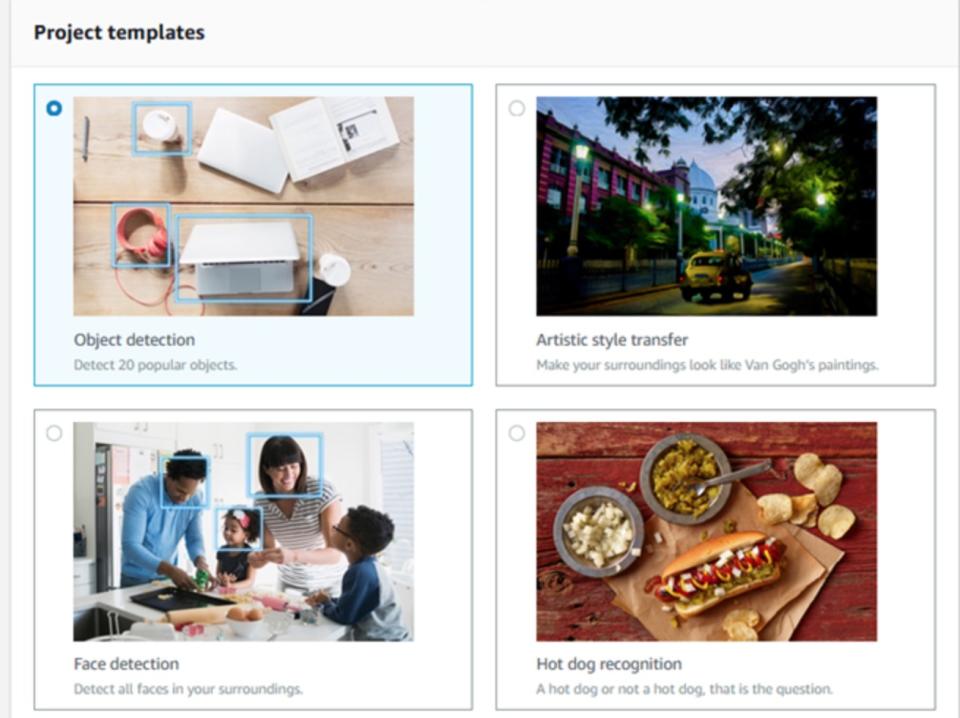
While primarily for developers right now, it's not hard to see possible cool consumer applications down the line. Amazon has already put together some templates for devs to practice with, letting them use the DeepLens camera to detect things like faces, dogs and cats, hot dogs (or not) and a variety of household items, along with various motions and actions. Imagine showing DeepLens a bottle of shampoo, which then is recognized and relayed to Amazon to order you another bottle, or an attached device that can recognize your pets and feed them appropriately.
Barr notes that many future projects will likely run both onboard the device and in the cloud. "With eyes, ears, and a fairly powerful brain that are all located out in the field and close to the action, it can run incoming video and audio through on-board deep learning models quickly and with low latency, making use of the cloud for more compute-intensive higher-level processing. For example, you can do face detection on the DeepLens and then let Amazon Rekognition take care of the face recognition."