humanembryo
Latest

CRISPR gene-editing could result in more successful birth rates
Gene-edited human embryos are offering new insights into the earliest stages of development, and could reduce the risk of miscarriage at the outset of pregnancy. In a new study, researchers from the UK's Francis Crick Institute used CRISPR Cas9 to block a gene (known as OCT4) in human embryos. By stopping it from functioning, the researchers saw that it no longer produced its resulting protein (also called OCT4). As a result, the human embryos ceased to attach or grow sufficiently. Their findings, published in the journal Nature, illustrate the importance of the gene in human development.
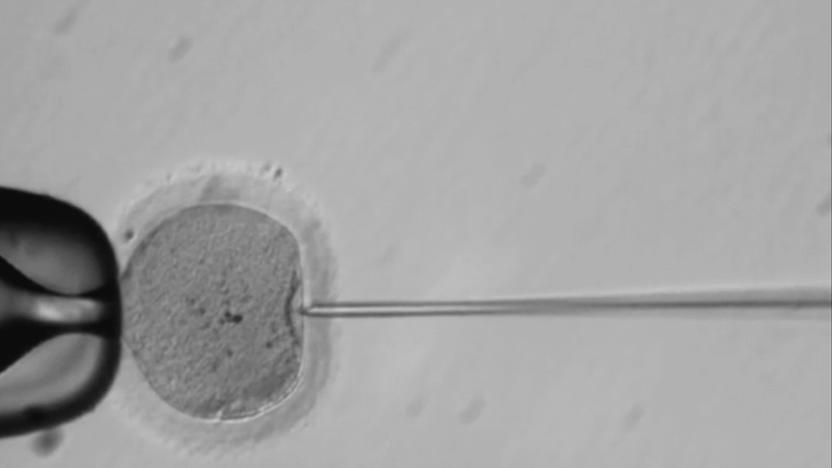
US scientists have genetically modified human embryos
A team of scientists from Oregon have performed the first known instance of gene editing on human embryos in the US, according to MIT's Tech Review. Shoukhrat Mitalipov from Oregon Health and Science University and his team have reportedly corrected defective genes that cause inherited diseases in "a large number of one-cell embryos" using CRISPR. Mitalipov refused to comment on the results of the project, but some of his collaborators already confirmed them to the publication.

UK scientists get permission to 'gene edit' human embryos
A team of British scientists has been approved to use "gene editing" techniques on human embryos, in the hope that it will better our understanding of early human life. A group at the Francis Crick Institute in London wants to research newly fertilised eggs and how they develop in the first seven days -- from a single cell to a blastocyst with roughly 250 cells. Using gene manipulation, the researchers want to glean new insights about our DNA and the exact requirements for a healthy embryo. With this information, specialists could find ways to improve post-IVF embryo development techniques and clinical treatments for infertility.


