MRI
Latest
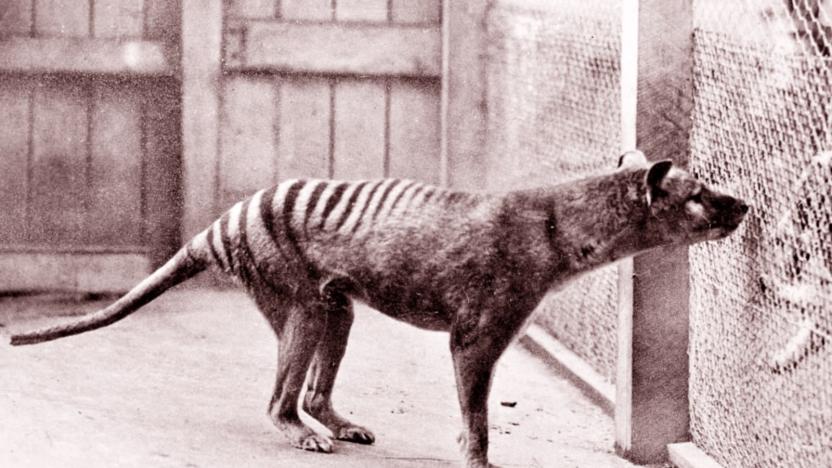

Brain scans shed light on an extinct species
It's not exactly easy to study the Tasmanian tiger. The marsupial has been extinct for over 80 years, and it wasn't given much scientific attention when it was alive -- settlers saw it as a threat to their livestock, not a curiosity. However, that isn't about to stop scientists from learning more about the sadly neglected species. Researchers have scanned two preserved Tasmanian tiger brains and discovered that the creatures were considerably more intelligent than many thought. While their brains were similar to those of Tasmanian devils, their larger frontal lobes suggest they were better at planning and making decisions. That backs the belief that they were hunters, not scavengers like their genetic cousins.

Humans have unique brain 'fingerprints,' scientists confirm
People say "our brains are wired differently," and now a team of scientists led by Carnegie Mellon researchers have proven that's literally the case. The group developed a way to "fingerprint" the human brain using diffusion MRI and found that its structural connections are so unique, they can be used to identify individuals. According to the team's paper published in PLOS, they used the diffusion MRI results of 699 subjects' brains. Diffusion MRI is called as such, because it uses the diffusion process of water molecules in biological tissues to generate contrast in images.

Atomic-sized MRI uses quantum bits to help discover new drugs
Researchers have used quantum computing tech to miniaturize a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner, making it small enough to pick up the structure of single biomolecules without damaging them or losing information in the process. This could make it a key tool for drug discovery and other biotech research.
Fluctuating brain networks help you handle complex tasks
Researchers already know that the human brain isn't static, but it's now clear just how dynamic the mind can be. A Stanford University team has discovered that the networking between brain regions will fluctuate depending on the complexity of tasks. If you're at rest, your brain's components are relatively isolated. Handle a complicated activity, however, and the level of networking ramps up. The more interconnected your brain is, the better your performance -- in a memory test, those with the most integrated brains were the quickest and most accurate.

Oculus exec Mary Lou Jepsen resigns to create new MRI tech
Dr. Mary Lou Jepsen is well known for her work in pioneering display technology as a co-founder of OLPC, former head of the display division at Google X and lately Oculus VR, which she joined about a year ago. Tonight during the Anita Borg Institute's Women of Vision awards banquet, the founder and former CEO of Pixel Qi capped off a keynote speech by announcing she will resign her post as Executive Director of Engineering and Head of Display Technologies at Oculus. Instead, she will focus on "curing diseases with new display technology," by bringing MRI machines to every doctor' office in the world. It's an ambitious goal, but a peek at Dr. Jepsen's history shows why she's the person to tackle it. For more info on what she might be working on, there's video of a recent TED talk with Dr. Jepsen discussing MRI and fMRI tech, which you can watch after the break.

The After Math: With great power
Well, this week as been rather terrible. With all the death and mayhem both at home and abroad, it's enough to make anyone feel rather helpless. It's times like these that we have to force ourselves to remember there is still a great deal of good left in the world. From life-saving medical advancements and clean energy promises to superior image scanners and kick-assier video games, this week's selection shows that humanity isn't all bad (just mostly).

ICYMI: 7-D heart MRI, astronaut cups and tech tats
#fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-906391{display:none;} .cke_show_borders #fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-906391, #postcontentcontainer #fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-906391{width:570px;display:block;}try{document.getElementById("fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-906391").style.display="none";}catch(e){}Today on In Case You Missed It: NASA just shipped the astronauts on the International Space Station a cup that will let them almost drink like earthlings. GE announced scanning tech that would reveal the intricacies of the heart far quicker than conventional MRIs. And temporary tats that can monitor health and beam the information right to a doctor are here, coming to sick little people or elderly folks someday. If you've ever been woken up a couple times a night in a hospital, so a nurse could loudly check your vitals, you know what a win these could be.

GE researchers invent a 7-dimensional heart scanner
While conventional MRI scans can produce highly detailed images of our internal organs, the process can take up to 45 minutes -- not the sort of delay you want when suffering from a heart attack. However, a new scanning technology from GE promises to cut that time by up to 30 minutes and deliver near-real time videos of the heart in unprecedented detail.

NASA's studying how zero gravity affects the brain
Because there's no up or down in zero gravity, the way our brains calculate 3D space stops working. As it turns out, that can be problematic, with astronauts finding it hard to complete basic tasks. It's a phenomenon that NASA wants to learn more about, which is why the agency has started to test a crew's spacial awareness before, during and after their trips to space. Whilst on the ground, participants are subject to MRI scans, and on the ISS they're asked to complete various tests requiring thinking and co-ordination. The reason that this is so interesting isn't just because the testing is going on above us right now, but because of what conclusions have already been drawn.

MRI scans used to create 3D-printed hearts for surgery practice
Heart surgeries could be so much safer if surgeons can see and feel an actual representation of the patient's organ before the procedure itself. A system developed by a group of researchers from MIT and Boston Children's Hospital might make that a viable option. By using MRI scans as a blueprint, it allows doctors to print out a model of the patient's heart within just three hours. When you do an MRI scan, the machine takes hundreds of cross-sectional images of your organs. In order to create an accurate 3D-printable model, though, the boundaries between each part of the organ must be determined. It's critical for each part to look distinct, especially if the patient needs surgery due to an unusual anatomy.

Scientists create a 'wormhole' for magnetic fields
Humanity is still a long way from creating space-time wormholes -- if they're even possible -- but that isn't stopping Spanish researchers from achieving something similar for magnetism. They've produced a wormhole-like effect that transports a magnetic field from one point in space to another through an "invisible" path. The trick was to transmit magnetic fields between two spheres linked by a multi-layer, spiraling cylinder whose materials hide the fields while they're in transit. It's as if they vanished, and then popped back into existence somewhere else.

GE's Neuro VR experience takes you inside a musician's brain
"Welcome to the complex universe inside Reuben's head." A mysterious voice boomed through the headphones. With an Oculus headset strapped on my face for GE's Neuro VR experience, I found myself moving through British musician Reuben Wu's mind. Bright pink globes and interlinked pipelines flashed before me. What was meant to be anatomical, felt more industrial. It was underwhelming. But soon, the globes made way for a dark abyss and I watched as the neurons inside his brain came to life. They gently sparked and burst into little bolts of neon lightning, replicating the magical, interconnected workings of the complex organ.

3D plant scans will help build lighter, stronger cars
Don't look now, but the plants in your backyard might just shape the next generation of cars. University of Freiburg researchers have found a way to study the junctions between living plants' branches and stems using MRI scans, giving insight into how they cope under strain. The 3D images should show how you can build a lightweight, fiber-based structure that can still take some punishment -- particularly helpful for cars and bikes, where fiber already helps shed a lot of unnecessary pounds. They could help produce sturdier buildings, too. While there's still plenty of work left before plant scanning is practical, it's possible that a tree or flower could make your future ride a lot nimbler and speedier.

Self-assembling gauss gun idea would heal patients from the inside
A research team from the University of Houston and Boston Children's Hospital debuted a novel new approach to internal medicine: using a swarm of tiny, noninvasive robots as a gauss gun to shoot medicine or clot-busting needles directly at the afflicted tissue. Much like rail guns, gauss guns rely on a series of magnets to accelerate objects -- the difference being that these guns transfer force through the magnets themselves, converting the stored magnetic energy into kinetic.

This is what the inside of your head looks like when you sing
There's a lot more that goes into producing human vocalizations than just the dual flaps of your larynx and a gust of air. More than 100 muscles throughout your face and neck coordinate to create the wide range of complex sounds people make. And thanks to a new MRI technique, researchers can watch that muscular symphony at work in real time. As you can see from the video below, the results are simply jaw dropping.

Nanotech has a future in monitoring tumors and diagnosing illness
A team of MIT researchers have developed nanoparticle sensors that could eventually be used to monitor tumors or other diseases, as well as act as a tool to diagnose illnesses. These nanoparticles are made of polymer chains that can bind to the sensors a doctor needs. For instance, in the scientists' tests, they used an MRI contrast agent called nitroxide along with Cy5.5, which glows when it encounters vitamin C, as sensors. These individual strands then merge to form the structure you see above, which the researchers call "branched bottlebrush polymer." As you can guess, the bottlebrush polymer the team developed for the study can perform MRI and detect vitamin C, as detailed in their paper recently published in Nature. Since nitroxide grabs electrons from the vitamin and remains inactive in its presence, the scientists don't get confused by the two different signals.

Allen Institute completes gene expression map of the human brain in high-resolution 3D
As a species, we've spent a lot of time learning how the human brain works, but we've had to go without a true, thorough map of how genes manifest themselves in our craniums; previous maps have been limited to the simpler minds of mice. The Allen Institute for Brain Science is now known to have solved that mystery by recently finishing an extensive, detailed 3D atlas of genetic expression within our own brain tissue. Accomplishing the feat required no small amount of resources, including the definition of 900 subdivisions, conducting over 62,000 gene expression probes and producing the MRI scans of two and a half brains, but the result is a potentially vital tool for neuroscience and education. Curious web users can see a visual map of gene expression based on virtually any criteria they need, whether it's a physical region of the brain, a disease type or the exact gene they'd like to track down. For many, the best news about the map may simply be that it's free and public: anyone with enough experience in genetics can learn more about what makes the mind tick through their browsers, and what they find might just lead to new discoveries.

Robopsy is a low-cost, disposable patient-mounted medical robot
In a less gelatin-centric demo, the Harvard-based team behind the Robotically Steerable Probe showed off some Robopsy devices during our visit to the school, rings that can help medical imaging technology like CT, ultrasound and MR physically pinpoint precise locations on patients. The devices, which can hold up to ten needles, are lightweight, mounting directly on patients via adhesives or straps. The medical robots are made largely of inexpensive injection molded plastic parts, making them disposable after they've been used on a patient, popping the motors and other control electronics onto another device. In all, the team says Robopsy rings are "orders of magnitude" cheaper and lighter than other medical robotic devices. Check out a video of the one of the Robopsy devices running after the break.%Gallery-161787%

New system lets you type with your brain using MRIs
This isn't mind reading, per say. Instead Bettina Sorger, Joel Reithler, Brigitte Dahmen and Rainer Goebel at Universiteit Maastricht have figured out a way to monitor the flow of blood in the brain and associate the images captured using an MRI with the letters of the alphabet. The whole system takes about an hour to learn and configure for each individual. Trials focused on healthy individuals, but clearly its the paralyzed and people suffering from diseases like ALS that have the most to gain. Sorger hopes to enable "locked-in" patients to finally be able to communicate with the outside world by thinking out letter at a time. Obviously, patients aren't going to be able to install an MRI in their homes, much less lug one around with them. The data collected could be used to finely tailor less accurate but more portable systems for patients that monitor electrical or light signals. If you're interested in the real nitty-gritty you can check out the complete research paper at the source link.

Daily Update for March 13, 2012
It's the TUAW Daily Update, your source for Apple news in a convenient audio format. You'll get all the top Apple stories of the day in three to five minutes for a quick review of what's happening in the Apple world. You can listen to today's Apple stories by clicking the inline player (requires Flash) or the non-Flash link below. To subscribe to the podcast for daily listening through iTunes, click here. No Flash? Click here to listen. Subscribe via RSS










