microchip
Latest
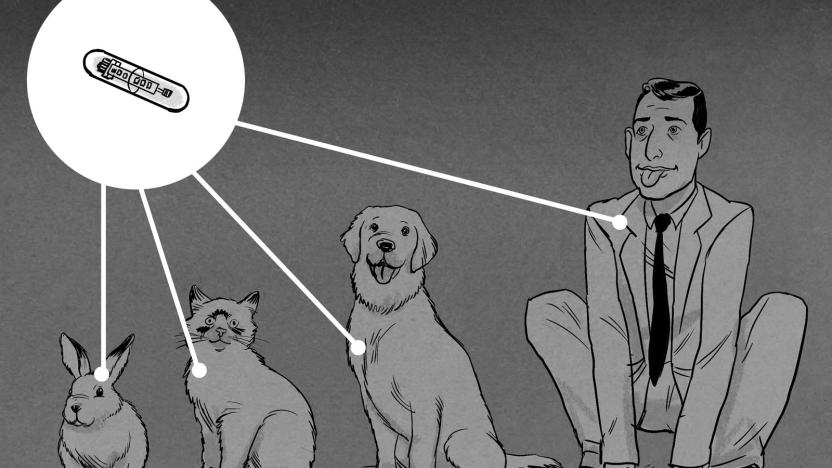

More companies are chipping their workers like pets
The trend of blundering into the void of adopting new tech, damn the consequences, full speed ahead, continues this week. The Telegraph tells us about "a number of UK legal and financial firms" are in talks with a chip company to implant their employees with RFID microchips for security purposes.

Apple told Congress it found no evidence of server tampering
In a letter to Congress, Apple reiterated that it found no evidence of microchip-based server tampering by Chinese agents that was reported by Bloomberg Businessweek. The company, along with Amazon and server manufacturer Super Micro, had previously released forceful denials of suspicions that its servers contained malicious components. The US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and UK cybersecurity officials had also chimed in, saying they have no reason to doubt Amazon and Apple's denials.
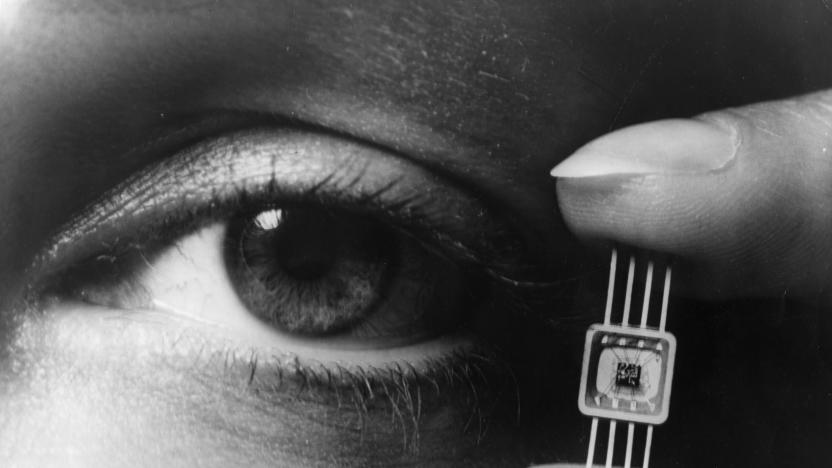
The marvel of microchips
Half a century ago, Westinghouse buried a time capsule at the 1964 New York World's Fair. In it were "Molecular Blocks," a company invention that squeezed "the functions usually performed by an entire assembly of electronic components" into "small solid blocks of material." If that sounds familiar, that's because it describes what we now know today as an integrated circuit (IC) or microchip. Westinghouse was one of several entities pursuing IC development at the time, including Texas Instruments, Fairchild, and many Japanese companies. Despite early cooperation, by 1964 most were embroiled in patent litigation. The image above shows one those early ICs, held by an unnamed person for scale. The chip comes from Westinghouse's WM-1000 series, and is either an oscillator or video amplifier. Sadly we're unable to verify which -- what's left of Westinghouse is now a licensing arm of CBS. It was included in the time capsule among other scientific developments of the era, including antibiotics, a computer memory unit, a plastic heart valve and birth control pills.

Dog microchipping becomes mandatory in the UK
If you own a dog, it's over eight weeks old and it's not fitted with a microchip, you'll be breaking the law as of tomorrow. Compulsory microchipping regulations were introduced in Northern Ireland four years ago, and come into force across the rest of the UK on April 6th. And if, somehow, the police or a local authority find your pooch lacking an electronic tag, you'll be given 21 days to get it chipped or face a £500 fine. The same is true for dogs that are chipped, but where the owner's details are out of date.

A 56-year-old prototype of the first microchip going up for auction
Without the integrated circuit (IC) basically none of the things you take for granted in your life would exist. And it's not just your smartphone, tablet or laptop. Your TV, microwave even your car is loaded with microchips. Auction house Christie's will be selling-off an early prototype of the integrated circuit built by Jack Kilby in 1958 while he was working at Texas Instruments. That was the year that he, along with Robert Noyce, first demonstrated a functioning IC which combines multiple electronic functions on a single slab. Most often that is silicon, but in the late 50s Kilby turned to germanium. Now you have a chance own a piece of computer history, which Kilby and his team eventually one a Nobel Prize for in 2000. Of course, you'll need to come up with the estimated $1 to $2 million the chip is expected to fetch at Thursday's auction.

England to mandate dog microchips by 2016
Thinking about injecting an identification chip in your pooch? If you live in the southern part of the UK, you won't have a choice. Come 2016, English and Welsh authorities will require all of the country's pups to have embedded microchips, so they can be returned to their owners if ever they run astray. The United Kingdom's Environment Department says some 60 percent of the country's 8 million dogs already have the tags, but beginning in three years, owners who don't spring for the device could be forced to pay fines of up to £500 (about $780). Cat microchipping will remain optional, since felines are less likely to wander outdoors. And "World's Cutest Dog" fans need not worry about their precious Boo getting the forced implant -- the famed Pomeranian (pictured above) is based in San Francisco, some 5,000 miles from the Queen's needle.

Jellyfish-mimicking device could snatch cancer cells right out of the bloodstream
If you think the picture above looks like droplets of blood being snared in a sticky tentacle, then you have a scarily active -- but in this case accurate -- imagination. It's actually a microfluidic chip that's been coated with long strands of DNA, which dangle down into the bloodstream and bind to any cancerous proteins floating past -- directly imitating the way a jellyfish scoops up grub in the ocean. If required, the chip can release these cells unharmed for later inspection. According to the chip's designers at Boston's Brigham and Women's Hospital, the catch-and-release mechanism can be put to both diagnostic and therapeutic use in the fight against Big C, and can also be used to isolate good things, like fetal cells. The next step will be to test the device on humans -- at which point we may owe an even greater debt of gratitude to our gelatinous friends. [Image credit: Rohit Karnik and Suman Bose]

AMD Piledriver CPU pre-order pricing leaks out
It's always just been a matter of "when" and "how much," but it looks as if PC gamers looking to score a powerplant upgrade can start planning on specific amounts. AMD's impending FX Piledriver CPUs are now up for pre-order at ShopBLT, an outlet that has proven reliable in the past when it comes to nailing down processor pricing. For those in need of a refresher, these are built using the Vishera design, with the range including between four and eight CPU cores. We're expecting 'em to best the Bulldozer family, and if all goes well, they could be available to the earliest of adopters in October. Presently, the FX-4300 ($131.62), FX-6300 ($175.77), FX-8320 ($242.05) and FX-8350 ($253.06) are listed, but CPU World seems to think launch day quotes will actually be a bit lower. Only one way to find out, right?

FDA approves Proteus Digital Health's e-pills for dose monitoring
An "ingestible sensor" doesn't sound like the tastiest of snacks, but soon it might be just what the doctor ordered. A tiny microchip which activates upon contact with stomach acid has recently been given the green light by the US FDA. When the sensor is swallowed, an external patch picks up its signal and shoots a message over to whoever it's supposed to. The technology is aimed at tackling an issue known in the healthcare biz as compliance -- or, following instructions. Correct timing and dose are important for many drugs, and lax schedules can be responsible for treatment failures or the development of nasty drug-resistant bugs. Although the pills have only been used in trials, one pharmaceutical heavyweight has already bagged a license to the technology for real-world applications. If you don't like the thought of a belly full of microchips, no need to worry -- the harmless sensors pass naturally after completing their mission.

MIT duo successfully tests wireless drug-delivery microchips, more consistent than injections
Despise those daily injections of essential medication? Well folks, relief could be on the way. Over a decade ago, two MIT professors, Robert Langer and Michael Cima, first considered developing a drug-delivery microchip that could be wirelessly controlled. This past week, researchers in Cambridge -- alongside scientists from MicroCHIPS, Inc. -- announced that they have successfully used the aforementioned chip to give osteoporosis patients their daily allotment of teriparatide. "You can do remote control delivery, you can do pulsatile drug delivery, and you can deliver multiple drugs," Langer noted. Chips used in this particular study housed 20 doses each and results indicated that the delivery showed less variation than administered injections. In theory, microchips like these could be used alongside sensors that monitor glucose levels -- creating tech that could adapt to changes in a patient's condition. More info on the trial awaits in the source link below.[Thanks, Lydia]

Google doodle celebrates Robert Noyce; Intel co-founder and 'Mayor of Silicon Valley'
The honor of having your own Google Doodle is bestowed upon only a few very special individuals like Gregor Mendel, Alexander Calder and Lucille Ball. Today's entrant celebrates the 84th birthday of the late Robert "Bob" Noyce, co-inventor of the microchip. After co-founding Fairchild Semiconductor and Intel, he mentored younger engineers to earn the nickname "the Mayor of Silicon Valley." Surf on over to the Google homepage and you'll see its logo imprinted over a microprocessor, which Bob helped to birth.

First molybdenite IC delivers silicon-crushing, chip-shrinking, graphene-blasting action
Never heard of molybdenite? We're not shocked. Its not nearly as hyped as graphene or quantum dots, but it could be the key to smaller, bendable microchips. The problem with silicon is that, in layers less than two nanometers thick, it can become unstable, oxidize and quickly deteriorate. Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), on the other hand, can be laid down in sheets just three atoms thick. The semiconductor also earns bonus points for being an abundant, naturally occurring mineral. Earlier this year researchers at the Laboratory of Nanoscale Electronics and Structures (LANES) demoed the first molybdenite transistor, but the team is moving fast and has already whipped up the first prototype of a complete integrated circuit (we assume with the aid of an all girl army of Kung Fu engineers). Things are looking good for this potential silicon usurper. And best of all, molybdenite is flexible. So, hello bendable computers!

IBM and 3M join forces to fab 3D microchips, create mini-silicon skyscraper valley
3D hype is fast wearing out its welcome, but there's at least one area of industry where the buzzed about term could usher in true innovation. Announced today as a joint research project, IBM and 3M will work towards the creation of a new breed of microprocessors. Unlike similar three-dimensional semiconductor efforts by Intel, the two newly partnered outfits plan to stack up to 100 layers of chips atop one another resulting in a microchip "brick." Under the agreement, IBM will contribute its expertise on packaging the new processors, while 3M will get to work developing an adhesive that can not only be applied in batches, but'll also allow for heat transfer without crippling logic circuitry. If the companies' boasts are to be believed, these powerhouse computing towers would cram memory and networking into a "computer chip 1,000 times faster than today's fastest microprocessor enabling more powerful smartphones, tablets, computers and gaming devices." That's a heady claim for a tech that doesn't yet exist, but is already taking swings at current faux 3D transistors. Official presser and video await you after the break.

World's biggest CMOS sensor could help doctors detect and treat cancer
Move over, Canon, because scientists at the University of Lincoln have just seized the crown for world's biggest CMOS image sensor with their new Dynamic range Adjustable for Medical Imaging Technology microchip -- or 'DyNAMITe,' for short. Measuring a hefty 12.8 square cm (or about five square inches), DyNAMITe is roughly 200 times bigger than the chips you'd find in most PCs, making it the largest imager ever made on a wafer of standard, eight-inch diameter. This extra girth allows the active pixel sensor to capture images in high detail, with a 100-micrometer pitch boasting 1280 x 1280p aligned next to a 50-micron layer, carrying 2560 x 2560p. DyNAMITe can also run at up to 90fps and withstand high levels of radiation for several years, making it ideal for medical imaging, including radiotherapy and mammography. Researchers say these enhanced images could help doctors detect cancer in its earliest phases, while allowing them to monitor radiotherapy treatments more closely. No word on when we should expect to see DyNAMITe pop up in hospitals (or a Hasselblad back), but physicists at the Institute of Cancer Research and Royal Marsden Hospital are busy looking for other, potentially life-saving applications. Full PR after the break.

Bionic eye closer to human trials with invention of implantable microchip
We've had our eye -- so to speak -- on Bionic Vision Australia (BVA) for sometime, and with the invention of a new implantable microchip it's coming ever closer to getting the bionic eye working on real-deal humans. The tiny chip measures five square millimeters and packs 98 electrodes that stimulate retinal cells to restore vision. Preliminary tests are already underway, and clinicians are in the process of screening human guinea pigs for sampling the implants -- the first full system is still on track for a 2013 debut. In the interest of future success: here's mud in your eye, BVA! Full PR after the break.

Active Book microchip provides hope for exercising paralyzed limbs
Scientists have been experimenting with muscles and technology to solve both human and robotic mobility issues for years. Now it looks as though a team of researchers from University College London, Freiburg University, and the Tyndall Institute in Cork have made a significant leap forward for paraplegics, thanks to a revolutionary microchip the team has dubbed "Active Book." What's notable about the chip is that it stimulates more muscle groups than existing technology without the need for external connections. This was accomplished via micro-packing and precision laser processing, which allowed tiny electrodes to be cut from platinum foil and rolled into a 3D book shape. These platinum foil "pages" close in around nerve roots, and are micro-welded to a hermetically sealed silicon chip. Once embedded into areas within the spinal canal, the chip can work to stimulate paralyzed muscles, implying patients could even "perform enough movement to carry out controlled exercise such as cycling or rowing." A press release from the Council which sponsored the research says the Active Book will begin trials sometime next year -- we can't wait to see the results.

Powercast and Microchip fire up interest at a distance with wireless power development kit
We're sure if you asked Powercast nicely it'd tell you a whale of a tale, about how the "more than 100 companies" who allegedly signed up to develop products that seemingly pull energy from the ether materialized into this light-up Christmas tree. Still, we'd be happy to forgive and forget if meaningful products emerged instead, and that's why we're moderately happy the company's announced a nice big development kit. $1,250 buys your firm or deep-pocketed hobbyist the spread pictured above, with a wireless transmitter to throw three watts and a pair of receiver boards to catch them from over 40 feet away, plus a low-power development board from Microchip equipped with that company's proprietary short-range wireless protocols and ZigBee functionality. We can't wait to see what people build, but we won't be snapping one up ourselves -- we're still holding out for the firm to go open-source and build an Arduino version. PR after the break.

NFL mulling microchips in footballs for those life-or-death goal line rulings
The NFL is serious business. So serious, in fact, that the idea of refs getting decisions wrong sends chills up and down Roger Goodell's spine. Yeah, we all know they do it habitually, but the League seems to be considering improving accuracy just a little bit with the help of some tech. Cairos Technologies, a German outfit that's been trying to sell its goal line technology to football (as in soccer) bigwigs for a while, has told Reuters that it's in discussions with the NFL about bringing its magnetic field hocus pocus to the gridiron. The idea would be for the ref to be alerted, via a message to his watch, any time the ball does something notable like crossing the goal line or first down marker. It should be a great aid for making difficult calls like whether a touchdown has happened at the bottom of a scrum, and might even help cut down on the number of frightfully dull replay challenges. Win-win, no? [Original image courtesy of NFL.com]

VIA reveals 1.6GHz Nano DC processor at Computex, shows it handling 720p (video)
Guess who showed up at Computex with an all-new dual-core processor? Nah, we're not referring to AMD or Intel (though they certainly did) -- we're talking about VIA. The company quietly (re)introduced a dual-core desktop chip here in Taipei, with the codename Nano DC being used to describe it for the time being. The device utilized a VN1000 Digital Media Chipset and fully supported dual-channel DDR3 memory. A Chrome 520 GPU was helping to push out a 720p movie trailer on the demo system, and the innate compatibility with HDMI and DisplayPort should keep home cinema owners happy. The 65nm chip was clocked at 1.6GHz, and we were told that it wouldn't be venturing into mobile machines in its current form. 'Course, this device has been a bit of unicorn for the past couple of years, but company representatives seemed certain that it would finally be ready to ship (using a different process technology, mind you) in around six months. We shall see. Live action video is just past the break. %Gallery-94153%

Verayo launches next-generation of 'unclonable' RFID chips, hackers get wide-eyed
If there's one thing a security company should avoid, it's tempting the hackers to unravel their promises. As we've seen time and time again, there are few (if any) completely uncrackable technologies, but Verayo sure seems confident about its next-generation RFID chips. Dubbed "unclonable," this new product family -- which is led by the Vera M4H -- promises to make mass transit tickets, secure IDs and access cards more secure, and unlike the original, this one touts a "non-networked, unlimited authentication" feature. We also get the impression that the company has worked to drive costs down with this newfangled line, but we're still not sure we'd trust our lives to this thing. Anyone down to really put these claims to the test?












