national oceanic and atmospheric administration
Latest
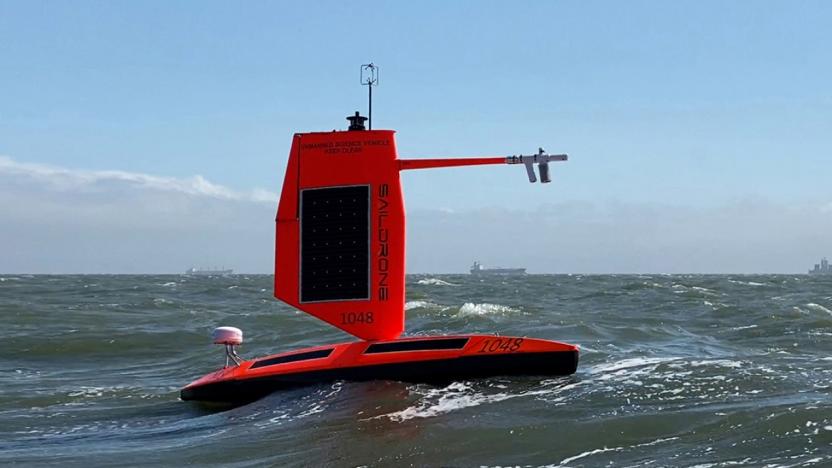

NOAA's surfing drone captured footage inside Hurricane Sam
The agency says data collected by saildrones could help improve storm forecasting.
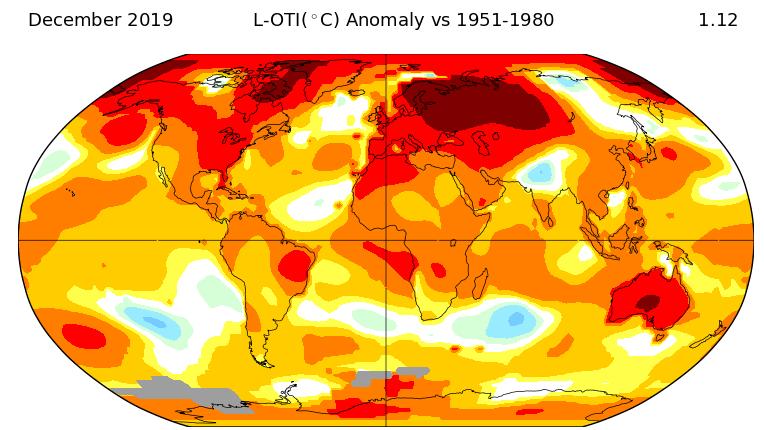
2019 was Earth’s second-warmest year on record
If the melting ice caps and recent wildfires didn't tip you off, NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) have hard data showing that the effects of climate change are only getting worse. According to the agencies, 2019 was the second hottest year since record keeping began in 1880, and was only topped by 2016's temperatures. The trend is clear: Every decade since the '60s has, on average, been warmer than the one before it. Even more alarming is the fact that the past five years have been the hottest five on record.

LightSquared faces Congressional hearing over proposed 4G network, submits revised plan
The LightSquared Express rolled in to Washington yesterday, where the House Committee on Science, Space and Technology held a hearing on the company's proposed 4G LTE network and its potential impact on GPS systems. According to some, the ramifications could be disastrous. David Applegate, associate director of natural hazards at the US Geological Survey, told legislators that interference with GPS mechanisms would make it more difficult for authorities to predict floods, landslides and volcanic eruptions, with a representative from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration adding that LightSquared's ground-based mobile network would pose challenges to weather forecasters, as well. The Department of Transportation also chimed in, telling the committee that the network would likely have an effect on systems used to prevent train collisions and, like other administration witnesses, called for further testing. LightSquared Executive Vice President Jeffrey Carlisle, meanwhile, defended his company's proposal, pointing to an amended version submitted to the FCC on Wednesday. In the revised document, LightSquared offered to reduce the network's power levels further, while providing a stable signal for GPS augmentation services to use at higher frequencies. "This is not a zero-sum game," Carlisle said, adding that only 500,000 to 750,000 high-end GPS services would be affected by LightSquared's low-frequency alternative (which, the company claims, will cost an additional $100 million to implement). Any interference issues, he continued, stem from pre-existing receiver problems that the GPS industry should've addressed by now. Most of the lawmakers sitting on the panel acknowledged the need to establish broader wireless coverage, but stressed the importance of doing so without jeopardizing critical transit and emergency response systems, with some calling for additional testing. Carlisle countered that previous tests have provided sufficient feedback, but ultimate approval lies in the hands of the FCC, which has not yet offered a timetable for its decision. Hit up the source link to read LightSquared's revised proposal, in its entirety.


