neurosurgery
Latest
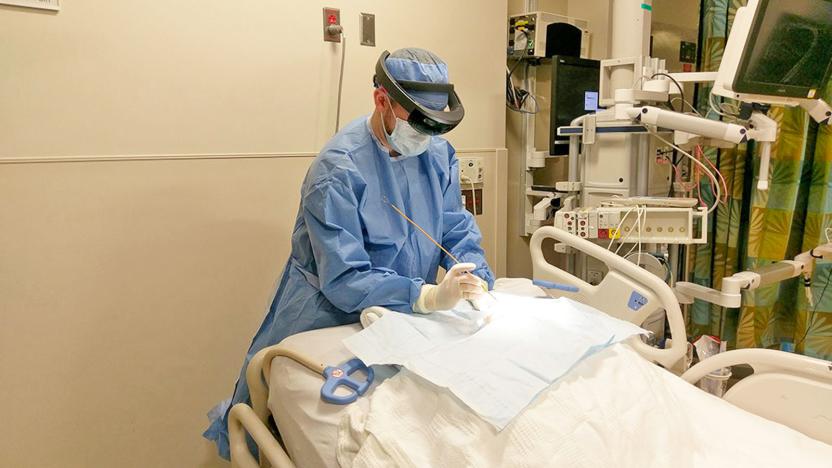
Duke hopes HoloLens will assist with tricky brain surgeries
When Microsoft envisioned the medical world embracing HoloLens in the future, it wasn't kidding around. Duke University is testing the augmented reality headset as an assistive tool for difficult brain surgeries like extraventricular drain placement, which relieves potentially fatal pressure. Instead of relying on CT scans and markers to insert a catheter into the skull during the draining procedure, Duke's doctors would use HoloLens to overlay a reconstructed CT scan on the patient's head. The virtual approach should not only be more accurate than conventional markers (the target is frequently too small or shifts around), but faster and simpler.

UCLA / Caltech researchers help patients move mouse cursors with their brains
It's certainly not a revolutionary new concept -- whiz kids have been tinkering with brain-controlled interfaces for years on end -- but a collaboration between UCLA scientists and colleagues from the California Institute of Technology has taken the idea one leap closer to commercialization. Itzhak Fried, a professor of neurosurgery at UCLA, kept a close watch (via embedded electrodes) on how a dozen humans reacted to certain images, and eventually, Fried and co. were able to show that Earthlings can "regulate the activity of their neurons to intentionally alter the outcome of stimulation." In other words, they were able to move a mouse cursor with just their mind, and brighten a test image with a 70 percent success rate. By honing the process of controlling what actions occur when focused on a given subject (or input peripheral), it opens up the possibility for paralyzed individuals to not only check their email, but also control prosthetic limbs. It's hard to say when this stuff will be put to good use outside of a hospital, but the video after the break definitely makes us long for "sooner" rather than "later."

French doctors use laser to destroy brain tumor in conscious patient
Neurosurgery with robotic assistance is getting pretty old hat nowadays, so it looks like scientists are trying to up the difficulty factor by keeping their patients awake -- a team of French doctors just completed the first successful removal of malignant brain tumor from a still-conscious patient, using a computerized laser and an MRI scanner to guide the probe. The fiber-optic laser was fed into the brain through a 3mm (.12 inch) hole in the patient's skull and guided via MRI to the tumor, where it fired for two minutes and completely destroyed the cancerous tissue. Once the tumor cells were dead, the cable was removed and the patient was allowed to return home -- all within a single day. That's pretty impressive, and it comes on the heels of 15 similar trials where five out six patients who underwent the total removal procedure were cancer-free nine months after surgery. The team says further research will cost an additional two million euros to progress, but if this technique works as well as they claim after peer review, we'd guess that money won't be hard to come by.[Via Fark]

