stimulation
Latest

Neuvana's stress-reducing earbuds are available to pre-order for $399
Neuvana's calming earbuds are nearly here after a long, long development process, although you may be in for a few surprises. The company has started taking pre-orders for its nerve-stimulating Xen buds at a $399 price ahead of their winter release. That's significantly higher than the $299 mentioned when we first saw Neuvana's tech in 2016 (and doesn't include the $4 per month premium for more waveforms and signals) but it's also considerably sleeker with a simple puck replacing the box we first saw. The intended effect remains the same, of course -- it's all about reducing stress and invoking inner peace.
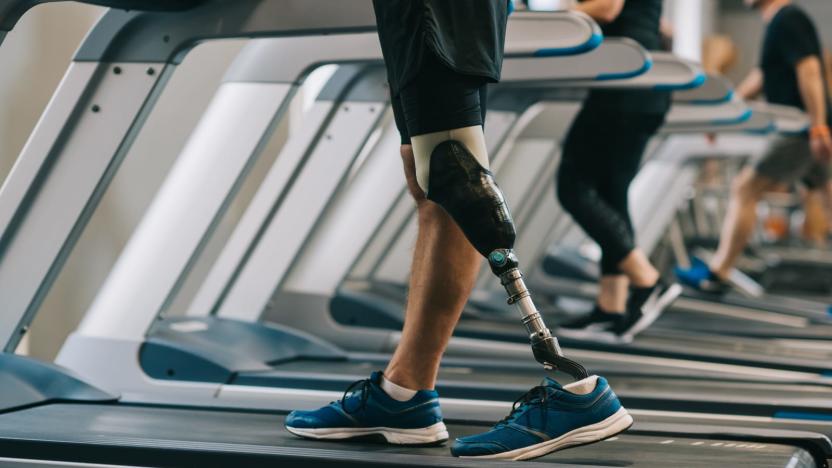
New prosthetic legs let amputees feel their foot and knee in real-time
There's been a lot of research into how to give robots and prosthesis wearers a sense of touch, but it has focused largely on the hands. Now, researchers led by ETH Zurich want to restore sensory feedback for leg amputees, too. In a paper published in Nature Medicine today, the team describes how they modified an off-the-shelf prosthetic leg with sensors and electrodes to give wearers a sense of knee movement and feedback from the sole of the foot on the ground. While their initial sample size was small -- just two users -- the results are promising.

Implant-free stimulation could treat brain conditions
Scientists know that stimulating the deeper regions of your brain can treat Parkinson's and other conditions. But there's a problem: they usually need to open your skull to place implants, which is both time-consuming and risky. Researchers may have a better way, though: they've invented a deep brain stimulation technique that only requires electrodes on your scalp. The trick is to create two high-frequency electrical currents that don't do anything by themselves, but interact with each other deep inside your brain. If you want to target different parts of the brain, you just change the frequencies and placement of the electrodes.

US military tries using small electric jolts to keep soldiers awake
Soldiers don't have many options for overcoming sleep deprivation outside of a good cup of coffee. If the Air Force Research Laboratory's experiments prove successful, though, troops may rely on tiny jolts of electricity to stay alert. By using a mild current to stimulate key parts of the brain, the military's scientists can keep people awake and focused for long periods -- up to 30 hours in recent trials. The existing technique produces modest side effects like skin irritation and short headaches, and it's unlikely to reach civilians any time soon. However, a refined version could eventually prove crucial to drone pilots and other warriors who can't afford to take naps during crucial missions. [Image credit: John Kricfalusi]

Chilly Chair uses static electricity to raise your arm hair, force an 'emotional reaction' (hands-on video)
Hiding in the back of the SIGGRAPH Emerging Technologies demo area -- exactly where such a project might belong -- is a dark wood chair that looks anything but innocent. Created by a team at the University of Electro-Communications in Toyko, Chilly Chair, as it's called, may be a reference to the chilling feeling the device is tasked with invoking. After signing a liability waiver, attendees are welcomed to pop a squat before resting their arms atop a cool, flat metal platform hidden beneath a curved sheath that looks like something you may expect to see in Dr. Frankenstein's lab, not a crowded corridor of the Los Angeles Convention Center. Once powered up, the ominous-looking contraption serves to "enrich" the experience as you consume different forms of media, be it watching a movie or listening to some tunes. It works by using a power source to pump 10 kV of juice to an electrode, which then polarizes a dielectric plate, causing it to attract your body hair. After signing our life away with the requisite waiver, we sat down and strapped in for the ride. Despite several minutes of build-up, the entire experience concluded in what seemed like only a few seconds. A projection screen in front of the chair lit up to present a warning just as we felt the hairs jet directly towards the sheath above. By the time we rose, there was no visual evidence of the previous state, though we have no doubt that the Chilly Chair succeeded in raising hair (note: the experience didn't come close to justifying the exaggerated reaction you may have noticed above). It's difficult to see how this could be implemented in future home theater setups, especially considering all the extra hardware currently required, but it could potentially add another layer of immersion to those novelty 4D attractions we can't seem to avoid during visits to the amusement park. You can witness our Chilly Chair experience in the hands-on video after the break.%Gallery-162116%

Magnetic fields shut down speech, permit love songs (video)
You already know the strange powers of Stephin Merritt, but today we're talking about real magnetic fields. Powerful electromagnets, it turns out, can do remarkable things to the brain -- in this case, prevent a volunteer from reciting "Humpty Dumpty." The carefully directed magnets temporarily disrupt the brain's speech centers; the volunteer can still sing the rhyme using different areas of the brain, but simply can't overcome a series of stammers when trying to merely recite it. Of course, it's not all mad scientist applications: the UK team experimenting with transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) thinks it can help us understand and treat migraines (as we've seen before with the Migraine Zapper), depression, and ADHD, among other ailments. But improving physical well-being doesn't make for nearly as entertaining media -- see the British inflict some involuntary quiet time in the video above.



