MassSpectrometer
Latest
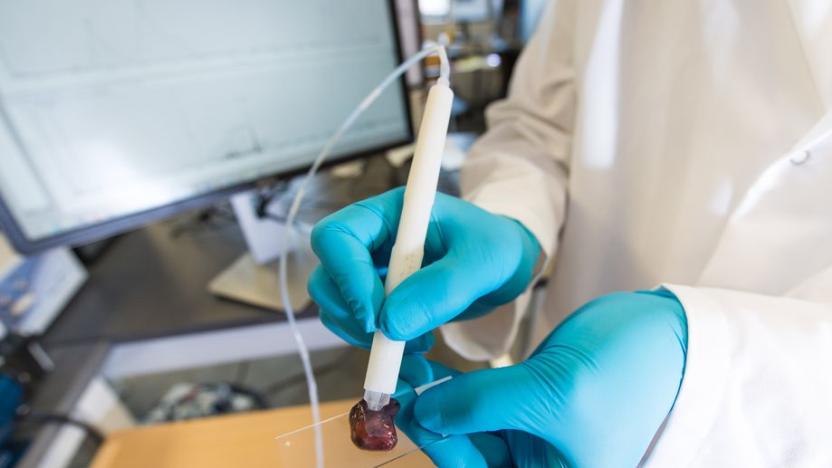
This pen can determine whether tissue is cancerous in ten seconds
When surgeons are removing a tumor from a patient, determining whether they have taken out all of the cancerous cells or if they should extract more tissue is a problem they all face. Typically, the margins of a tumor are assessed after the surgery is completed and if it looks like some cancer was left behind, another surgery might be in order. So, developing a way to test tissue for cancerous cells in real-time would be incredibly useful for both surgeons and patients. In a study published this week in Science Translational Medicine, researchers present a device that does just that.

Researchers develop a drug-sniffing car that can pinpoint your stash
A chemistry professor in Texas has equipped an electric Ford sedan with a unique (and possibly unconstitutional) aftermarket upgrade: a drug-sniffing device that can recognize small amounts of illegal substances in the air and locate the source with surprising accuracy.

This is what brain synapses look like in 3D
Many know that brains are inherently complex things; there are trillions of synapses converting chemical and electrical signals in a human mind. However, did you know that even those synapses are very complex? If not, it should be perfectly clear now. German scientists have used a mix of extremely high-resolution microscopes (both electron and fluorescent), mass spectrometry and protein detection to create a super-detailed 3D map of a synapse in a rat's brain. It's almost like a miniscule city -- those dots you see represent 300,000 proteins, and only a tiny portion (the glowing red patch at the bottom) is transmitting chemicals.

NASA looks to send landers to Europa in 2020, wants to break the ice
There's still a lot of mystery surrounding Jupiter's moon Europa, but researchers at NASA seem fairly certain that there's a watery ocean lurking beneath its icy exterior. Their theories may finally be put to the test later this decade, thanks to a concept mission crafted by astronomers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. According to Space.com, JPL researchers have come up with a plan that would send a pair of landers to Europa by 2026, in the hopes of finding out whether the rock has ever supported life forms. The endeavor certainly wouldn't be easy, since Jupiter blankets its moon in heavy radiation, but researchers think they can mitigate these risks by sending in an extra lander as backup, and by keeping the mission short and sweet. Under the plan, each 700-pound robot would use a mass spectrometer, seismometers and a slew of cameras to search for any organic chemicals that may be lodged within the moon's ice. Neither craft will sport a protective shield, so they'll only stay around the planet for about seven days, so as to avoid any radiation damage. At this point, the mission is still in the concept phase, though the JPL is hoping to launch both landers by 2020. JPL researcher Kevin Hand was quick to point out, however, that this would be a "habitability mission," and that NASA doesn't expect to find any signs of current life on Europa. Lars von Trier was unavailable for comment.

NASA finds DNA components in meteorites, says they originated in space (video)
So, this is kinda wild: scientists at NASA have uncovered new evidence that DNA components found in meteorites can originate in space, lending new credence to the theory that life on Earth may have arisen from a pre-existing "kit" of materials delivered via asteroid. The discovery is outlined in a new paper from Dr. Michael Callahan, whose team of researchers closely analyzed samples from 12 different meteorites, using a mass spectrometer and liquid chromatography. In their samples, they found traces of adenine, guanine, and a variety of molecules known as nucleobase analogs -- including three that are rarely found on Earth. Scientists have long known that meteorites can contain DNA elements, but were unsure whether these materials actually originate in space. The presence of these three molecules, however, suggest that they do, potentially raising new questions about the dawn of life on Earth, and beyond. It's all quite heady, but steam ahead for a NASA video that might help clarify things, after the break.


