magnet
Latest
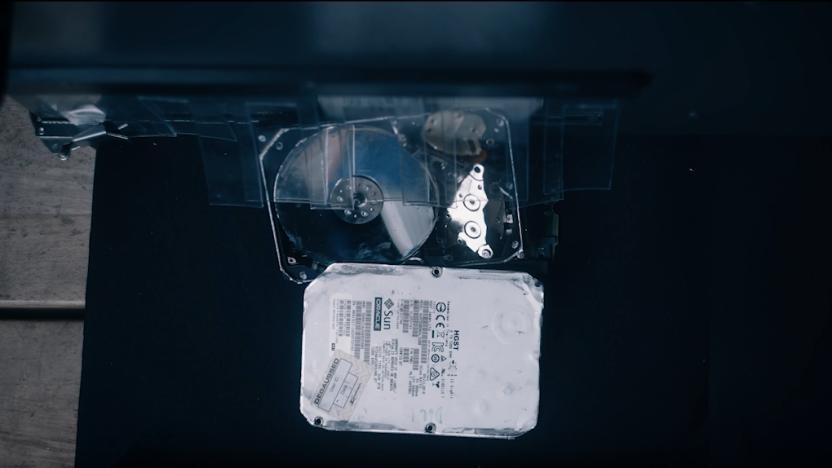

Watch a recycling machine shake apart old hard drives to recover components
A company called Garner Products has invented a machine that can shake traditional hard drives apart to help recover useful components. The DiskMantler can seemingly dismantle an HDD in as little as eight seconds.
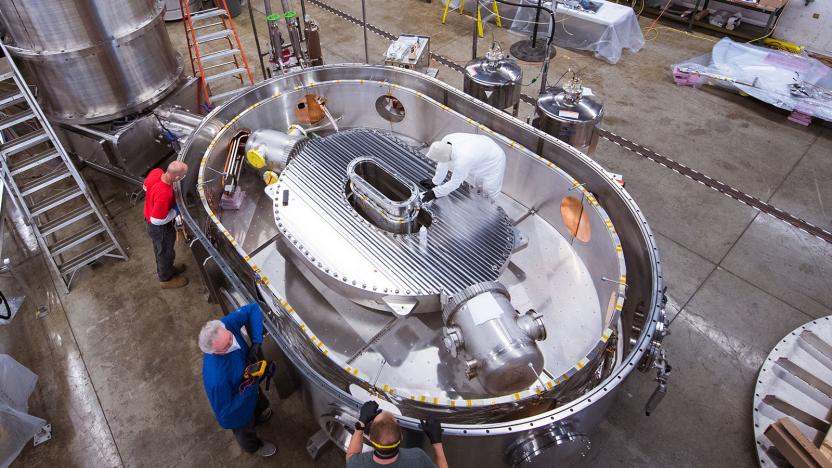

Fusion energy nears reality thanks to an ultra-powerful magnet
Fusion energy is closer to becoming a practical reality after researchers successfully tested an extremely powerful magnet.
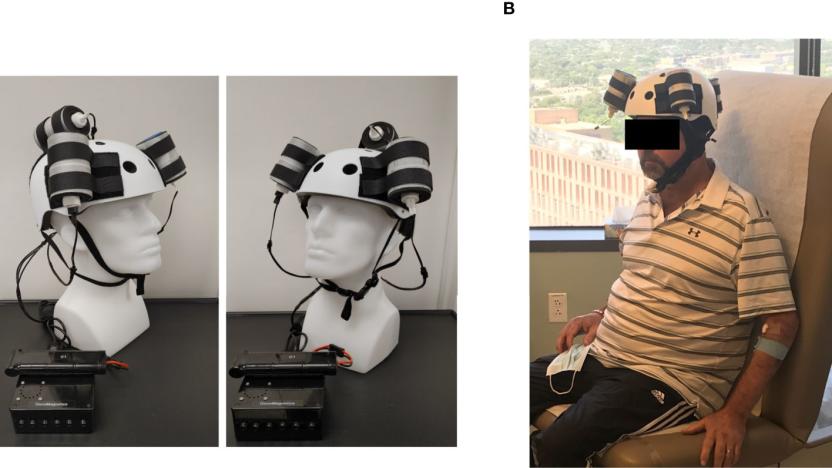
A magnetic helmet shrunk a deadly tumor in world-first test
Scientists have created a helmet that uses magnetic therapy to reduce deadly brain tumors.

MagSafe makes a full comeback for your USB-C MacBooks
One feature that seasoned MacBook users may miss is the good ol' MagSafe connector, because no one wants to accidentally drag a pricey laptop off the table. Alas, ever since Apple made the jump to USB-C, it decided to retire its handy magnetic invention -- it even stopped short at releasing a MagSafe-to-USB-C adapter. There have since been a few third-party alternatives, with the earlier ones handling just power delivery (like Griffin's BreakSafe cable), followed by the more advanced data transmitting types with mixed reviews -- they tend to be bulky, nor did they support Thunderbolt 3's full bandwidth, apparently. This is where ThunderMag comes in. Developed by Innerexile over the past three years, this little gadget is claimed to be the world's first truly Thunderbolt 3-compatible magnetic adapter. In other words, ThunderMag can pass through data at up to 40 Gbps (or video at up to 5K) while also delivering 100W of power, thanks to its 24 pins and delicate magnetic shaping -- the latter to protect the cable's high-frequency signal. And of course, the ThunderMag isn't exclusive to MacBooks; just plug it into any Thunderbolt 3 or USB-C port on a device and you're good to go.

Toyota's next EV motor could use 50 percent less rare earth metals
Toyota has designed a magnet that halves the amount of rare earths needed in its electric cars, which could help mitigate the fall out of a looming materials shortage. Like other electric carmakers, Toyota has traditionally used neodymium, terbium and dysprosium in its electric vehicles, but it believes demand for these materials will outstrip supply come 2025. The new magnet uses the rare earths lanthanum and cerium instead, which are more plentiful and cost 20 times less than neodymium.

Computer models help form new magnetic materials
Magnetic materials are extremely difficult to find. They're rare in nature, and creating one in the lab usually involves both a lot of experimentation and a little luck. Duke University, however, has found a way to take the mystery out of the process: its researchers have used computer modelling to help generate two new kinds of magnetic materials. The models whittled down the potential atomic structures from a whopping 236,115 combinations to just 14 candidates by subjecting the structures to increasingly tougher tests. How stable are they? Do they have a "magnetic moment" that determines the strength of their reaction to an outside magnetic field? After that, it was just a matter of synthesizing the few remaining materials to see how well they worked in real life.

Super-fast magnetic motor keeps tiny satellites on track
Satellites often rely on reaction wheels, or constantly spinning flywheels, to tweak their attitudes without using precious fuel. However, they tend to be very delicate -- since they use ball bearings, they spin relatively slowly (under 6,000RPM), take up a lot of space, need tightly controlled environments and aren't very precise. Thankfully, researchers at Celeroton have a better way. They've created a magnetically levitated motor that achieves the effect of a regular reaction wheel with virtually none of the drawbacks. Since its rotor floats in a magnetic field, it can spin much faster (up to 150,000RPM) without wearing out, creating vibrations or requiring a special, lubricated environment. And given that it produces the same angular momentum as a much larger reaction wheel, it's perfect for CubeSats and any other tiny satellite where internal space is at a premium.

Newly discovered magnetism is a big boost for quantum computers
Until now, humanity has only known two forms of magnetism: ferromagnetism (the kind you see on your fridge) and antiferromagnetism (a sort of negative magnetism found in hard drives). However, MIT researchers just confirmed the existence of a third kind... and it could be the key to making quantum computing a practical reality. The team made and supercooled a crystal that exhibits a quantum spin liquid state, where the magnetic directions of each particle never line up. That odd behavior, in turn, leads to quantum entanglement (in which distant particles affect each other's magnetism) that would be ideal for computers.

Ferrofluid 'font' produces trippy, one-of-a-kind art
You may have seen ferrofluid (aka magnetic ink) used for clever science demonstrations in school, but it might just get a much cooler application before long. Linden Gledhill and Craig Ward have developed Fe2O3 Glyphs, wild-looking characters created by putting a ferrofluid between glass plates and subjecting it to spinning magnetic fields. The result is a sort of anti-font -- while the "letters" look like they could be part of an alien language, they're so unique that you'd likely never produce the same effect twice.
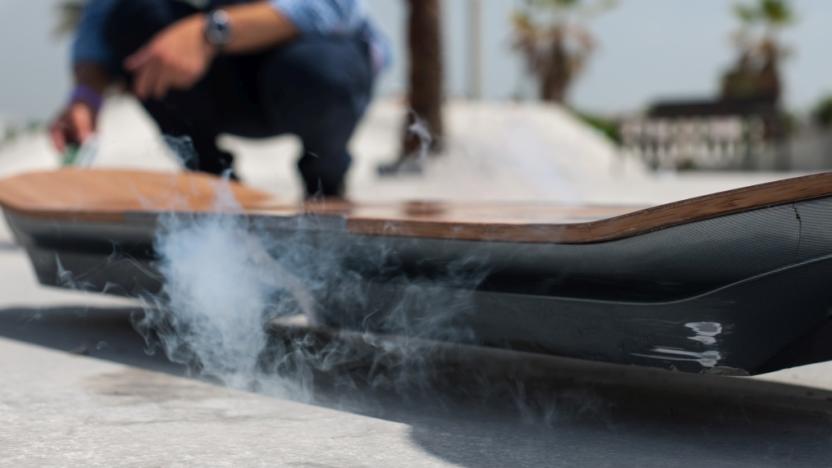

Lexus let skateboarders put its hoverboard to the test
After weeks of teasing, Lexus is finally showing off its latest Amazing in Motion project in full. The Slide video posted today shows skateboarders riding the company's superconducting hoverboard at a specially built skate park in Spain. Similar to the $10,000 Hendo hoverboard before it, this board only works if you have the combination of a liquid nitrogen cooled cryostat onboard and a special magnetic track, so no -- it's not for sale. As you can see in the video, skaters who got their crack at it pulled off some cool gliding tricks (including one across a stretch of water), but it's still not quite the same thing as the decks that they're used to, and seemed to have less control available than the Hendo board. Back to the Future it ain't, but it's real, and it's cool (-197°C).

Cable-free elevator moves you in any direction
Elevators are absolutely vital in tall buildings, but they have their limits -- they can only move so quickly, and they can't usually move sideways to fetch you from the far side of a building. Both of those problems should be solved at once if German firm ThyssenKrupp has its way. Its new Multi elevators ditch cables in favor of magnetic linear motor technology (also used in maglev trains) to move both horizontally and vertically, letting them service very wide or unusually shaped buildings. They can operate in loops and aren't limited by heights, either, so it's easy to put multiple elevator cars in one shaft. You'll ideally never wait longer than 30 seconds for a lift, and the space-saving design lets building owners offer more (or at least larger) apartments and offices.

Laptops to get maglev keyboards that reduce their thickness
Magnetic levitation keyboards have been around for a while, but they've never really taken off, or floated our boats, or attracted much atten... Anyway, a Taiwanese manufacturer called Darfon is persevering with the idea, and it's discovered that maglev keys, which rest on opposing magnets instead of mushy membranes or mechanical switches, can make laptop keyboards significantly thinner. Unfortunately, according to a CNET journalist who played with a couple of prototypes at Computex, the keys can be hard to type on if skinniness is taken to the extreme. Then again, there's scope to change the resistance of the keyboard electronically to suit your preference, and Darfon claims it has already received orders from laptop makers who are targeting launches later this year. If that's true, perhaps the technology isn't so repellant after all. [Image credit: Aloysius Low / CNET]

Watch a tiny, magnetically powered robot construction crew go to work
A robot doesn't have to big, powerful and terrifying to be worthwhile, and many people are working on miniature machines that are just as cool. Some of these endeavors show promise in medicine, but there are plenty of potential uses for microbots, especially when you can persuade a swarm of them to work together. Research outfit SRI reckons tiny automatons have a bright future in manufacturing, thanks to its new method for precisely controlling individuals within a larger group. You see, one of the best ways of propelling and controlling microbots is by using magnets. and it's because there's no need for an on-board power source that we can make 'em so small. This poses a problem, however, as a pack of bots will all respond to a magnetic field in the same way, making it hard to give anything but a blanket order.

Miselu launches C.24 wireless music keyboard for iPad, we go hands-on (video)
The last time we covered Miselu was during Google I/O 2012 when we took a second look the Neiro Android-powered synth. Fast forward a year and the company's shifted its focus on a completely new product -- the Miselu C.24 wireless music keyboard for iPad -- which is launching today for $99 on Kickstarter. The device is a high-quality two-octave (24-key) collapsible music keyboard designed to be a magnetic iPad cover when stowed. It features Bluetooth 4.0 Low Energy, micro-USB connectivity and a sealed Li-ion battery which provides 5-6 hours of operation. As such, it's compatible with any Core MIDI iOS app and any OS X, Windows or Linux software that supports MIDI over USB. The C.24 integrates a capacitive ribbon divided into two areas -- eight buttons with four LEDs each on the left (octave selection by default) and a linear controller on the right with 32 LEDs (pitch bend by default). Miselu plans to ship the product with a companion iOS app in time for the holidays. We briefly played with a prototype and came away extremely impressed. Hit the break for our first impressions and hands-on video / interview. %Gallery-193358%

Panasonic preps SD cards that survive heat, water and X-rays, will probably outlast you
Much ado has been made of weather-resistant cameras, but it's all a moot point if the memory card dies, isn't it? Panasonic wants that level of survivability in its SDHC and SDXC cards, and its new UHS-I-level SDAB and SDUB lines are tested for the kind of abuse that could see the camera give up the ghost first. The cards can take the kinds of punishment that we often associate with rugged gear, such as temperatures from -13F to 185F, immersion in 3.3 feet of water for half an hour and the usual steep drops. It's beyond this that the resistance levels become truly exotic: the cards are also built to survive zaps of electricity, proximity to magnets and exposure to X-rays. If it all becomes too much to bear, the design will even fuse on the inside to prevent fire burning the card from within. Those who like what they see will only have to decide whether or not they want the SDAB range's 95MB/s read speeds and 80MB/s writes or are willing to settle for the SDUB line's respective 90MB/s and 45MB/s transfers. We have yet to see if or when the SD cards cross the Pacific after their September 8th launch in Japan, although we hope so -- with that kind of extra-tough design, our photos are more likely to endure than we will.

Google's Nexus 7 discovered to have Smart Cover-like magnetic sensor
You won't find this on its official specs list, but Google's Nexus 7 tablet apparently has a magnet-enabled sensor that'll automatically set the display to sleep -- it's hard not to think of the iPad's Smart Cover. YouTube user wwscoggin was able to discover and pin-point the functionality near the bottom left of the device by gliding a magnet along its bezel. As Android Police notes, the feature is seldom found on Android tablets, and there's no word on whether ASUS' decidedly Smart Case-esque cases will make use of it. We've been able to replicate the action on our end, but don't take our word for it, catch the video after the break.

IndoorAtlas uses disturbances in the (geomagnetic) force to map interiors, plot a path to aisle 3 (video)
Interior navigation is only just coming into its own, but IndoorAtlas has developed a technology that could make it just as natural as breathing -- or at least, firing up a smartphone's mapping software. Developed by a team at Finland's University of Oulu, the method relies on identifying the unique geomagnetic field of every location on Earth to get positioning through a mobile device. It's not just accurate, to less than 6.6 feet, but can work without help from wireless signals and at depths that would scare off mere mortal technologies: IndoorAtlas has already conducted tests in a mine 4,593 feet deep. Geomagnetic location-finding is already available through an Android API, with hints of more platforms in the future. It will still need some tender loving care from app developers before we're using our smartphones to navigate through the grocery store as well as IndoorAtlas does in a video after the break.

Microsoft applies to patent MagSafe-like magnetic power and data coupling
Microsoft has applied to patent a magnetic power and data coupling that's similar to the power-only MagSafe. Using the technology, the unit would snap onto the base of your phone (in the example) in either direction, pushing juice and information without the needless fiddling with a micro/miniUSB port. Since it's just an application, it's not likely to arrive in a product yet, but it does make us hopeful that more companies aim to end our cable-based annoyances.

ZeroN slips surly bonds, re-runs your 3D gestures in mid-air
Playback of 3D motion capture with a computer is nothing new, but how about with a solid levitating object? MIT's Media Lab has developed ZeroN, a large magnet and 3D actuator, which can fly an "interaction element" (aka ball bearing) and control its position in space. You can also bump it to and fro yourself, with everything scanned and recorded, and then have real-life, gravity-defying playback showing planetary motion or virtual cameras, for example. It might be impractical right now as a Minority Report-type object-based input device, but check the video after the break to see its awesome potential for 3D visualization.

Apple snags a patent for the Smart Cover's magnetic know-how
No, it doesn't cover the totality of the Smart Cover itself (or any case that folds into a triangle), but Apple has now managed to obtain a patent for one of the accessory's key bits of functionality. First filed in July of 2011 and published by the USPTO today, the patent described as an "accessory device with magnetic attachment" details how magnets can be used in a particular manner to attach a cover to a device (like an iPad) and secure it in place, yet still allow it to be easily released. Again, that doesn't cover all cases that use magnets -- just magnets used in this very specific way. Hit the source link below for all the details in patent-speak.












