self-repairing
Latest
Self-repairing material plucks carbon from the air
Scientists might have a particularly clever way to help the environment: they've developed a material that can not only heal itself, but could reduce CO2 levels in the process. The substance uses its combination of a gel-like polymer with chloroplasts (cell elements that handle photosynthesis in plants) to grow by snatching carbon from the air after exposure to light. If you cracked or scratched an already-solidified piece of this material, the newly exposed sides would promptly expand and fill the gap without requiring heat, ultraviolet light or other special reactions like you see with existing self-healing products.
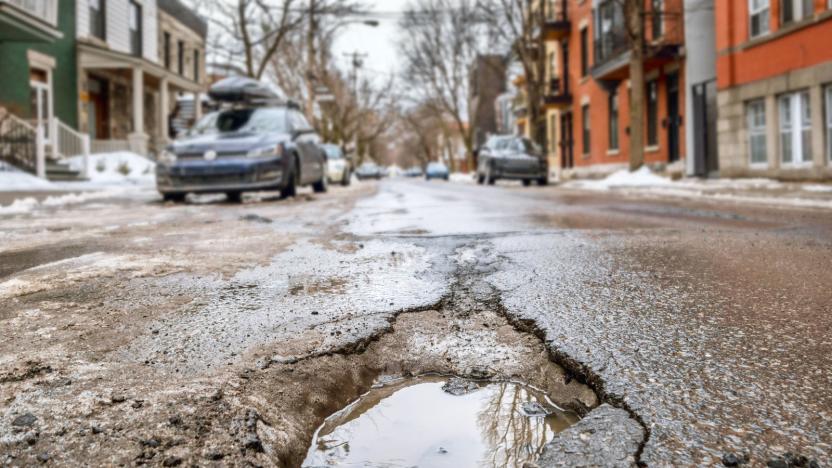

Self-repairing roads could also charge your electric car
Potholes are bad enough for the jarring rides, car damage and safety hazards they create, but it's also problematic to fix them. You're looking at lane and road closures that can last for days, assuming the city can even spare the resources. However, Dutch researchers might have a solution that not only helps the road fix itself, but promises to solve range anxiety for electric car drivers. Delft University's Erik Schlangen tells The Verge that there are plans to test self-repairing asphalt whose conductive steel fibers and bacteria would both fix small cracks in the pavement and send electricity to EVs above. The trial will charge your vehicles when you're stopped at intersections, giving you a little bit of extra range in those moments you're waiting for the light to turn green.

Future wearables could use magnetic circuits to self-heal
Smart clothing might be huge, except for one problem: The printed "ink" electronics are delicate, so you can break them just by stretching the wrong way. However, researchers from the Jacobs School of Engineering have developed a self-healing magnetic ink that can repair multiple cuts in as little as 50 milliseconds. That could eventually yield batteries, electrochemical sensors and wearable electronic circuits that fix themselves autonomously, making the smart textile industry more feasible.

Toray unveils new self-repairing film for devices, fixes scratches in under 10 seconds
Toray's advanced film department has finished its new self-cure coating and is set to start using it as a decorative layer on a series of as-yet unannounced notebooks. Fortunately, the company is already chasing down more pervasive uses on smartphones and touch-panels. The science involves a wet coating method that adds a special recovering layer to PET film. Alongside that mutant healing factor, the layer responsible also throws in some elastic and cushioning properties. During Toray's demonstration (what, no video?) scratches made with a metal brush apparently repaired themselves, resulting in the rehabilitated glossy surface you see above. According to the Japanese manufacturer, the ability to heal improves at lower temperatures, but room temperature is apparently enough to make scratches disappear in 10 seconds or less -- more than fast enough to differentiate Toray's offering from existing solutions. The film can repair itself around 20,000 times in succession, although if pierced beyond the layer, it's -- unsurprisingly -- unable to recover any damage done. The screen is also softer than the typical protective surfaces found to devices. Maybe Toray and Gorilla Glass should get together. GorillToray?

Researchers tout self-repairing multi-core processors
The race for ever-tinier computer chips is on, and barring physical limitations, doesn't seem to be slowing anytime soon -- but with chips, as with humans, the smaller they get, the more fragile they become. A team of researchers called CRISP (Cutting edge Reconfigurable ICs for Stream Processing) is working to create a self-repairing multi-core processor that would allow on-chip components to keep on shrinking, while combating concerns over accelerated degradation. Basically, the team's conceptualized a chip that allows for 100 percent functionality, even with faulty components. With multiple cores sharing tasks, and a run-time resource manager doling out those tasks, the chip can continue to degrade without ever compromising its intended functions -- a process CRISP calls graceful degradation. Once one core fails, the on-chip manager assigns its task to another core, continuing on in this fashion for the complete lifetime of the chip. Of course the technology is still in its infancy, but if CRISP's chips comes to fruition, we could see virtually indestructible processors that make 14nm look bulky by comparison.

Synthetic rubber mends itself after being sliced
Self-healing materials are far from revolutionary, but a team of gurus at France's National Center for Scientific Research has teamed up with Arkema to create a newfangled material that can literally reattach itself if simply pressed together after a break. Reportedly, the self-mending takes place due to weak hydrogen bonds that mesh networks of ditopic and tritopic molecules back together, essentially acting as a kind of "atomic glue." The matter is able to reconnect with any long lost pieces at room temperature (at least 68°F), and apparently, creators are already looking to commercialize their discovery and get products on the shelves within two years. So much for breakaway cables, eh?[Via Physorg]




