sensory
Latest
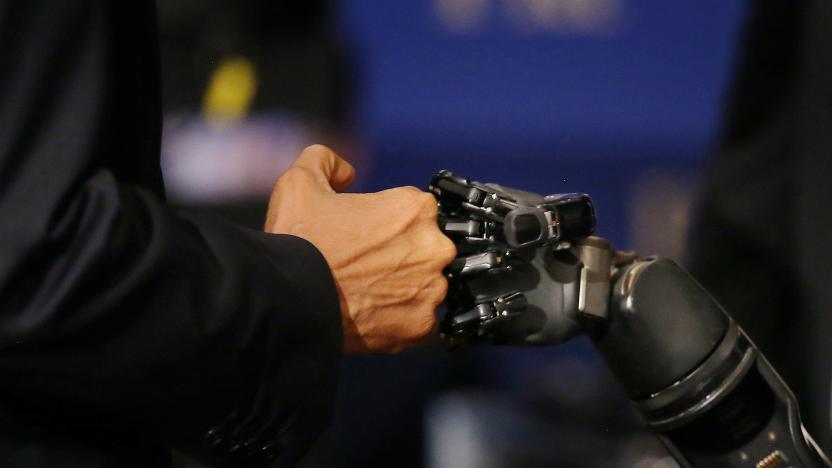

Researchers boost robotic arm movement by adding a sense of touch
Researchers helped a paralyzed man to move his robotic arm even faster by adding tactile feedback to the process.
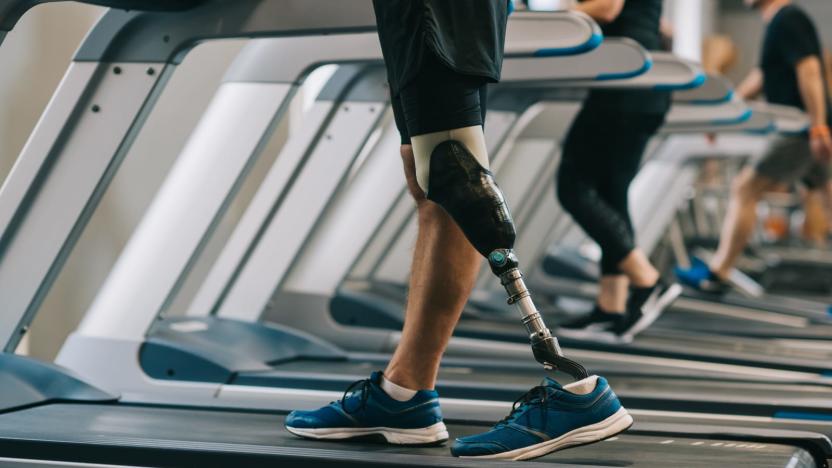
New prosthetic legs let amputees feel their foot and knee in real-time
There's been a lot of research into how to give robots and prosthesis wearers a sense of touch, but it has focused largely on the hands. Now, researchers led by ETH Zurich want to restore sensory feedback for leg amputees, too. In a paper published in Nature Medicine today, the team describes how they modified an off-the-shelf prosthetic leg with sensors and electrodes to give wearers a sense of knee movement and feedback from the sole of the foot on the ground. While their initial sample size was small -- just two users -- the results are promising.
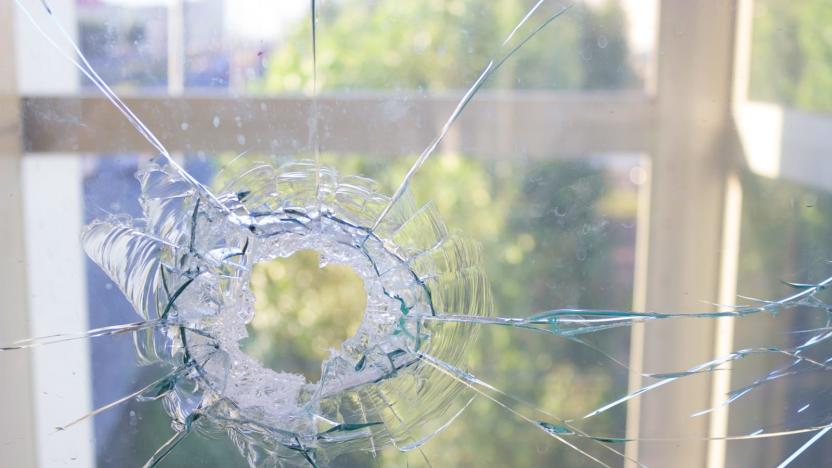

Sensory AI can recognize sounds in your home
Wouldn't it be great if home devices like smart speakers can ping you if they hear anything unusual, such as the sound of breaking glass? A software company called Sensory has developed an AI that can identify the sounds it hears and take action if needed. It says the technology, called TrulySecure Sound ID, is like "Shazam for sounds in the home."
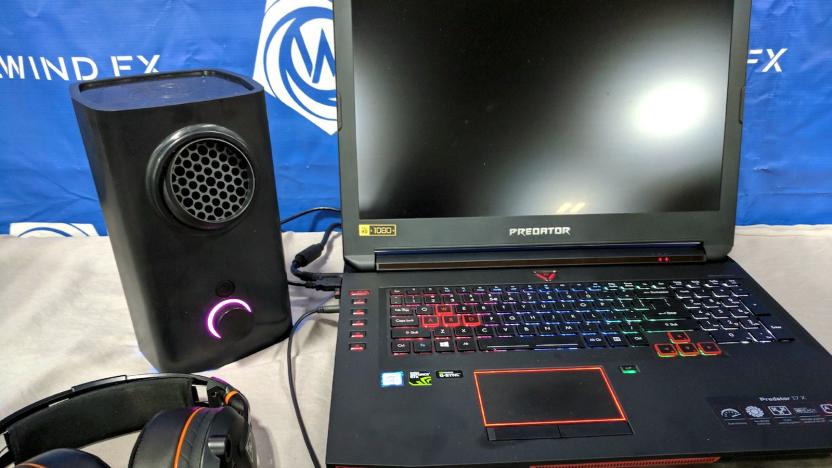

Vortx blows air at your face while you're gaming, and it's great
Vortx is ridiculous. It's a cube that you place on your desk, next to your PC or laptop, and it blows hot or cold air in your face, depending on what's happening on-screen. The air responds dynamically to the action: If you're running through the fiery hellscape of Doom, the fan blows hot and fast, but if you're watching a YouTube video about climbing Mount Everest, it shoots out gusts of frigid air. So, yes, it's ridiculous -- but it's also really cool in action.

Neural implants and robot arms allow paralyzed man to feel again
After breaking his neck more than a decade ago, Nathan Copeland has finally regained his sense of touch. The only catch is that those feeling are fake -- artificially generated by a robotic arm and an array of tiny electrodes embedded in his brain by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center.

Telesar V robot brings new meaning to escapism (video)
The esoteric art of telepresence is all about that sweetest of dreams: being somewhere you'd rather be. So far, though, it's hardly teleported much beyond our head movements and kisses. What we really need is a fully-fledged avatar that can also feed sensory information back to us -- and that's exactly what the Telesar V claims to be. The user dons a pair of VR goggles that control the robot's head and see through its eyes. A pair of gloves not only control the Telesar's hands, but also transmit force and temperature data back from its sensors. Drag yourself away from that violent BF3 simulator and check out the smoochiness after the break. (And yes, the inventor's surname is just about perfect.)

Monkeys control virtual arm with their brains, may herald breakthrough for paraplegics
Monkey mind-controlled arm: It sounds like the name of an awesomely terrible sci-fi film or a fledgling grindcore group, but it's a very real phenomenon, and one that could pay significant dividends for paraplegics everywhere. Neurobiology professor Miguel Nicolelis and his team of researchers at Duke University recently devised a method by which monkeys (and, perhaps one day, humans) can control a virtual arm using only their brains. It's a concept similar to what DARPA has been pursuing with its mind-controlled "Luke" arm, with one important difference: Nicolelis' system not only allows users to remotely execute motor functions, but provides them with near-instantaneous sensory feedback, as well. Most similar techniques use electrode implants to stimulate brain activity, but this can create confusion when a patient's brain sends and receives signals to and from a prosthetic arm. Nicolelis circumvented this problem with a new interface that can read and transmit brain signals to an artificial limb, before switching to a receptive mode in just milliseconds. After designing the technology, Nicolelis and his colleagues tested it on two, electrode-equipped rhesus monkeys. One set of electrodes was placed in the motor cortex of each animal, with the other implanted within their brains' sensory regions. They then trained the monkeys to look at a three identical objects on a computer screen and to "touch" each object with a virtual arm, controlled by signals sent from the brain electrodes. Only one of the three objects had a so-called "virtual texture," which, if selected with the on-screen arm, would send a sensory signal back to the monkey's brain (while triggering a tasty squirt of fruit juice for the lucky contestant). The two rhesus species ended up passing the test with flying colors, resulting in a "proof of principle" that Nicolelis' system can send tactile signals to the brain in almost real-time. The scientists have already developed a way for monkeys to control the arm wirelessly, and are now embedding their technology within a full-body, mind-controlled exoskeleton for paralyzed patients, as well. Of course, the technology still needs to be tested on actual humans, though Nicolelis seems confident that he and his team have already cleared the most difficult hurdle: "Since we cannot talk to the monkeys, I assume with human patients, it's going to be much easier."

Touch pad prototype works without movement, makes fingertips feel like they're sliding (video)
This comes from the same touchy-feely Kajimoto lab in Japan that brought us the tactile kiss transmission device and we totally see where they're going with it: maximum sensation, minimum effort. You only have to exert the gentlest of pressures on this prototype touch pad and it zaps your fingertip with little electrical signals, mimicking the feeling of sliding your finger over a surface. We imagine it's a bit like the little red pointing stick in the middle of a Lenovo ThinkPad keyboard, for example, but with the addition of "position-dependent data input" to create the illusion that your finger is actually touching different areas of the screen. For now though, if you don't mind stretching a finger to your old-stylee mouse or trackpad, then check out the video after the break.

$2 Sensory chip could give toys (and other products) improved speech recognition, additional capabilities
Sensory Inc. may stay behind the scenes most of the time, but the company's speech recognition chips are already used in toys from JVC, Mattel, Hasbro and others, and it's now announced a new chip that could lead to toys with some significantly improved capabilities. Costing just $2 apiece (in quantities over 100K/year), the company's NLP-5X chip not only boasts support for speech recognition and text-to-speech that lets it "generate thousands of voices on the fly," but support for sound samples and MIDI playback as well. What's more, the chip uses what's described as an "incredible algorithm" that allows it to be on all the time and simply listen and activate itself when needed -- or when you least suspect it. Of course, while toys are one application, the company also sees the chip being used in a whole range of other consumer electronics -- Sensory even gives the example of an internet-connected oven that could let look up a recipe and then have a conversation with your oven about how you'd like to cook it.

BrainPort lets you see with your tongue, might actually make it to market
We first saw the crazy BrainPort in 2006, but the intervening time hasn't been wasted by its developers, who've brought the quirky visual aid to the cusp of commercial viability. If you'll recall, the device translates signals from a head-mounted camera to electrical pulses that lightly zap your tongue in response to visual stimuli -- early results have shown people can regain a good bit of their spatial awareness and even read large writing. The next step is FDA approval, which is expected by year's end, meaning that the BrainPort could arrive as early as 2010. There is a steep entry fee though, with prices expected to begin at $10,000, but the very fact you'll be able to buy it is a milestone in our book. Edifying video after the break. [Thanks, Toy]

Sensory Sweep Studios join the ranks
According to a job posting on their official site, independent development team Sensory Sweep Studios is looking for talent to aid in the development of an action title for the Wii. Looking for junior and senior game designers to help in level and character design for this title, Sensory Sweep's most recent releases include Need For Speed: Most Wanted and Tiger Woods PGA Tour on the DS.While we can't be all that enthused about this development considering the only major titles of note from the company were on a handheld, the more support for Nintendo's newest console the better. [Via Codename Revolution]








