oakridgenationallaboratory
Latest

AMD and Cray are building the 'world's most powerful supercomputer'
The US may be set to hang onto the crown of having the world's most powerful supercomputer for some time. Cray Computing and AMD are building an exascale machine with the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The system is set to debut in 2021, the same year Cray and Intel are scheduled to deliver the Aurora exascale supercomputer to the Argonne National Laboratory.

The US again has the world's most powerful supercomputer
The Department of Energy pulled back the curtain on the world's most powerful supercomputer Friday. When Summit is operating at max capacity, it can run at 200 petaflops -- that's 200 quadrillion calculations per second. That smokes the previous record holder, China's Sunway TaihuLight (which has a 93 petaflop capacity). Summit is also about seven times faster than Titan, the previous US record holder which is housed at the same Oak Ridge National Lab in Tennessee. For perspective, in one hour, Summit can solve a problem that it would take a desktop computer 30 years to crack.
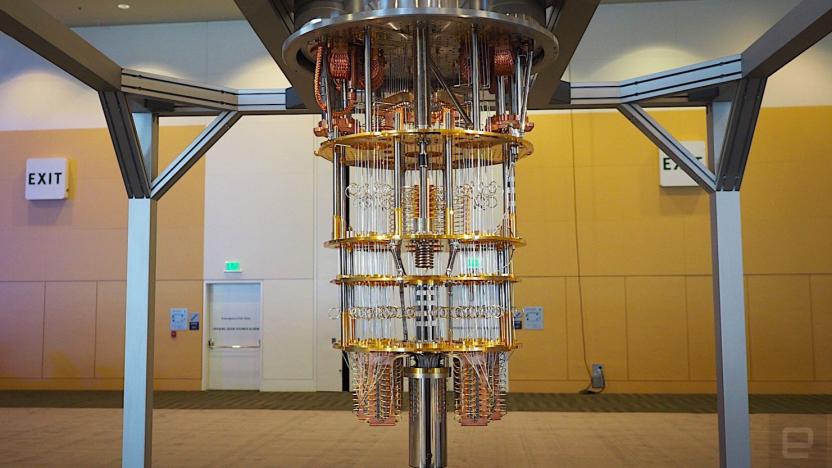

Not even IBM is sure where its quantum computer experiments will lead
Despite the hype and hoopla surrounding the burgeoning field of quantum computing, the technology is still in its infancy. Just a few years ago, researchers were making headlines with rudimentary machines that housed less than a dozen qubits -- the quantum version of a classical computer's binary bit. At IBM's inaugural Index Developer Conference held in San Francisco this week, the company showed off its latest prototype: a quantum computing rig housing 50 qubits, one of the most advanced machines currently in existence.
NVIDIA helps the US build an AI for cancer research
Microsoft isn't the only big-name tech company using AI to fight cancer. NVIDIA is partnering with the US Department of Energy and the National Cancer Institute to develop CANDLE (Cancer Distributed Learning Environment), an AI-based "common discovery platform" that aims for 10 times faster cancer research on modern supercomputers with graphics processors. The hardware promises to rapidly accelerate neural networks that can both spot crucial data and speed up simulations.

Electron microscope draws nano-sized patterns in metal ink
One of the greatest challenges in designing electronics is drawing very fine details. You normally need lithography, which complicates the process by requiring masks. However, Oak Ridge National Laboratory has now found a way to write at an extremely fine level -- and even get a little bit creative. Its researchers have developed a technique that relies on an electron microscope to draw nanoscale patterns using metal ink. The team first creates a grayscale template to guide its work, and uses the microscope to shoot electrons into palladium chloride cells along that template. The cells neatly deposit raw palladium wherever the microscope goes.

ICYMI: Pollution concrete, EV wireless charging and more
#fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-431877{display:none;} .cke_show_borders #fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-431877, #postcontentcontainer #fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-431877{width:570px;display:block;} try{document.getElementById("fivemin-widget-blogsmith-image-431877").style.display="none";}catch(e){} Today on In Case You Missed It: Scientists at UCLA have made concrete by first extracting greenhouse gases from power plant smokestacks. An EV prototype to wirelessly charge cars is making the rounds, and the group's big plan is to design a 50 kilowatt charger that can juice up cars as they drive. You could put that future charger inside your garage where a new opener comes with extra modules that can detect obstacles and about 10 other things. Finally, we were tickled by the idea of a robot that can best you at Settlers of Catan, so please check that out. As always, please share any great tech or science videos you find by using the #ICYMI hashtag on Twitter for @mskerryd.

Wireless charging system for EVs is nearly as good as plugging in
Wireless charging for electric cars is already affordable, but it's still pretty limited: it isn't the quickest option, and it's not even on the radar if you're driving large vehicles like trucks. Scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory are close to licking those problems once and for all, though. They've developed a 20-kilowatt wireless charging system that, at 90 percent efficiency, should be much more practical than existing pads -- it should not only charge at reasonable speeds, but avoid wasting gobs of electricity in the process. The new design is safe despite all the extra power, since its magnetic fields drop off rapidly and won't run through the whole vehicle.

Mini bioreactor makes life-saving drugs in the field
Paramedics and field medics can patch up some wounds on the spot, but they're usually stuck if they have to administer specialized drugs. What if you need medicine that health care workers don't have on hand? You might not have to rush back to the hospital in the future. Researchers have created tiny, microfluidic bioreactors that generate the proteins you need for medicine. At its heart are two very long (16 feet) channels wound into an extremely tight pattern, and divided by a customized, porous membrane -- one channel feeds chemicals, while the other hosts the reactions that produce your drug. You only have to shake the device to send protein from one side to the other and get the medicine you need.

Nanowires three atoms wide could lead to paper-thin gadgets
What's that odd shape, you ask? That's the world's thinnest nanowire -- and it could be the key to a future wave of flexible devices. In blasting single-layered, semiconducting materials with an electron beam, Vanderbilt University student Junhao Lin has created wires that measure just three atoms wide while remaining strong and very bendy. Since there are already transistors and memory gates made out of the same material, Lin envisions circuits and whole devices that are paper-thin, yet can stand up to abuse; in the long run, he envisions rollable tablets and TVs that could fit in your pocket. The technique could help produce 3D circuitry, too. We're still a long way from either of those becoming practical realities, but the discovery at least shows that they're technically possible.

Titan supercomputer to be loaded with 'world's fastest' storage system
If you figured Titan's title of the world's most powerful supercomputer would give the folks at Oak Ridge National Laboratory reason to rest on their laurels, you'd be mistaken. The computer is set to have its fleet of 18,688 NVIDIA K20 GPUs and equal number of AMD Opteron processors paired with what's said to be the planet's speediest storage system, making its file setup six times faster and giving it three times more capacity. Dubbed Spider II, the new hardware will endow the number cruncher with a peak performance of 1.4 terabytes a second and 40 petabytes of storage spread across 20,000 disk drives. Behind the refresh are 36 of Datadirect Networks' SFA12K-40 systems, which each pack 1.12PB of capacity. For more on the herculean rig's upgrade, hit the jump for the press release.

Cray's Jaguar supercomputer upgraded with NVIDIA Tesla GPUs, renamed Titan
Cray's Jaguar (or XK7) supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory has been loaded up with the first shipping NVIDIA Tesla K20 GPUs and renamed Titan. Loaded with 18,688 of the Kepler-based K20s, Titan's peak performance is more than 20 petaflops. Sure, the machine has an equal number of 16-core AMD Opteron 6274 processors as it does GPUs, but the Tesla hardware packs 90 percent of the entire processing punch. Titan is roughly ten times faster and five times more energy efficient than it was before the name change, yet it fits into the same 200 cabinets as its predecessor. Now that it's complete, the rig will analyze data and create simulations for scientific projects ranging from topics including climate change to nuclear energy. The hardware behind Titan isn't meant to power your gaming sessions, but the NVIDIA says lessons learned from supercomputer GPU development trickle back down to consumer-grade cards. For the full lowdown on the beefed-up supercomputer, hit the jump for a pair of press releases.

Superconducting sapphire wires are as cool as they sound
Copper wire's relatively cheap, pliable and can conduct electricity, but it's hardly ideal. Powering cities requires cables meters wide and the metal loses a lot of energy as heat. Fortunately, a team from Tel Aviv University thinks it's solved the problem. Borrowing a fiber of sapphire from the Oakridge National Lab in Tennessee, it developed a superconducting wire barely thicker than a human hair that conducts 40 times the electricity of its copper brethren. Cooled with liquid nitrogen, the sapphire superconductors carry current without heating up, which is key to their efficiency. The team is now working on practical applications of the technology -- because it's so small and pliable (unlike previous superconductors) it could replace copper in domestic settings and its cold efficiency makes it perfect to transmit power long distances from green energy stations. The wire's going on a world tour as we speak and will touch down at the ATSC conference in Baltimore in October. Anyone who makes jokes about wires and Baltimore will be asked to leave, politely.

ORNL energy harvester turns heat waste into electricity, converts hot machines into cool customers
We've heard of turning yesterday's lunch into tomorrow's electricity, but a new energy converter coming out of Oak Ridge National Laboratory harnesses the power of a different type of hot waste. The as-of-yet unnamed thermal waste-heat converter has the potential to cool electronic devices, solar cells, and computers while generating electricity from excess heat. Its creators see the new conversion process being used to reduce the massive amounts of heat generated by petaflop computers. The converter employs up to one thousand tiny cantilevers attached to a one square inch surface (e.g. a computer chip) to produce between one and ten milliwatts of electricity -- admittedly a very small amount of energy. However, it's creators are quick to point out that a slew of these converters could generate enough power to perform small tasks in the heat-generating device -- things like sensing when a server room gets too hot for comfort. Sure it's a small step, but if they can get this stuff to save our future babies from cooking, we're all in. Full PR after the break.

Nanocones make solar cells more efficient, sinister looking
Going green is de rigeur, so the sun is becoming a much-preferred source of power. However, solar cells' inefficient harvesting of heliacal energies is a major reason they haven't usurped the power of petroleum. Good thing the big brains at Oak Ridge National Laboratory are looking to change that with nanocone-based solar technology. The teeny-tiny cones are made of zinc oxide and create "an intrinsic electric field distribution" to improve electrical charge transport within solar cells. We aren't sure what that means, but we do know the prickly-looking design provides a 3.2 percent light-to-power conversion efficiency that's a substantial improvement over the meager 1.8 percent offered by today's flat photovoltaics made of similar materials. That's 80 percent more efficient, and 100 percent more awesome.

Cray Jaguar leaps past IBM Roadrunner as world's fastest supercomputer and pun generator (video)
Cray has finally clawed IBM back from the lead position on the Top500 Supercomputer chip-measuring contest. After just missing out on the title to IBM's Roadrunner last year, Cray's XT5 supercomputer (aka, Jaguar) at Oak Ridge National Lab in Tennessee received an update from quad- to six-core Opteron processors to boast a 2.3 petaflop per second performance peak (theoretical) and 1.75 petaflops as measured by the Linpack benchmark; a feat requiring almost a quarter million AMD cores. IBM's Roadrunner, the very first supercomputer to race past the petaflop per second threshold, managed just 1.042 petaflops by comparison. Remember, one petaflop per second is equivalent to one quadrillion calculations per second. Of course, chip makers put their own spins on the list by noting that 4 of the top 5 systems depend on AMD for performance while Intel can be found powering 402 of the Top500. Video of the AMD processor upgrade procedure can be found after the break.

ORNL's laser-based surveillance / monitoring system takes on RFID
Amazingly, the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is actually not located in the UK, but we wouldn't doubt if the latest development to emerge from its confines somehow ends up across the pond. Nevertheless, scientists at the lab have developed a Laser-Based Item Monitoring System that "addresses surveillance requirements in places where video would be unacceptable because of the presence of proprietary information or other privacy concerns." Essentially, this optical monitoring system uses low-cost reflective tags placed on objects, and then maps the precise location of high-value items to sense tampering. The laser can purportedly detect minute changes (movements of less than a centimeter) by utilizing "a high-resolution two-axis laser scanner capable of looking at a 60-degree field of view in 0.0005-degree increments," meaning that it can divide its field of view into more than 10 billion individual pointing locations. The crew also noted that this system was generally superior to bar code and RFID alternatives as the LBIMS would not be susceptible to jamming or interception, but there's no word just yet on when the Department of Energy (or anyone else) will be putting this stuff to good use.[Via Smartmobs, photo courtesy of Primidi]








