ArtificialLimb
Latest
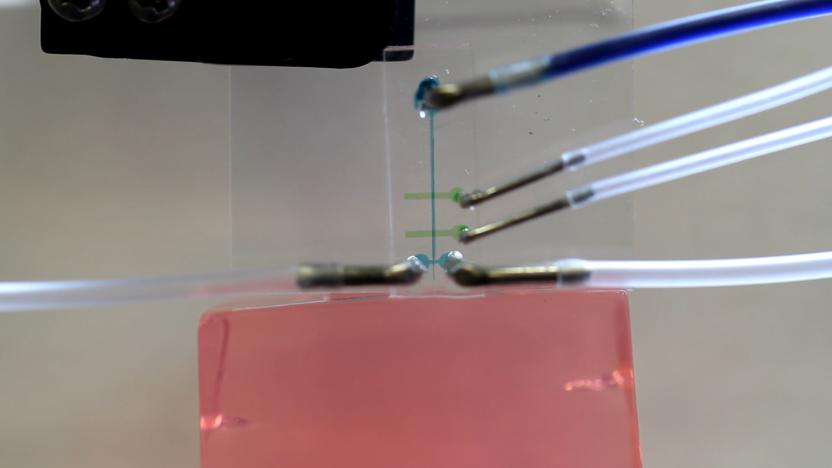
Researchers create less invasive method for placing brain electrodes
Our neurons are firing all the time, receiving signals from other neurons and sending signals of their own. To get a better understanding of how the brain works, scientists often listen in to those signals to see what kind of messages certain neurons send and how often they send them. Doing that often requires researchers to implant an electrode into the brain, which when it's close enough to a neuron, can pick up on the electrical signals that propagate through the neuron. However, getting an electrode into the brain isn't so easy. They either have to be rigid enough to penetrate the brain and remain straight or be inserted through needles that can keep them straight until they're safely in place. The problem is those rigid structures cause damage as they move through the brain and minimizing that damage is a goal that scientists are constantly working towards.

Prosthetic arms inspired by 'Deus Ex' are coming next year
Remember that prosthetic arm, inspired by Metal Gear Solid, that Konami developed for a British amputee? Well, it seems the company has started a trend. Square Enix and Eidos-Montréal have now teamed up with Open Bionics, a specialist in low-cost prosthetics, to develop some designs based on the world of Deus Ex. The franchise delves deep into a possible future where human augmentation is commonplace, changing society and warfare in equal measure. Two arms -- one based on Adam Jensen, the hero of Mankind Divided, another on the wider Deus Ex universe -- will be released next year as royalty-free designs that anyone can use.

AMP-Foot 2.0 prosthesis gives the power of real feet, keeps a light step (video)
It was five years ago that prosthetics took a very literal step forward when Arizona State University's SPARKy foot offered a more natural walk, capturing the inherent kinetic energy that previously needed a big motor to replicate. Belgium's Vrije Universiteit Brussel may well carry the torch for the next wave of artificial limbs. Its second-generation Ankle Mimicking Prosthetic Foot (AMP-Foot 2.0) uses a pair of force sensors to determine the leg's relative position and let an actuator build energy when the foot bends, locking the power away to use only when the owner pushes off. The efficiency produces all the torque needed to let a 165-pound person walk, but with just a 30W to 60W motor versus SPARKy's 150W -- a big help to battery life that also reduces the AMP-Foot 2.0's weight to that of the fleshy kind. We don't know how likely it is the Belgian prosthesis goes beyond the prototype phase; if we had our way, it would move just as quickly as future wearers undoubtedly will.

Mind-operated robot arm helps paralyzed woman have her cup o' joe (video)
Researchers at the Braingate2 consortium have made a breakthrough that allows people with spinal cord or stroke injuries to control robotic limbs with their minds. The original project allowed subjects with motor cortex-implanted chips to move cursors on a screen with their minds, but they can now command DEKA and DLR mechanical arms to grasp foam balls and sip coffee. Researchers noted that dropped objects and missed drinks were frequent, but improved brain sensors and more practice by subjects should help. To see the power of the mind move perhaps not mountains, but good ol' java, jump to the video below.

Stanford builds super-stretchy skin sensor out of carbon nanotubes (video)
An artificial skin that senses pressure, pinches and touch sounds like a macguffin from The Outer Limits (the episode "Valerie 23" if we recall correctly), but that's what a team from Stanford University has cooked up on the back of its pick-up truck. Sensors made of silicon films with a matrix of liquid carbon nanotubes ensure the material snaps back to its original shape no matter how frequently it's pulled about. When compressed, the electrical conductivity of the skin changes, and by measuring where and by how much, it knows the location and pressure of where you jab your fingers. The team wants to combine this super stretchy film with a much more sensitive sensor and if it can do it, then the technology could end up as an artificial skin for burn victims, covering prosthetic limbs or even replacing your multitouch display -- just be careful, you might hurt Siri if you pinch-to-zoom her too hard.

Monkeys control virtual arm with their brains, may herald breakthrough for paraplegics
Monkey mind-controlled arm: It sounds like the name of an awesomely terrible sci-fi film or a fledgling grindcore group, but it's a very real phenomenon, and one that could pay significant dividends for paraplegics everywhere. Neurobiology professor Miguel Nicolelis and his team of researchers at Duke University recently devised a method by which monkeys (and, perhaps one day, humans) can control a virtual arm using only their brains. It's a concept similar to what DARPA has been pursuing with its mind-controlled "Luke" arm, with one important difference: Nicolelis' system not only allows users to remotely execute motor functions, but provides them with near-instantaneous sensory feedback, as well. Most similar techniques use electrode implants to stimulate brain activity, but this can create confusion when a patient's brain sends and receives signals to and from a prosthetic arm. Nicolelis circumvented this problem with a new interface that can read and transmit brain signals to an artificial limb, before switching to a receptive mode in just milliseconds. After designing the technology, Nicolelis and his colleagues tested it on two, electrode-equipped rhesus monkeys. One set of electrodes was placed in the motor cortex of each animal, with the other implanted within their brains' sensory regions. They then trained the monkeys to look at a three identical objects on a computer screen and to "touch" each object with a virtual arm, controlled by signals sent from the brain electrodes. Only one of the three objects had a so-called "virtual texture," which, if selected with the on-screen arm, would send a sensory signal back to the monkey's brain (while triggering a tasty squirt of fruit juice for the lucky contestant). The two rhesus species ended up passing the test with flying colors, resulting in a "proof of principle" that Nicolelis' system can send tactile signals to the brain in almost real-time. The scientists have already developed a way for monkeys to control the arm wirelessly, and are now embedding their technology within a full-body, mind-controlled exoskeleton for paralyzed patients, as well. Of course, the technology still needs to be tested on actual humans, though Nicolelis seems confident that he and his team have already cleared the most difficult hurdle: "Since we cannot talk to the monkeys, I assume with human patients, it's going to be much easier."

First woman gets bionic arm
As The Washington Post reports, 26-year old Claudia Mitchell has become the fourth person and first woman to get outfitted with a bionic arm (well, besides Lindsay Wagner), with which she's able to perform functions simply by thinking about them. The arm was designed by researchers at the Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago -- who are part of a larger project funded by DARPA -- and works by detecting the movement's of Mitchell's chest muscle, which has been rewired to the nerves that once served her left arm. Eventually, researchers say, the arm could even give Mitchell the sense of touch, with electrodes in the hand sending signals to her chest skin, which her brain would recognize as a sensation. This being part of a DARPA project though, we're sure they're also working on things they're not telling us, like crazy swinging grappling hook action.[Thanks, Spluch]






